😗
If these organisms are eating viruses in nature, it could change the way scientists think about global carbon cycling.

Scientists from UNSW Sydney have demonstrated a novel technique for creating tiny 3D materials that could eventually make fuel cells like hydrogen batteries cheaper and more sustainable.
In the study published in Science Advances (“Synthesis of hierarchical metal nanostructures with high electrocatalytic surface areas”), researchers from the School of Chemistry at UNSW Science show it’s possible to sequentially ‘grow’ interconnected hierarchical structures in 3D at the nanoscale which have unique chemical and physical properties to support energy conversion reactions.
In chemistry, hierarchical structures are configurations of units like molecules within an organisation of other units that themselves may be ordered. Similar phenomena can be seen in the natural world, like in flower petals and tree branches. But where these structures have extraordinary potential is at a level beyond the visibility of the human eye – at the nanoscale.
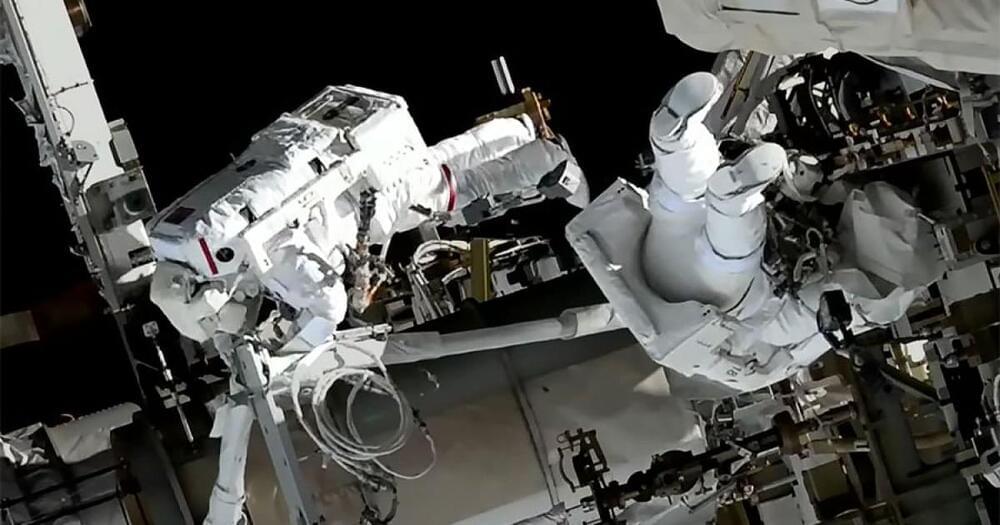

Two astronauts from the International Space Station (ISS) yesterday performed the first spacewalk of the year, working on the exterior of the station as part of a long-term program to upgrade the ISS power system. The spacewalk took place on Friday, January 20, and lasted over seven hours, though one troublesome strut wasn’t bolted into place as planned.
The two astronauts performing the spacewalk were NASA astronaut Nicole Mann and Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Koichi Wakata, and this was the first spacewalk for each of them.
The ISS solar arrays which provide power to the station are getting old, so in a long-term project astronauts are installing new arrays called iROSAs at an offset on top of the old arrays — allowing both sets of arrays to provide power. The aim of the spacewalk yesterday was to install two mounting platforms, which would be used to install new solar arrays later this year.

Jan. 20 (UPI) — Two astronauts embarked on the first spacewalk of 2023 on Friday as they work toward upgrading the International Space Station’s power generation system.
NASA astronaut Nicole Mann teamed up with Koichi Wakata of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency for the morning spacewalk, expected to last about 6 1/2 hours. They will install a modification kit at the far end of the ISS, allowing for the future installation of the roll-out solar array.
The spacewalk was scheduled to start at 8:15 a.m., EST, but NASA officials said the operation was ahead of schedule with both astronauts setting their spacesuits to battery power about a minute earlier, marking the official start of the mission.

