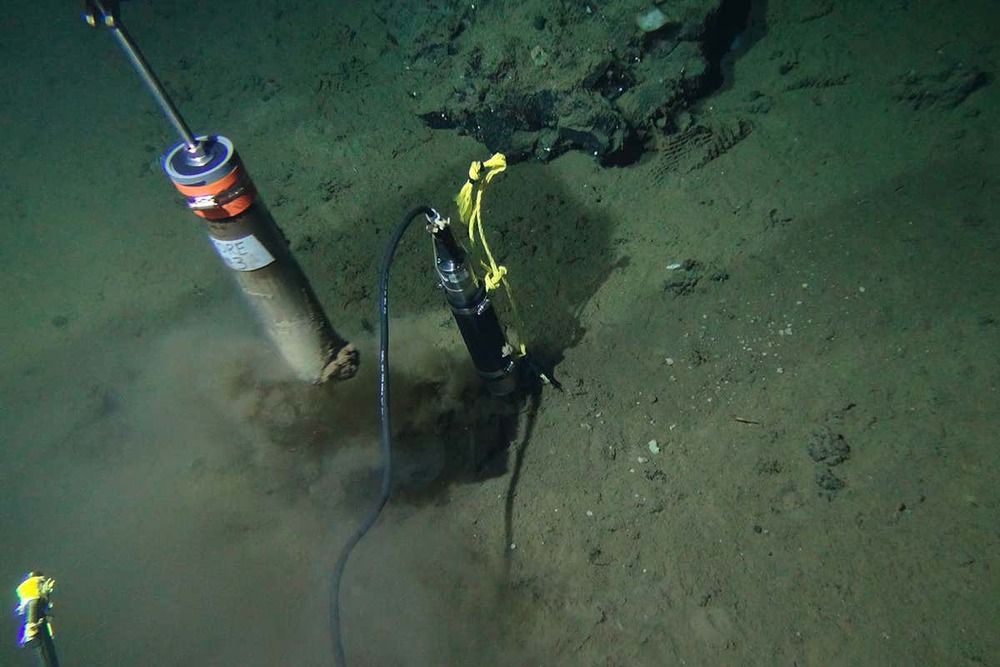
There is so little food in the mud at the bottom of the Pacific Ocean that individual microbes living there use just 0.00000000001 joules of energy each year.
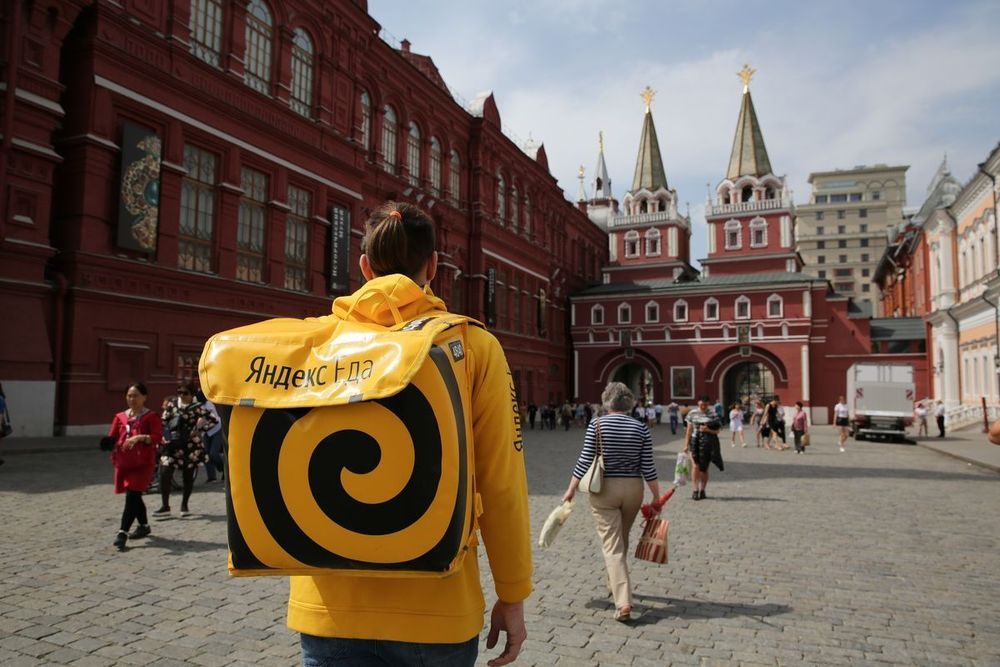




Five years ago, Yandex was just a search engine trying hard to fend off Google in its local market. Since then it has bought Uber Technologies Inc.’s Russia business, built its voice assistant into cars and home appliances, and more than doubled its revenue. Yandex now claims to have 108 million monthly users, which is about 75% of Russia’s population.
