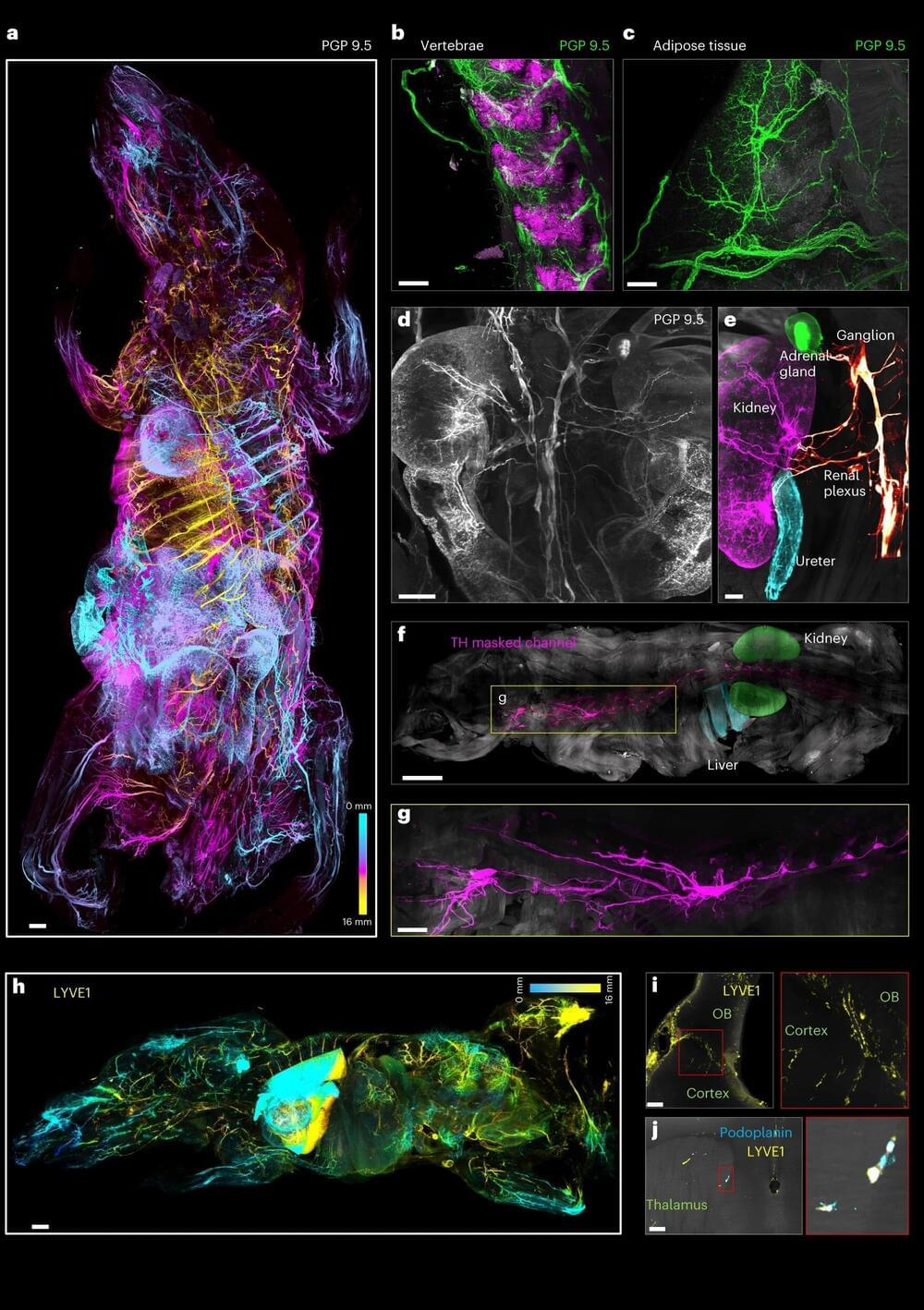
Researchers developed a new method called wildDISCO that uses standard antibodies to map the entire body of an animal using fluorescent markers. This revolutionary technique provides detailed 3D maps of structures, shedding new light on complex biological systems and diseases. WildDISCO has the potential to transform our understanding of intricate processes in health and disease and paves the way for exciting advancements in medical research. This technology was now introduced in Nature Biotechnology.
In the past, scientists relied on genetically modified animals or specialized labels to make specific structures and cells of interest visible in the entire body of an animal. But these approaches are expensive and time-consuming to create, especially when it comes to body-wide systems such as the nervous system.
A team of scientists from Helmholtz Munich, the LMU University Hospital and the Ludwig-Maximilians Universität München (LMU) now introduced a new method called wildDISCO, which makes use of standard antibodies to map whole bodies of mice. This ultimately enables the creation of detailed three-dimensional maps of normal and diseased structures in mammalian bodies in an easy-to-use and cost-efficient way.