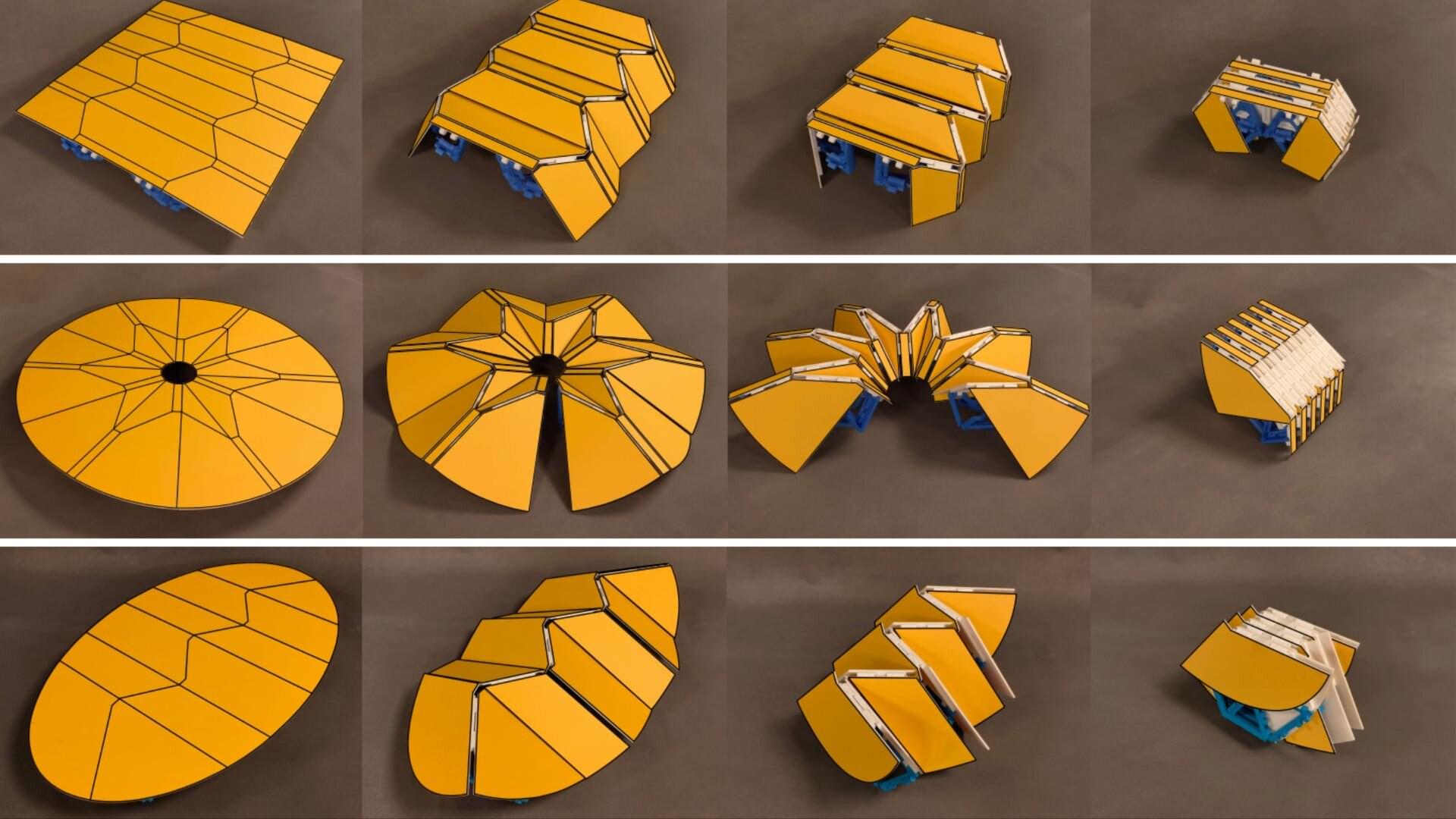
A study published in Nature Communications presents a way to create deployable structures that transform from compact folded states into expansive configurations with perfectly smooth surfaces.


