
Category: genetics – Page 338

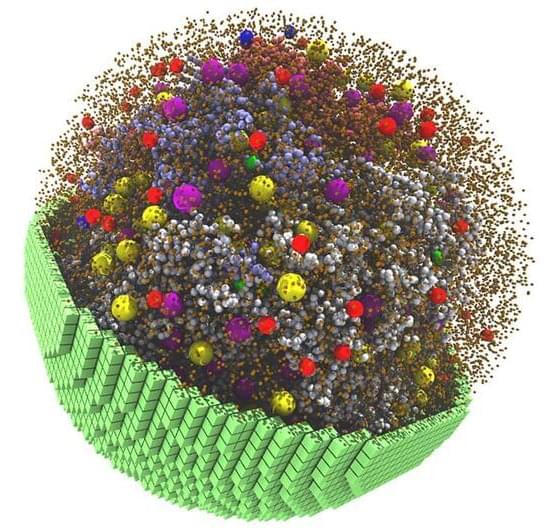
NVIDIA GPUs Enable Simulation of a Living Cell
Researchers from the University of Illinois developed GPU-accelerated software to simulate a cell that metabolizes and grows like a living cell.
Every living cell contains its own bustling microcosm, with thousands of components responsible for energy production, protein building, gene transcription and more.
Scientists at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign have built a 3D simulation that replicates these physical and chemical characteristics at a particle scale — creating a fully dynamic model that mimics the behavior of a living cell.
Published in the journal Cell, the project simulates a living minimal cell, which contains a pared-down set of genes essential for the cell’s survival, function and replication. The model uses NVIDIA GPUs to simulate 7,000 genetic information processes over a 20-minute span of the cell cycle – making it what the scientists believe is the longest, most complex cell simulation to date.
The Future Of Medicine: Fighting Deadly Diseases With Smart Devices And Digital Biomarkers
What are biomarkers? They are medical signals that can measure health in an accurate and reproducible way. Common examples include blood pressure readings, heart rate, and even genetic test results.
Modern digital devices measure several health parameters. Fitbit trackers use sensors such as accelerometers to tell how many steps we’ve taken in a day or how fast we’ve been walking. When can such novel health measures function as medical biomarkers?
The measures must be objective, quantifiable, and reproducible. Additionally, scientific evidence needs to show that the health attribute measured by the device maps consistently and accurately to a clinical outcome. For example, voice signals from a smartphone’s microphone can detect mild cognitive impairment due to Alzheimer’s disease. World War II, commanders and troops communicated using hand-sent Morse codes. To avoid capture by enemies, telegraph operators had to remain anonymous. Any clues about operator identity or location could influence battle outcomes.
The Generation of Superhumans — Can We Edit Our Genes?
New technologies have considerably improved scientists’ ability to locate the genetic variations that distinguish our DNA from that of other people. In some instances, these genetic differences give rise to diverse superhuman abilities. There is growing interest in identifying genes associated with special abilities, many of which seem to be inherited. Some consider people like Wim Hof a.k.a the iceman known for the Wim Hof method as a person with superhuman abilities.
As for the future, according to prominent scientists within 30 years, it will probably be possible to make essentially any kind of change to any kind of genome.
#superhuman #science #sciencetime.
Sources:
Supergenes — https://arep.med.harvard.edu/gmc/protect.html.
George Church — Genetic Superpowers: Changing Your Genome and Environment, Harvard Medical School.
3 Rejuvenation Strategies For Aging
Blood plasma, cellular reprogramming, endogenous.
You may have heard a lot of talk recently about cellular reprogramming, rejuvenation or even “rejuvenation programming”, but what does that all mean and what are the 3 main strategies that several researchers and companies (maybe Altos Labs) will be further investigating?
Well i discuss in this video.
Find me on Twitter — https://twitter.com/EleanorSheekey.
Support the channel.

