Crosstalk between commensal E. coli that express flagellin and intestinal epithelial cells coordinate intestinal macrophage recruitment to support gut barrier homeostasis in mice.
Learn more in ScienceImmunology.
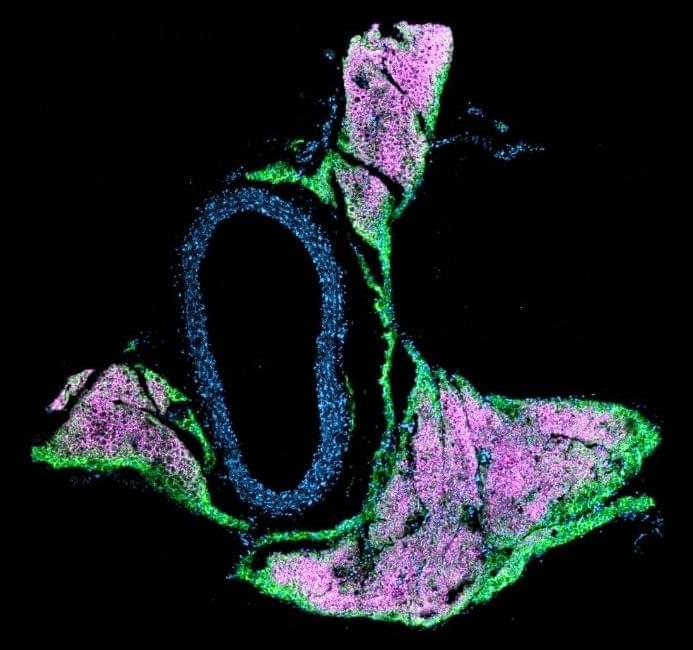
The colonic epithelium is an important boundary between internal tissues and luminal contents including the microbiota. The gut microbiota drives immune cell accumulation and effector function (6, 10, 12), but how colonic epithelial cells mediate these processes is incompletely understood. To understand how intestinal epithelial sensing of adherent microbes regulates immune-supported intestinal barrier repair, we used the E. coli strain 541–15, which we previously found increased LP macrophages and promoted their IL-10 production, protecting against inflammatory pathology in mouse colitis models (12, 23, 24).
Here, we demonstrated that E. coli 541–15 colonization promotes LP recruitment of mature macrophages after antibiotic treatment. Using HCMs, we determined that E. coli 541–15 induced expression of immune regulatory genes including the monocyte-recruiting chemokine CCL2 exclusively in UD cells, which promote monocyte migration. In vivo, CCL2 produced by epithelial cells in response to E. coli 541–15 colonization promoted colon LP macrophage expansion and protected mice from DSS colitis. We further identified flagellin as the key microbial factor that induced epithelial CCL2 expression. Last, epithelial TLR5 and E. coli flagellin were both required for LP recruitment of mature macrophages and protection against DSS challenge. In both in vitro and in vivo systems, epithelial stem cells had higher TLR5 expression than mature IECs, indicating a crypt specific role for flagellated bacteria detection. Our findings are consistent with previous studies showing that TLR5-deficient mice develop spontaneous colitis in the presence of the pathobiont H. hepaticus (20), suggesting a potential protective role for TLR5 in intestinal homeostasis. Moreover, other studies report that H. hepaticus induces colitis in IL-10–deficient mice (52, 53), highlighting a possible link between TLR5 and IL-10+ macrophages in H. hepaticus pathogenesis. Here, we demonstrate that TLR5 signaling is essential for mucosal protection by promoting the recruitment of CCR2+ cells and the maturation of LP macrophages, which are key producers of IL-10 in the gut, highlighting a possible link between TLR5 and IL-10+ macrophages in H. hepaticus pathogenesis.
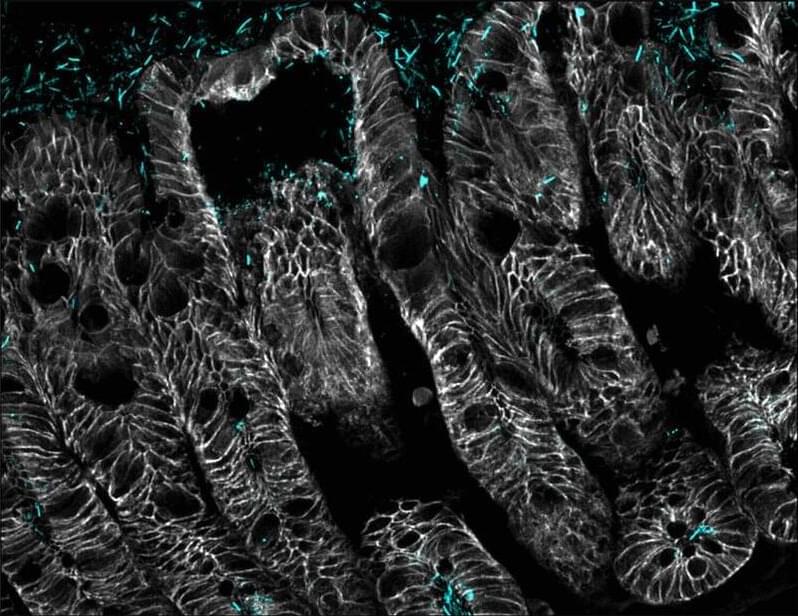
Previous work demonstrated that TLR5 expression differs by intestinal region, with expression restricted to Paneth cells in the small intestine crypt but distributed more broadly among colonic epithelial cells (54). Three-dimensional (3D) mouse Paneth cells enriched small intestinal organoids, and colonoids (which contain both undifferentiated and differentiated cells) responded to flagellin and up-regulated chemokines (54); however, the specific flagellin-responsive colonic cell types remained undefined. In addition, early studies using human epithelial cell lines showed that TLR5 localizes to the IEC basolateral surface, suggesting that flagellin sensing is limited to situations where bacterial products cross the epithelial barrier (55, 56). Our current study advances this understanding by using HCMs that allow for functional separation of DF IECs and UD stem-like cells, which express higher TLR5. After apical or basolateral treatment, UD, but not DF, HCMs responded to TLR5 stimulation. Similar to HCMs, in the mouse epithelium, we found higher Tlr5 expression in LGR5+ stem cells than mature LGR5− IECs. These results suggest that colonic stem cells in humans and mice, such as Paneth cells in the small intestine, act as critical sensors of flagellated microbes and highlight a conserved mechanism to spatially restrict microbial recognition to the crypt base to safeguard the stem cell niche. Under homeostatic conditions, stem cells are physically shielded from microbial stimulation by mucus, secretory immunoglobulin A (IgA), and antimicrobial peptides (13). However, multiple studies showed colonization of cecal and colonic crypts with select flagellated commensal bacteria at homeostasis, which could induce TLR5 signaling (47–49, 57). Furthermore, disruption of the epithelial barrier during injury and resulting expansion of the stem cell zone may increase stem cell and microbial interactions. We propose that compartmentalized TLR5 signaling provides a protective strategy, which promotes tonic macrophage expansion in the steady state and enables amplification when epithelial integrity is compromised or after colonization with microbes that can reach the base of the crypt.