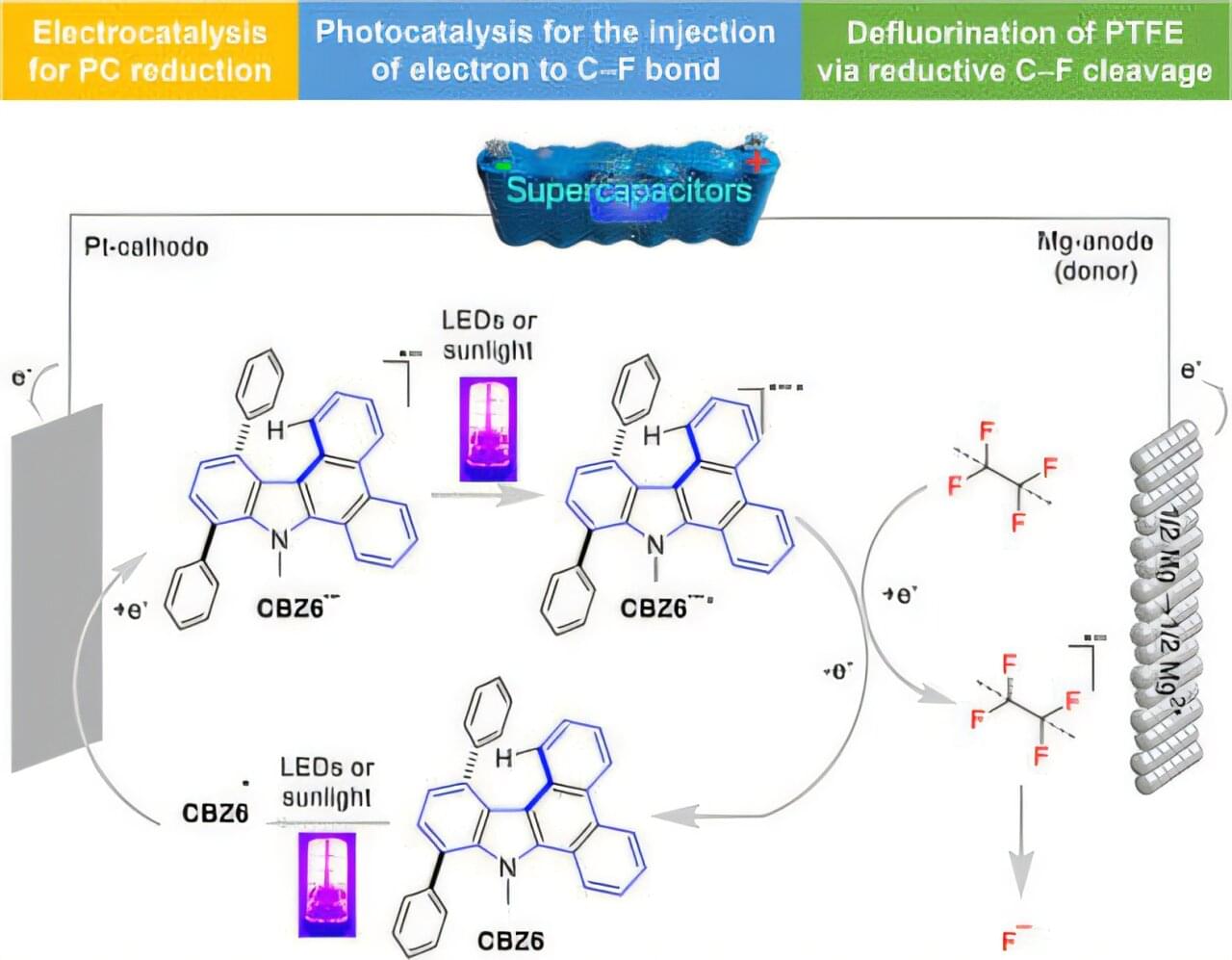
A research team led by Prof. Kang Yanbiao from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) has developed a supercapacitor (SC)-assisted electrophotocatalysis for the efficient defluorination of the polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) and poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) at low temperatures.
