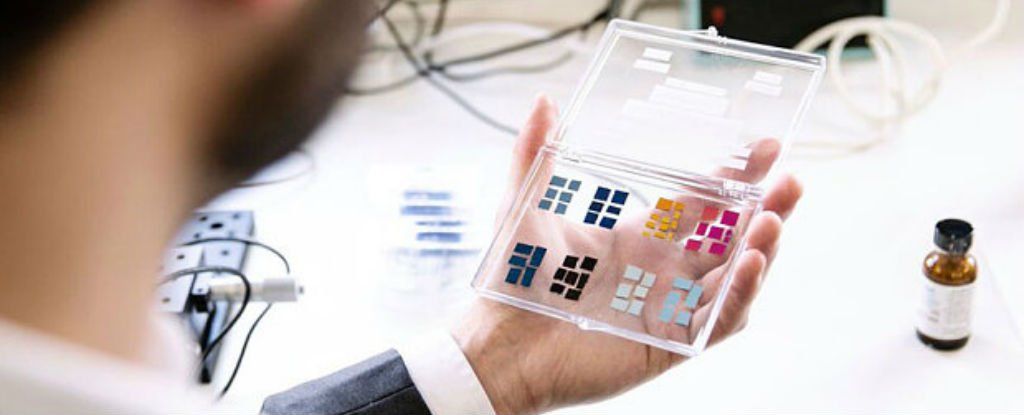
Scientists in the UK have invented a new type of touchscreen material that requires very little power to illuminate, offering up a cheap alternative to today’s smartphone and tablet screens, with vivid colours and high visibility in direct sunlight.
The team is already in talks with some of the world’s largest consumer electronics corporations to see if their new material can replace current LCD touchscreens in the next couple of years, which could spell the end for daily smartphone charging. “We can create an entire new market,” one of the researchers, Peiman Hosseini, told The Telegraph. “You have to charge smartwatches every night, which is slowing adoption. But if you had a smartwatch or smart glass that didn’t need much power, you could recharge it just once a week.”
Developed by Bodie Technologies, a University of Oxford spin-off company, the new display is reportedly made from a type of phase-change material called germanium-antimony-tellurium, or GST. The researchers are being understandably cagey about exactly how it’s made as they shop the technology around, but it’s based on a paper they published last year describing how a rigid or flexible display can be formed from microscopic ‘stacks’ of GST and electrode layers.