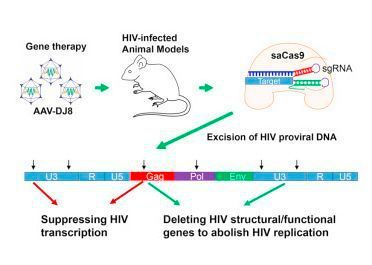
- With Chinese scientists announcing that they have tested CRISPR on a human for the first time, the U.S. must decide soon whether it will be a leader or a follower in advancing the tech.
- While gene editing technology could be used in nefarious ways, it could also cure diseases and improve millions of lives, but we won’t know how effective it is until we begin human trials.
While the middle part of the 20th century saw the world’s superpowers racing to explore space, the first global competition of this century is being set in a much smaller arena: our DNA.