I’m woken up by an alarm on a home speaker designed by Yandex NV. I go to work in Yandex taxi listening to the company’s music-streaming service. My lunch is delivered by Yandex. Eats. I buy sneakers on the company’s Beru marketplace, and catch up on a series on its Kinopoisk smart-TV app in the evening.
You get the picture. Not so long ago, most decisions in Russia were decided by the state. Now, Russia’s largest tech company can cater to your every need.
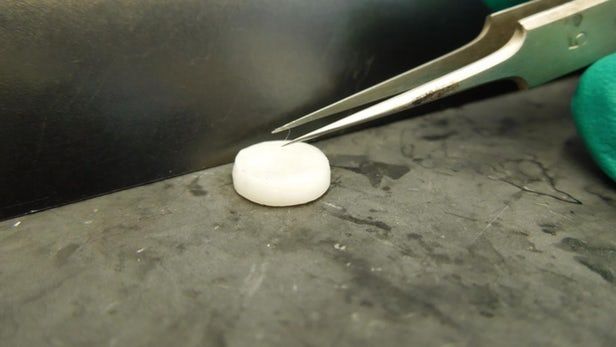
An exciting breakthrough from Columbia University researchers demonstrates a new way to grow human hair follicles using 3D printed molds. This is the first time human hair follicle cells have been grown completely in lab conditions, opening up a potentially unlimited source of hair follicles for future hair restoration surgical procedures.
O.o!
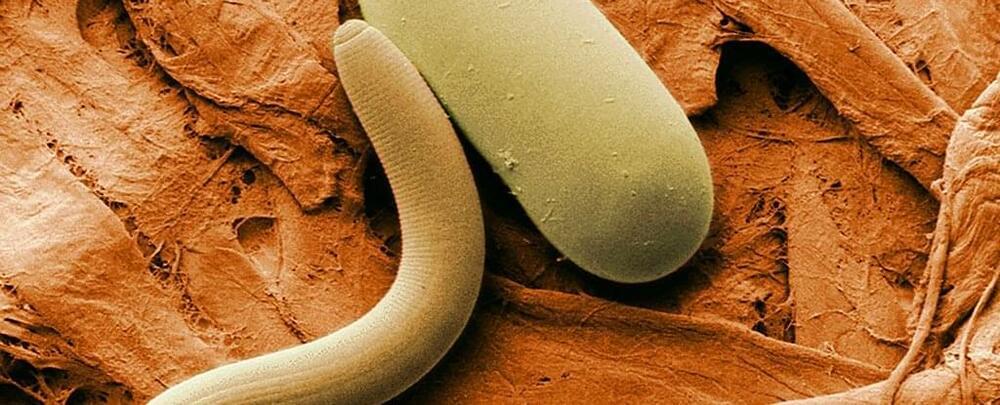
Samples of permafrost sediment frozen for the past 42,000 years were recently thawed to reveal living nematodes.
Within weeks the roundworms began to move and eat, setting a record for the time an animal can survive cryogenic preservation.
Aside from revealing new limits of endurance, it just might prove useful when it comes to preserving our own tissues.
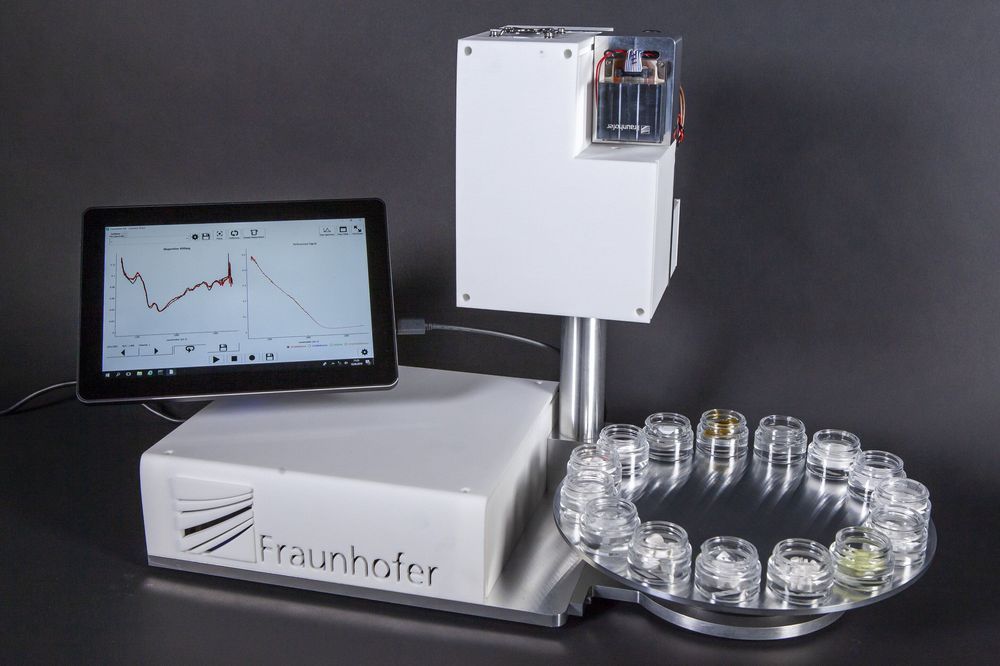
To guarantee high quality pharmaceuticals, manufacturers need not only to control the purity and concentration of their own products, but also those of their suppliers. Researchers at the Fraunhofer Institute for Applied Solid State Physics IAF have developed a measuring system capable of identifying a wide variety of chemical and pharmaceutical substances remotely and in real time. It is perfect for the use in the pharmaceutical, chemical and food industry.
