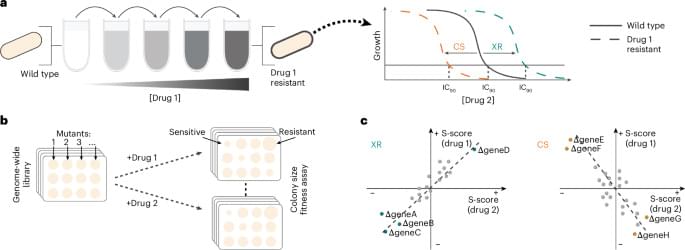
Resistance to one antibiotic can make bacteria resistant or sensitive to another antibiotic, opening paths for combinatorial treatments. This study presents an approach to systematically discover and understand such antibiotic relationships.

Join us on Patreon! https://www.patreon.com/MichaelLustgartenPhD
Discount Links/Affiliates:
Blood testing (where I get the majority of my labs): https://www.ultalabtests.com/partners/michaellustgarten.
At-Home Metabolomics: https://www.iollo.com?ref=michael-lustgarten.
Use Code: CONQUERAGING At Checkout.
Clearly Filtered Water Filter: https://get.aspr.app/SHoPY
Epigenetic, Telomere Testing: https://trudiagnostic.com/?irclickid=U-s3Ii2r7xyIU-LSYLyQdQ6…M0&irgwc=1
Use Code: CONQUERAGING
NAD+ Quantification: https://www.jinfiniti.com/intracellular-nad-test/

Scientists from the Longevity Research Institute (LRI), which was formed by the merger of SENS Research Foundation and Lifespan.io, have achieved expression of an essential mitochondrial gene in the nucleus and proper functioning of the protein. This could pave the way for curing diseases caused by mitochondrial mutations [1].
The fragile mitochondrial DNA
The prevailing scientific consensus is that mitochondria were once independent microorganisms that entered a symbiotic relationship with larger cells. This duo gave rise to eukaryotic cells: the building blocks of all multicellular life. Without that fateful “marriage,” complex life would not exist, as mitochondria provide cells with essential energy via oxidative phosphorylation.
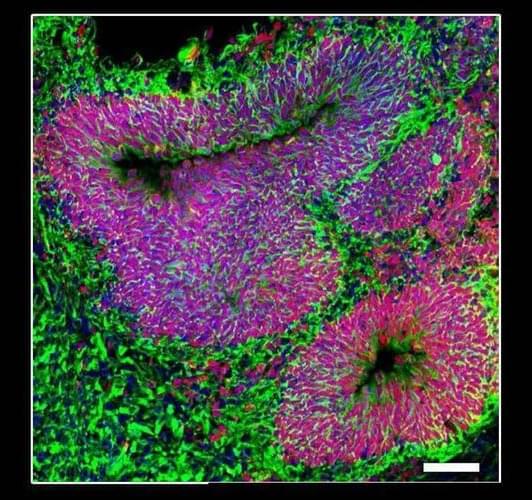
Cleveland Clinic Genome Center researchers have unraveled how immune cells called microglia can transform and drive harmful processes like neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease. The study, published in the journal Alzheimer’s & Dementia, also integrates drug databases with real-world patient data to identify FDA-approved drugs that may be repurposed to target disease-associated microglia in Alzheimer’s disease without affecting the healthy type.
The researchers, led by study corresponding author Feixiong Cheng, Ph.D., hope their unique approach of integrating genetic, chemical and human health data to identify drug targets and corresponding drugs will inspire other scientists to take similar approaches in their own research.
Microglia are specialized immune cells that patrol our brains, seeking and responding to tissue damage and external threats like bacteria and viruses. Different types of microglial cells use different methods to keep the brain safe. Some may cause neuroinflammation—inflammation in the brain—to fight invaders or kickstart the repair process in damaged cells. Others may work to “eat” dangerous substances in the brain, and clean up damage and debris. However, during Alzheimer’s disease, new types of microglia can form that promote disease progression.
Its a problem, but im sure ASI by 2035 will solve for a way to use a Crispr type tool with zero unintended alterations. Look for a way to use w/ out alterations in meantime, but worst case ASI will solve it.
Genome editing with various CRISPR-Cas molecule complexes has progressed rapidly in recent years. Hundreds of labs around the world are now working to put these tools to clinical use and are continuously advancing them.
CRISPR-Cas tools allow researchers to modify individual building blocks of genetic material in a precise and targeted manner. Gene therapies based on such gene editing are already being used to treat inherited diseases, fight cancer and create drought-and heat-tolerant crops.
The CRISPR-Cas9 molecular complex, also known as genetic scissors, is the most widely used tool by scientists around the world. It cuts the double-stranded DNA at the exact site where the genetic material needs to be modified. This contrasts with newer gene-editing methods, which do not cut the double strand.

A recent study investigates the relationship between exercise and the expression of MYC in skeletal muscles over time, revealing that even minimal doses can promote muscle growth without physical activity.
Researchers have long known that there is a relationship between the cancer-associated gene MYC (pronounced “Mick”) and exercise adaptation. When human muscles are exercised, MYC is found to increase transiently in abundance over 24 hours. But as we age, the MYC response to exercise is blunted, perhaps explaining a reduced ability to recover from exercise and maintain or gain muscle.
Knowing the precise mechanisms by which MYC drives muscle growth could prove instrumental in creating therapies that reduce muscle loss from aging, potentially improving independence, mobility, and health.

