Using an experimental technique called “Oz,” researchers stimulated the human retina such that people saw a brand-new color.


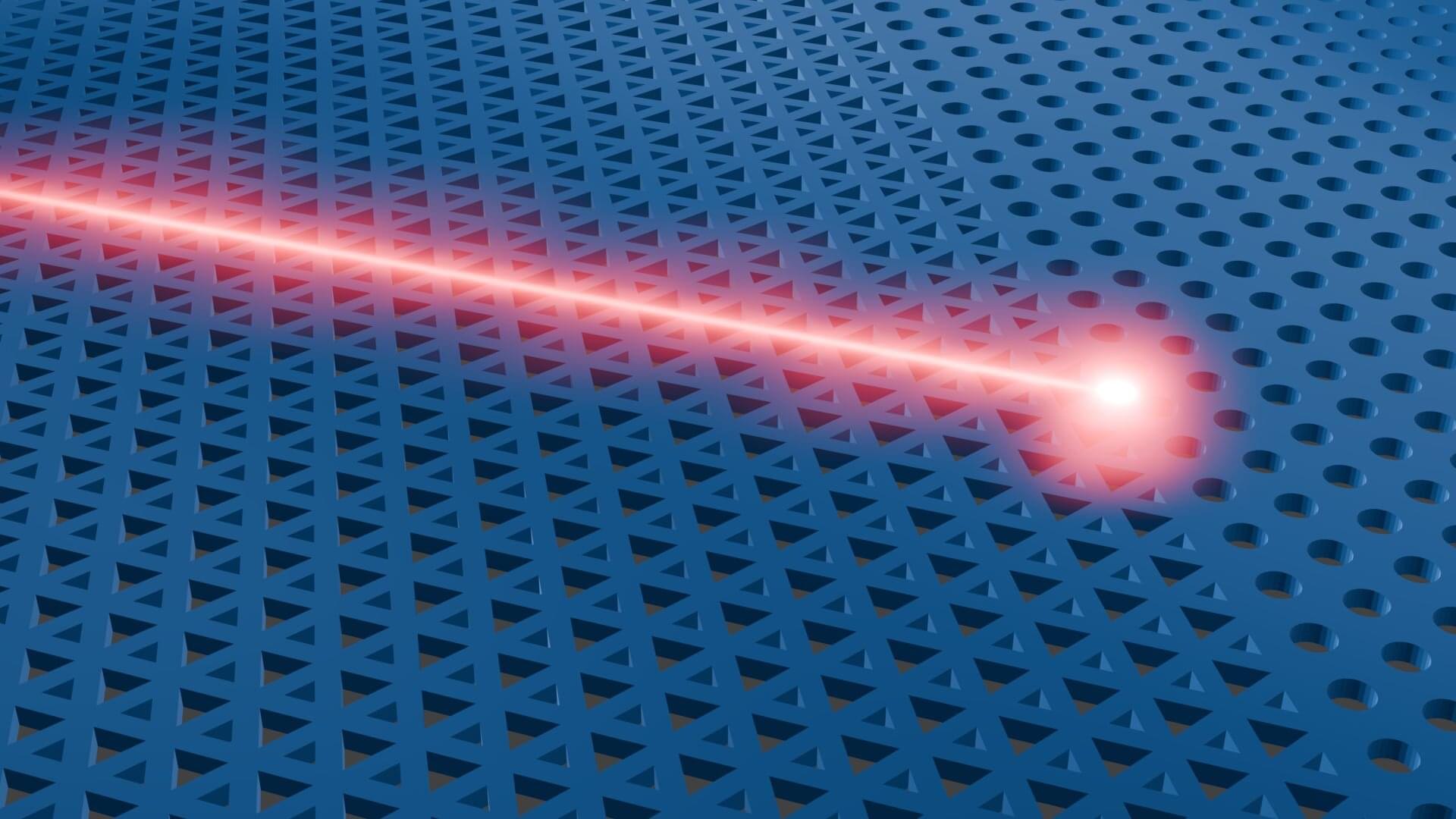
Concentrating light in a volume as small as the wavelength itself is a challenge that is crucial for numerous applications. Researchers from AMOLF, TU Delft, and Cornell University in the U.S. have demonstrated a new way to focus light on an extremely small scale. Their method utilizes special properties of a photonic crystal and works for a broader spectrum of wavelengths than alternative methods. The researchers published their findings in Science Advances on April 18.

I’m writing this from a laptop that’s stalling and refusing to switch between tabs because it’s gotten too warm in the early Indian summer. It’s not like I’m running a hectic workload of video and audio editing tools and multiple browsers at once: this old machine just can’t move heat away from the processor and other internals quickly enough.
That results in throttling, or reducing the clock speed at high temperatures, in order to prevent overheating and damage to the internal components. But a new finding from the University of Virginia School of Engineering and Applied Science could make that a thing of the past – with crystals.
When electronic components like the processor in your laptop are working at full tilt, they can get pretty hot. The same can be said for chips in a range of other devices, and even batteries in electric cars. Now, if these components are squashed into tight spaces, you’re going to see heat build up there and take a long time to dissipate.



Hello everyone! It’s time for a me to talk about a show that isn’t Family Guy again! But this time it is not about Family Guy. It’s actually about the new Adult Swim show called Common Side Effects which is really good. You should all go watch Common Side Effects after you watch this video telling you to go watch Common Side Effects.
New Video Every Friday!
Twitter: / iammrcow.
My Music: https://open.spotify.com/artist/3srW2… / @mrcow.
Subscribe: / @mrcow