HumanityMars NEW YEAR 2030 PARTY IN MARS CITY!
FeaturedRead our 3 books at https://lifeboat.com/ex/books.
The Lifeboat Foundation is a nonprofit nongovernmental organization dedicated to encouraging scientific advancements while helping humanity survive existential risks and possible misuse of increasingly powerful technologies, including genetic engineering, nanotechnology, and robotics/AI, as we move towards the Singularity.
Lifeboat Foundation is pursuing a variety of options, including helping to accelerate the development of technologies to defend humanity, such as new methods to combat viruses, effective nanotechnological defensive strategies, and even self-sustaining space colonies in case the other defensive strategies fail.
We believe that, in some situations, it might be feasible to relinquish technological capacity in the public interest (for example, we are against the U.S. government posting the recipe for the 1918 flu virus on the internet). We have some of the best minds on the planet working on programs to enable our survival. We invite you to join our cause!
Visit our site at https://lifeboat.com. Participate in our programs at https://lifeboat.com/ex/programs. Follow our Twitter feed at https://twitter.com/LifeboatHQ and our GETTR feed at https://gettr.com/user/LifeboatHQ. Watch our YouTube channel at https://youtube.com/lifeboathq. Read our blog at https://lifeboat.com/blog. Join our LinkedIn group at https://www.linkedin.com/groups/35656. Subscribe to our newsletter at https://lifeboat.com/newsletter.cgi.
Interact with the author of “The Human Race to the Future: What Could Happen—and What to Do” at https://www.facebook.com/groups/thehumanracetothefuture.
First Molecular Electronics Chip Developed — Realizes 50-Year-Old Goal
A platform for single-molecule measurement of binding kinetics & enzyme activity.
The first molecular electronics chip has been developed, realizing a 50-year-old goal of integrating single molecules into circuits to achieve the ultimate scaling limits of Moore’s Law. Developed by Roswell Biotechnologies and a multi-disciplinary team of leading academic scientists, the chip uses single molecules as universal sensor elements in a circuit to create a programmable biosensor with real-time, single-molecule sensitivity and unlimited scalability in sensor pixel density. This innovation, appearing this week in a peer-reviewed article in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), will power advances in diverse fields that are fundamentally based on observing molecular interactions, including drug discovery, diagnostics, DNA
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is a molecule composed of two long strands of nucleotides that coil around each other to form a double helix. It is the hereditary material in humans and almost all other organisms that carries genetic instructions for development, functioning, growth, and reproduction. Nearly every cell in a person’s body has the same DNA. Most DNA is located in the cell nucleus (where it is called nuclear DNA), but a small amount of DNA can also be found in the mitochondria (where it is called mitochondrial DNA or mtDNA).

After First Pig-to-Human Heart Transplant, Scientists Aim to Make It Routine
“It was either die or do this transplant. I want to live. I know it’s a shot in the dark, but it’s my last choice,” said Bennett.
The heart was provided by Revivicor, a company based in Virginia that has been engineering pig organs for roughly two decades. In several experiments for pig-to-baboon transplants, the organs survived up to nine months, until the animals passed away due to a lung infection unrelated to the transplant.
Overall, the heart had 10 hefty genetic edits. Three of them wiped out sugar molecules on the outside of cells that provoke an immune response. Six bolstered the chance of the human host accepting the heart—amping up an anti-inflammatory response, preventing blood vessel damage, and dampening any antibodies against the organ. Finally, the last edit limited the pig heart’s size. Although it generally matched the size of a human heart, the team wanted to prevent the pig organ from overgrowth inside Bennett’s chest once it was transplanted—something they previously noticed happened in baboons.
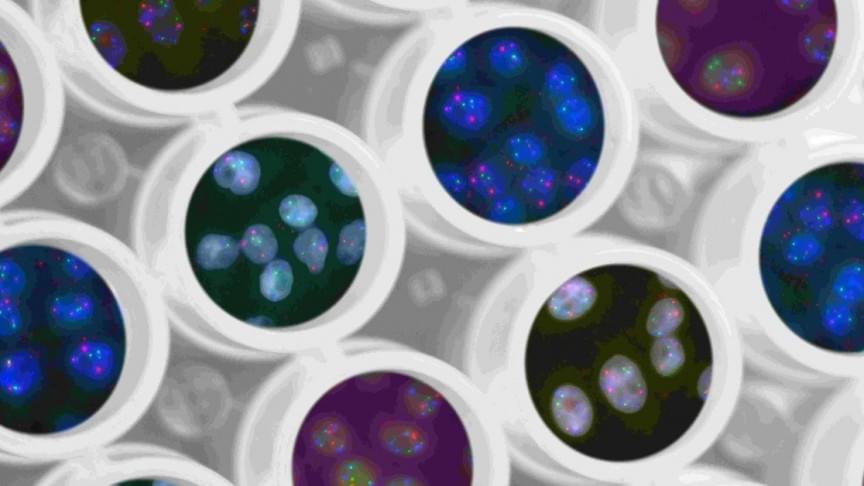
New Gene Sequencing Method Cuts Cost and Is Five Times Faster, Study Says
And it took less than a full workday. Stanford Medicine scientists and their collaborators have engineered a new genome sequencing technique that can diagnose rare genetic diseases in an average of eight hours. This is a record-breaking time frame that is leap and bounds ahead of other current advanced technologies.
Gene sequencing is crucial to advancing science! Check out why cutting time and cost is key.

CRISPR might be the banana’s only hope against a deadly fungus
Circa 2019
The race to engineer the next-generation banana is on. The Colombian government confirmed last month that a banana-killing fungus has invaded the Americas — the source of much of the world’s banana supply. The invasion has given new urgency to efforts to create fruit that can withstand the scourge.
Scientists are using a mix of approaches to save the banana. A team in Australia has inserted a gene from wild bananas into the top commercial variety — known as the Cavendish — and are currently testing these modified bananas in field trials. Researchers are also turning to the powerful, precise gene-editing tool CRISPR to boost the Cavendish’s resilience against the fungus, known as Fusarium wilt tropical race 4 (TR4).
Breeding TR4 resistance into the Cavendish using conventional methods isn’t possible because the variety is sterile and propagated by cloning. So the only way to save the Cavendish may be to tweak its genome, says Randy Ploetz, a plant pathologist at the University of Florida in Homestead. The variety accounts for 99% of global banana shipments.