Dear Colleagues.
A good number of insect pests are known for harboring various bacterial symbionts. Herbivore-associated bacterial symbionts such as Wolbachia and Spiroplasma are widespread in diverse arthropods and mostly act as reproductive parasites. Both have been reported to significantly improve reproductive performance of various insects, including spider mites, aphids, Drosophila, etc. These insect-associated symbionts influence herbivore fitness, growth, and development, as well as interfere with plant defenses by changing plant physiology. Both Wolbachia and Spiroplasma are maternally inherited endosymbionts in arthropods and are able to co-exist and infect the same host. Understanding these complex interactions is very important for the development of an effective insect pest management program. We look forward to receiving your contributions to this Special Issue in the form of original research papers and review articles focusing on, but not limited to, the latest research on the occurrence, genetic diversity, and physiological functions of Wolbachia and/or Spiroplasma symbionts in various primary hosts. Although our focus will be on these two major facultative insect symbionts, articles reporting work carried out on other bacterial species are also welcome.
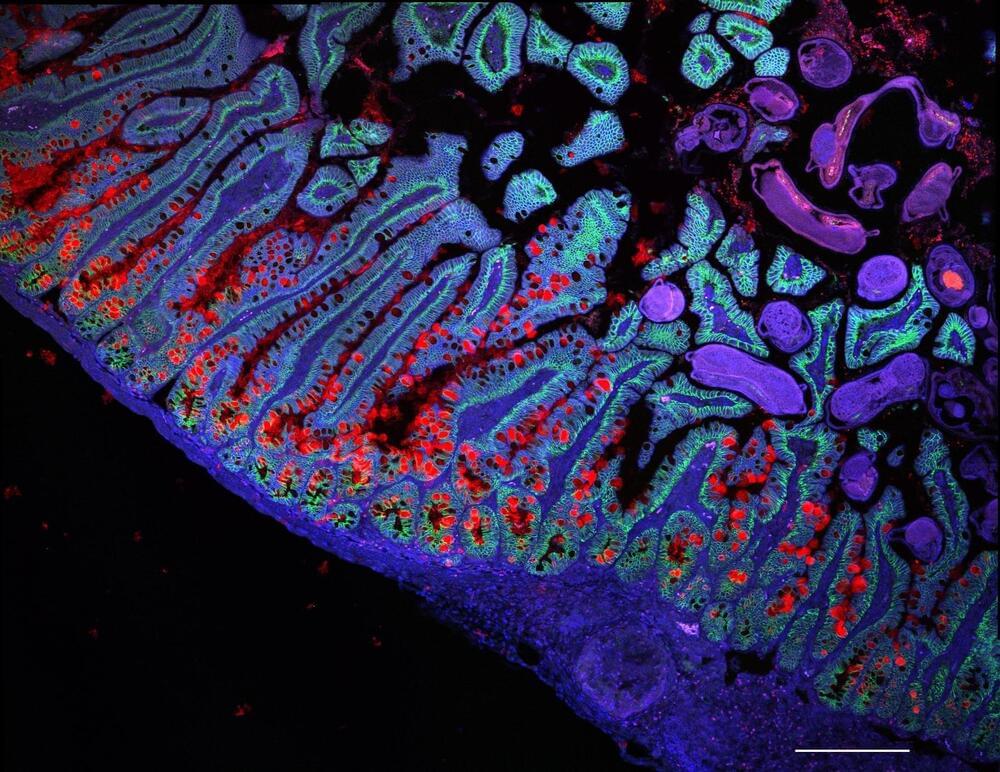
New research from the Human Cell Atlas offers insights into cell development, disease mechanisms, and genetic influences, enhancing our understanding of human biology and health.
The Human Cell Atlas (HCA) consortium has made significant progress in its mission to better understand the cells of the human body in health and disease, with a recent publication of a Collection of more than 40 peer-reviewed papers in Nature and other Nature Portfolio journals.
The Collection showcases a range of large-scale datasets, artificial intelligence algorithms, and biomedical discoveries from the HCA that are enhancing our understanding of the human body. The studies reveal insights into how the placenta and skeleton form, changes during brain maturation, new gut and vascular cell states, lung responses to COVID-19, and the effects of genetic variation on disease, among others.

THIS IS HUGE!! New study suggests that aging could be preventable, delayable and even reversible! A recent study published in Engineering proposes a new theory called pro aging metabolic reprogramming (PAMRP)
Aging is a complex process that has long puzzled scientists. A recent study published in Engineering proposes a new theory called pro-aging metabolic reprogramming (PAMRP), which could change our understanding of aging.
The traditional debate on aging has centered around whether it is a programmed process or a result of stochastic events. The PAMRP theory combines these two perspectives. It suggests that aging is driven by degenerative metabolic reprogramming over time. This involves both the buildup of pro-aging substrates (PASs) through metabolic changes and the emergence of pro-aging triggers (PATs). The combination of PASs and PATs leads to metabolic reprogramming, which in turn causes cellular and genetic reprogramming, ultimately resulting in the aging process.
Metabolism plays a crucial role in the PAMRP theory. As organisms age, there are significant changes in metabolic pathways, such as shifts in energy production and nutrient utilization. These changes initially serve as an adaptive mechanism but can become maladaptive over time, contributing to aging. The theory also distinguishes between different types of metabolic reprogramming, such as adaptive and adverse, and between regenerative and degenerative processes.