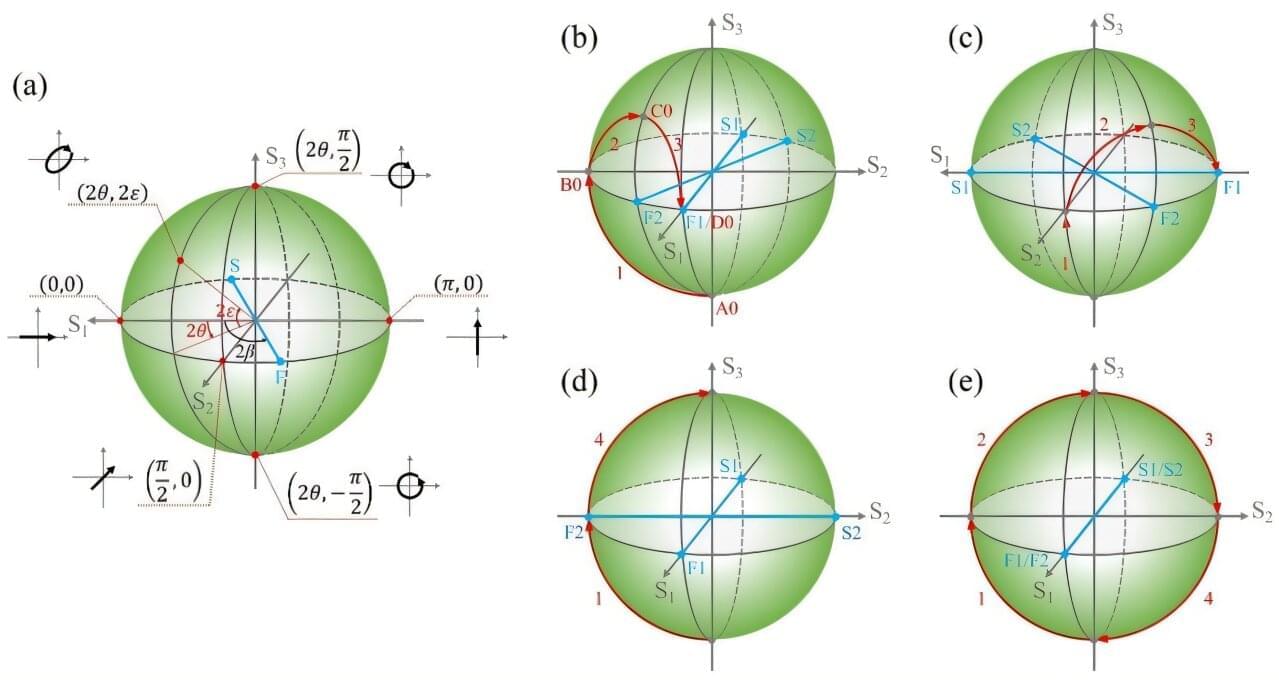
A research team led by Associate Prof. Wang Anting from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) proposed a method for multidimensional manipulation of polarization and phase based on a single geometric phase element. They managed to generate and control high-order vector vortex beams (VVBs).
The study is published in Laser & Photonics Reviews.
Since lasers emerged, multidimensional control of laser light fields has always been at the forefront of optical research. Among them, VVBs with various physical characteristics under the coordinated control of spin-orbit angular momentum (OAM) are highly favored.
