Year 2020 face_with_colon_three
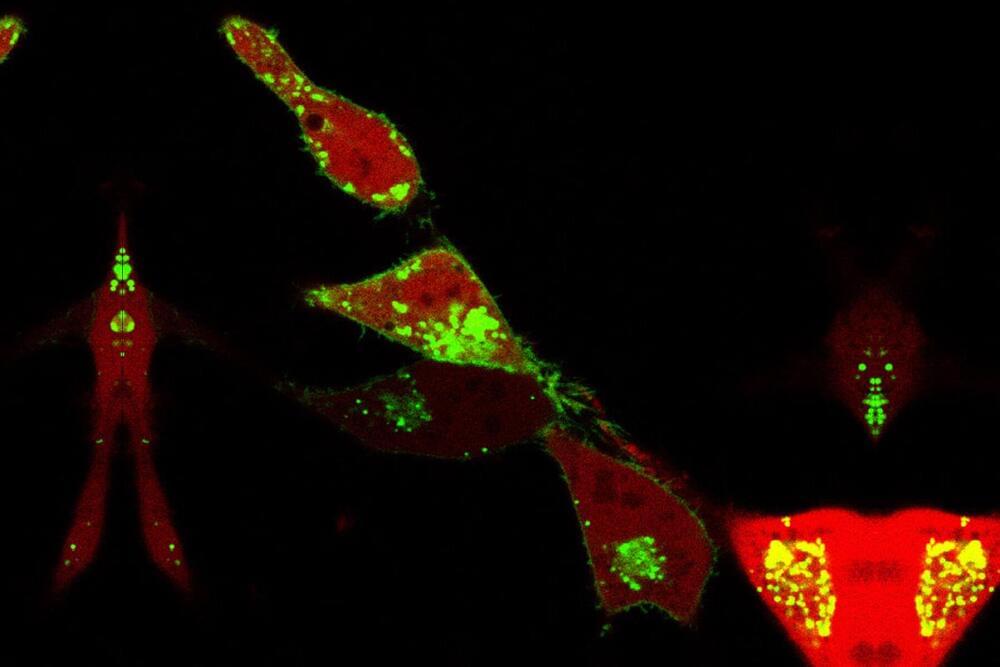
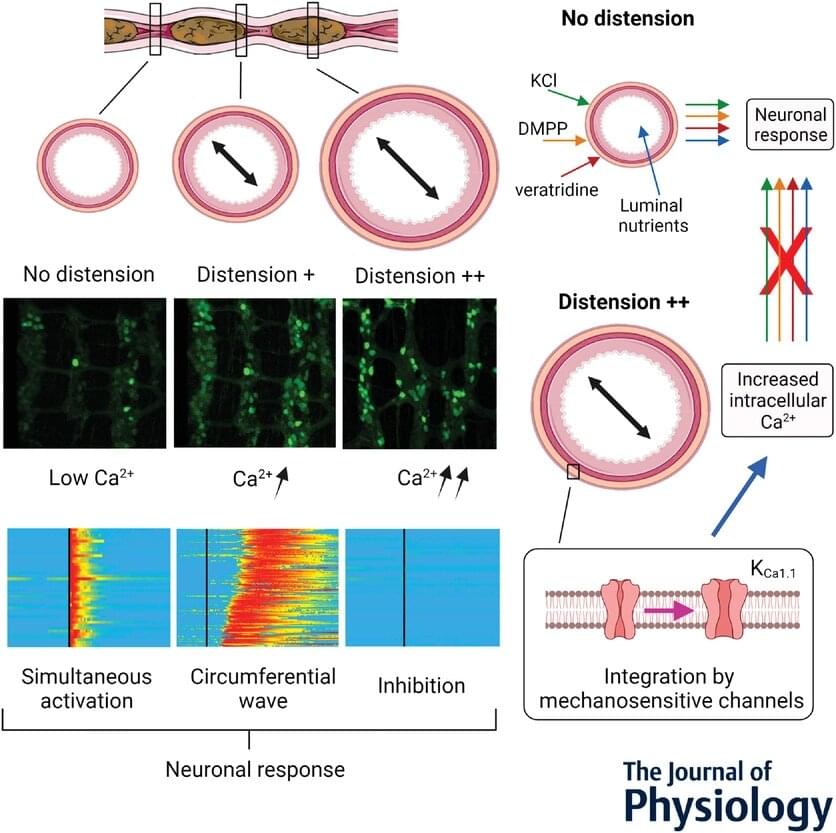
Frontotemporal dementia (FTD) and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) are two fatal and incurable neurodegenerative diseases linked by a shared genetic cause – a heterozygous hexanucleotide (GGGGCC) repeat expansion in a single allele of the C9orf72 gene. The goal of this work is to develop novel CRISPR based therapeutic gene editing technologies and test whether gene editing can reverse the cellular pathology caused by this repeat expansion in patient derived cells. The results of these studies will advance our use of CRISPR technologies for therapeutic editing in FTD/ALS, inform our understanding of the regulation of C9orf72 gene, and will be applicable to many other repeat expansion and single gene disorders.