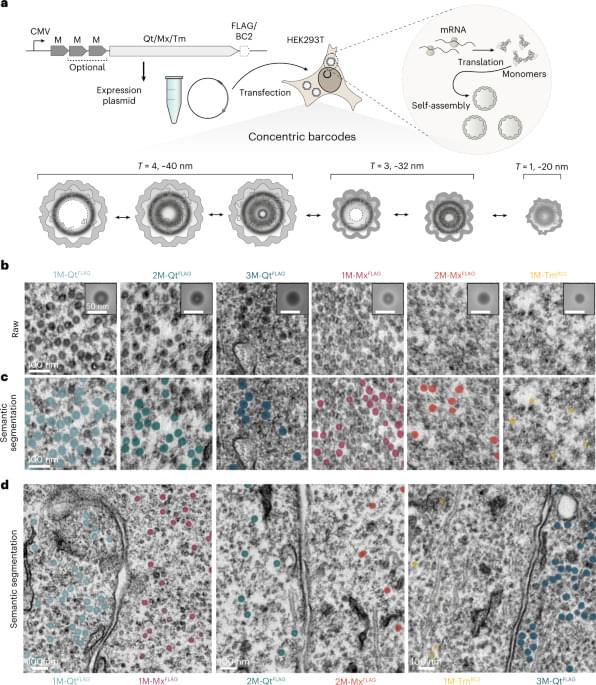
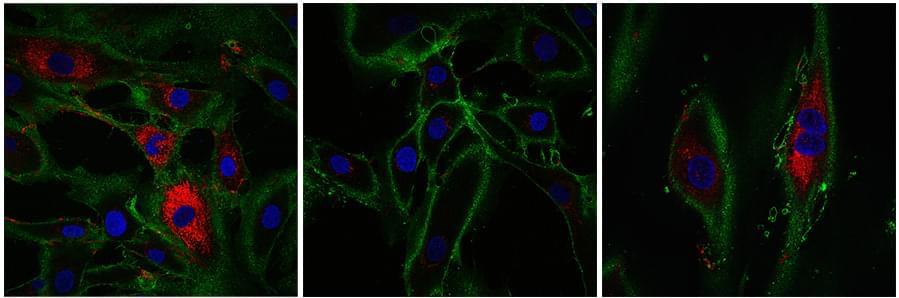
I’d place Sigmund et al. as one of my favorite papers that I have read this year! They leverage protein engineering to create genetically encoded nanocages which accumulate metals and appear as concentric circles when imaged by electron microscopy. Six classes of distinct “EMcapsulins” could be differentiated by training a machine learning model (a convolutional neural network) to recognize and classify them within images. Fusion of fluorescent protein domains to the EMcapsulins also allowed correlative imaging between fluorescence microscopy and electron microscopy. The authors demonstrated 3D imaging of EMcapsulins via serial section transmission electron microscopy and focused ion beam… More.
Multiplexable barcodes for electron microscopy are applied to brain imaging.