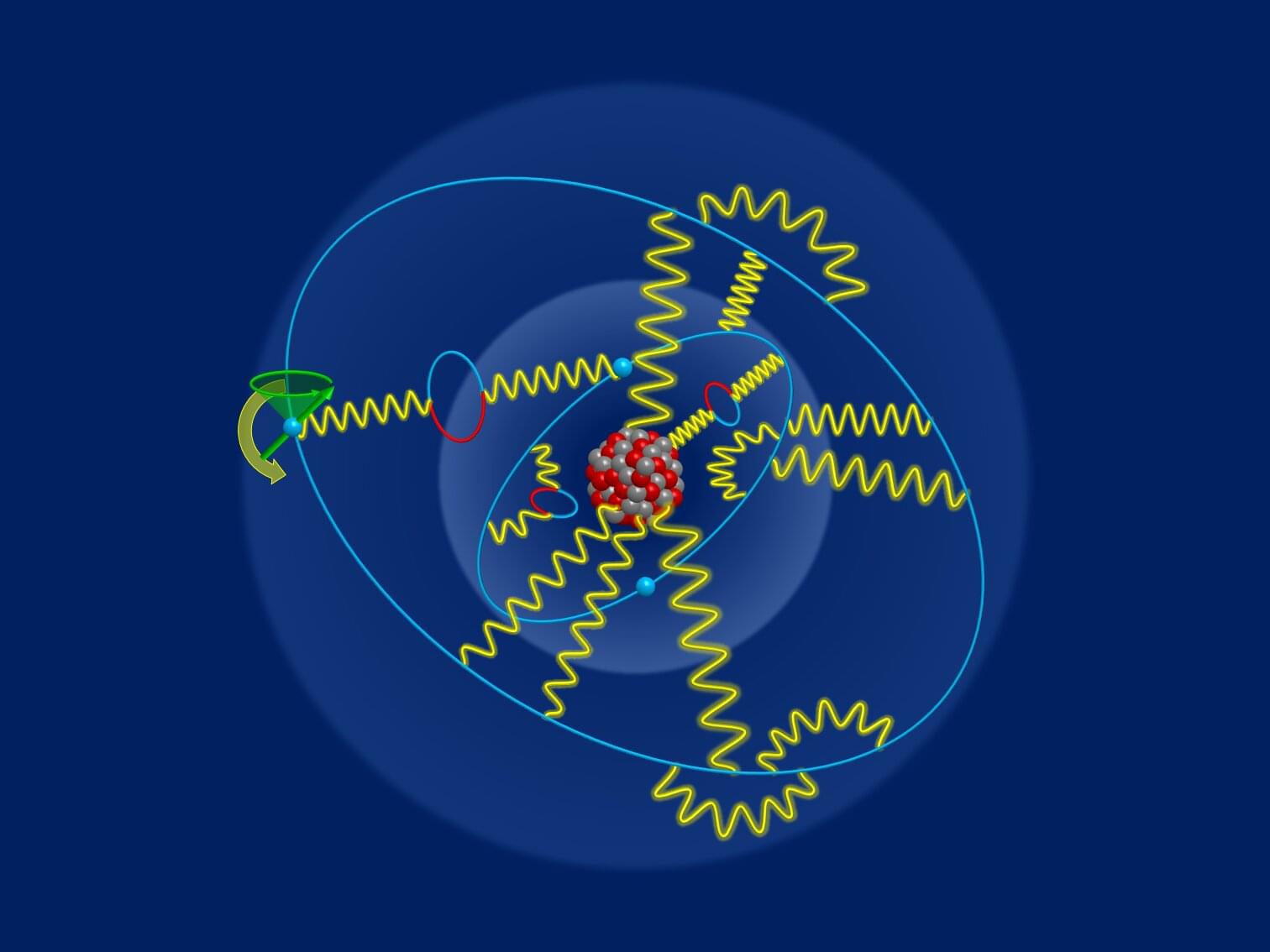
Researchers from the Max-Planck-Institut fuer Kernphysik present new experimental and theoretical results for the bound electron g-factor in lithium-like tin, which has a much higher nuclear charge than any previous measurement. The paper is published in the journal Science.
The experimental accuracy reached a level of 0.5 parts per billion. Using an enhanced interelectronic QED method, the theoretical prediction for the g-factor reached a precision of 6 parts per billion.

A weakness in Apple’s Safari web browser allows threat actors to leverage the fullscreen browser-in-the-middle (BitM) technique to steal account credentials from unsuspecting users.
By abusing the Fullscreen API, which instructs any content on a webpage to enter the browser’s fullscreen viewing mode, hackers can exploit the shortcoming to make guardrails less visible on Chromium-based browsers and trick victims into typing sensitive data in an attacker-controlled window.
SquareX researchers observed an increase use of this type of malicious activity and say that such attacks are particularly dangerous for Safari users, as Apple’s browser fails to properly alert users when a browser window enters fullscreen mode.