When it comes to star formation in interstellar clouds of gas and dust, there’s an ongoing tug-of-war between two cloud-shaping processes. Young, massive stars inject energy into their surroundings in a way that both disrupts star formation by shredding the surrounding medium and encourages it by collecting dense gas shells that are prone to gravitational collapse. Which of these feedback processes dominates has been unclear, but new observations by Lars Bonne of NASA’s Ames Research Center and his colleagues suggest that stellar feedback significantly suppresses star formation. These findings—presented earlier this month at the 241st Meeting of the American Astronomy Society in Seattle—provide a missing piece in understanding why proposed rapid star-formation rates have long misaligned with observations.
Recent observations suggest that the formation of high-mass stars—ones greater than 8 times the mass of the Sun—is associated with the gravitational collapse of the surrounding cloud of molecular gas. This collapse leads to a high concentration of material, which should induce further star formation. However, the expected high star-formation rates are not observed, with typically only a few percent of the molecular cloud’s mass becoming new stars. “If stellar feedback indeed disperses the collapsing molecular cloud on the same timescale that new stars form, it could prevent these proposed high star-formation rates,” Bonne says. But predicting the impact and role of stellar feedback on the surrounding molecular cloud remains extremely difficult.
Now with data from NASA’s Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy (SOFIA, now retired) and the Chandra X-ray Observatory, Bonne and his colleagues have tracked the process in real time. The first observation target was a star-forming complex called RCW 36, which is several light-years across and is located 2,900 light-years away in a molecular cloud within the constellation Vela. Like other star-forming complexes, RCW 36 consists of a large region of ionized atomic hydrogen (HII, pronounced “H-two”). This region includes a cluster of young stars and two low-density cavities that extend outward in opposite directions. A ring of gas forms a waist between the two cavities, resulting in an hourglass-like shape.
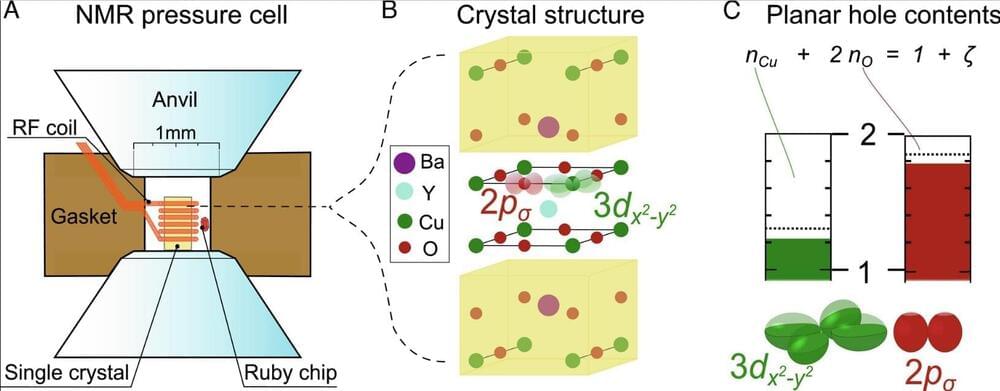
Physicists at Leipzig University have once again gained a deeper understanding of the mechanism behind superconductors. This brings the research group led by Professor Jürgen Haase one step closer to their goal of developing the foundations for a theory for superconductors that would allow current to flow without resistance and without energy loss. The researchers found that in superconducting copper-oxygen bonds, called cuprates, there must be a very specific charge distribution between the copper and the oxygen, even under pressure.
This confirmed their own findings from 2016, when Haase and his team developed an experimental method based on magnetic resonance that can measure changes that are relevant to superconductivity in the structure of materials. They were the first team in the world to identify a measurable material parameter that predicts the maximum possible transition temperature —a condition required to achieve superconductivity at room temperature. Now they have discovered that cuprates, which under pressure enhance superconductivity, follow the charge distribution predicted in 2016. The researchers have published their new findings in the journal PNAS.
“The fact that the transition temperature of cuprates can be enhanced under pressure has puzzled researchers for 30 years. But until now we didn’t know which mechanism was responsible for this,” Haase said. He and his colleagues at the Felix Bloch Institute for Solid State Physics have now come a great deal closer to understanding the actual mechanism in these materials.
It generates energy by forcing the stream to form a vortex.
Without employing any blades, the transportable hydraulic turbine SETUR from Vortex Hydrokinetics serves as a power source. The water source could be rivers, tidal streams, ocean currents, or even canals.
The portable equipment is lightweight as a result of the 3D-printed bladeless hydraulic turbine.
Vortex Hydrokinetics.
As reported by Designboom, the turbine, shaped like an atomic bomb, generates energy by forcing the stream to form a vortex and then using that vortex as a source of current. According to the design team, the cost-effective SETUR can be used both independently and as part of a multi-unit hydropower farm.
Claiming a system-level energy density 5X higher than batteries, Amogy has rolled out “the world’s first ammonia-powered, zero-emission semi truck.” It holds about 900 kWh of energy, like the Tesla Semi, but you can refuel it in about eight minutes.