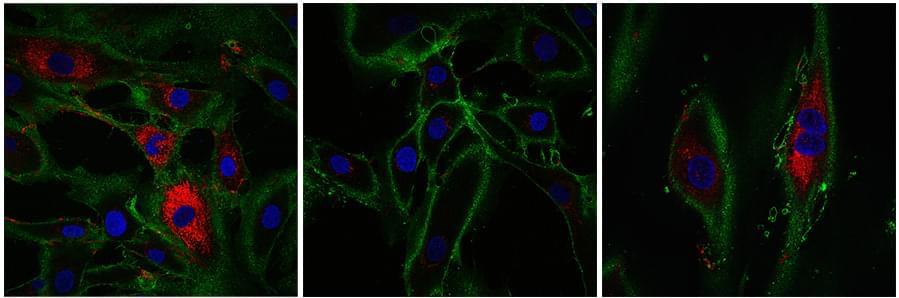
Busso also said we don’t yet know the long-term effects of these treatments on normal cells or what the long-term impact of killing zombie cells might be. Additionally, because zombie cells play an important role in wound healing, “We don’t want to remove all of them,” he said. “We don’t know the ideal regimen, daily versus weekly versus monthly.”
Hopefully, we won’t have to wait long for answers about the best way to get rid of zombie cells on the skin. “Major breakthroughs and contributions to delaying of the aging process are expected in the near future,” Busso said.
Although it’s still unclear whether zombie cells can be safely and effectively cleared from the skin, it is possible to prevent some zombie cells from forming in the first place. Collins explained that zombie cells are formed as the result of both biological and environmental factors. “The internal factors, like aging or genetic disease, are not so much within our control,” but the external factors can be controlled, she said.