Especially for pharmaceutical and food productions a continuous control of ingredients is indispensable. Usually, this would be done by a sampling and a laboratory analysis via chromatography or spectrometers. However, such a process is time-consuming and allows only for spot checks. At Fraunhofer IAF, researchers have developed a measuring system capable of a quality control in real time. It identifies even smallest amounts of substances based on their molecular composition.

Would you like fries with your nano-nuggets?
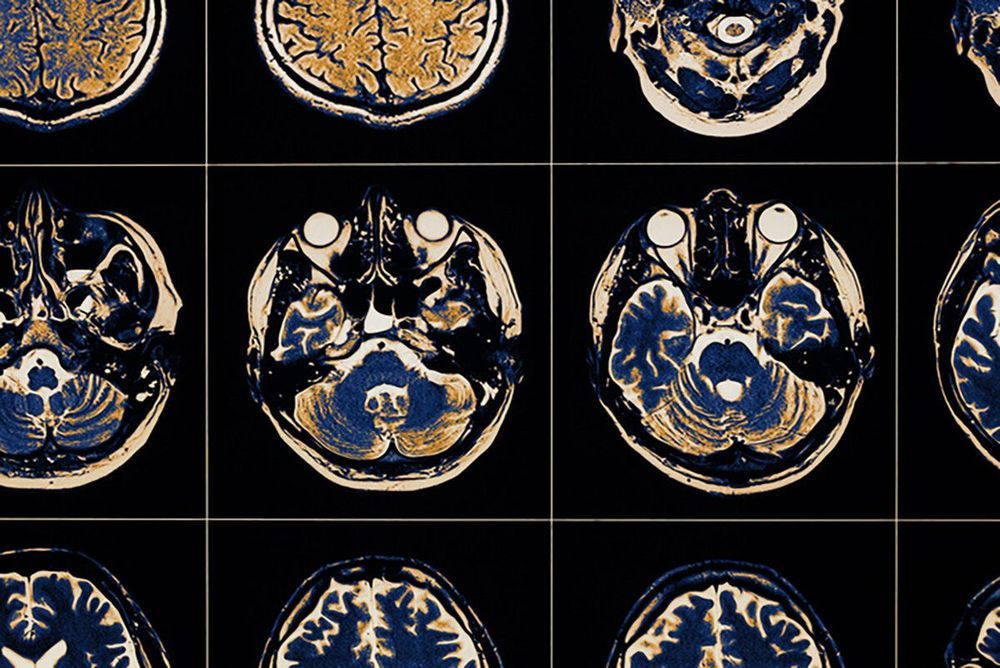
More than three decades ago, scientists discovered that a chemical found in a synthetic opioid, MPTP, induced the onset of a form of Parkinson’s disease. In a new study led by scientists from the School of Veterinary Medicine, researchers found that an enzyme in the body can metabolize compounds formed in the brain from alkaloids present in certain foods and tobacco into MPTP-like chemicals, triggering a neurodegenerative condition in mice.
The researchers, led by Narayan Avadhani and Mrittika Chattopadhyay, suggest that the enzyme, mitochondrial CYP2D6, presents a potentially powerful new target for Parkinson’s treatment.
“Over the past two or three decades, researchers have tried inhibiting the process by which they believed MPTP was metabolized, with mixed success,” says Avadhani. “We believe that mitochondrial CYP2D6 is the more direct drug target, which might prove better in treating idiopathic Parkinson’s disease.”