‘The most radical new university to open in decades.’ — The Times. Teaching students to tackle the world’s most complex problems.



We just released a curated list of 125+ essays about biology and science. These articles cover pharmaceuticals, the history of molecular biology, timeless arguments and theories, and more. All of them inspired or taught or challenged us to think more deeply.
Check it out here on Substack or on our custom website: https://read.asimov.com

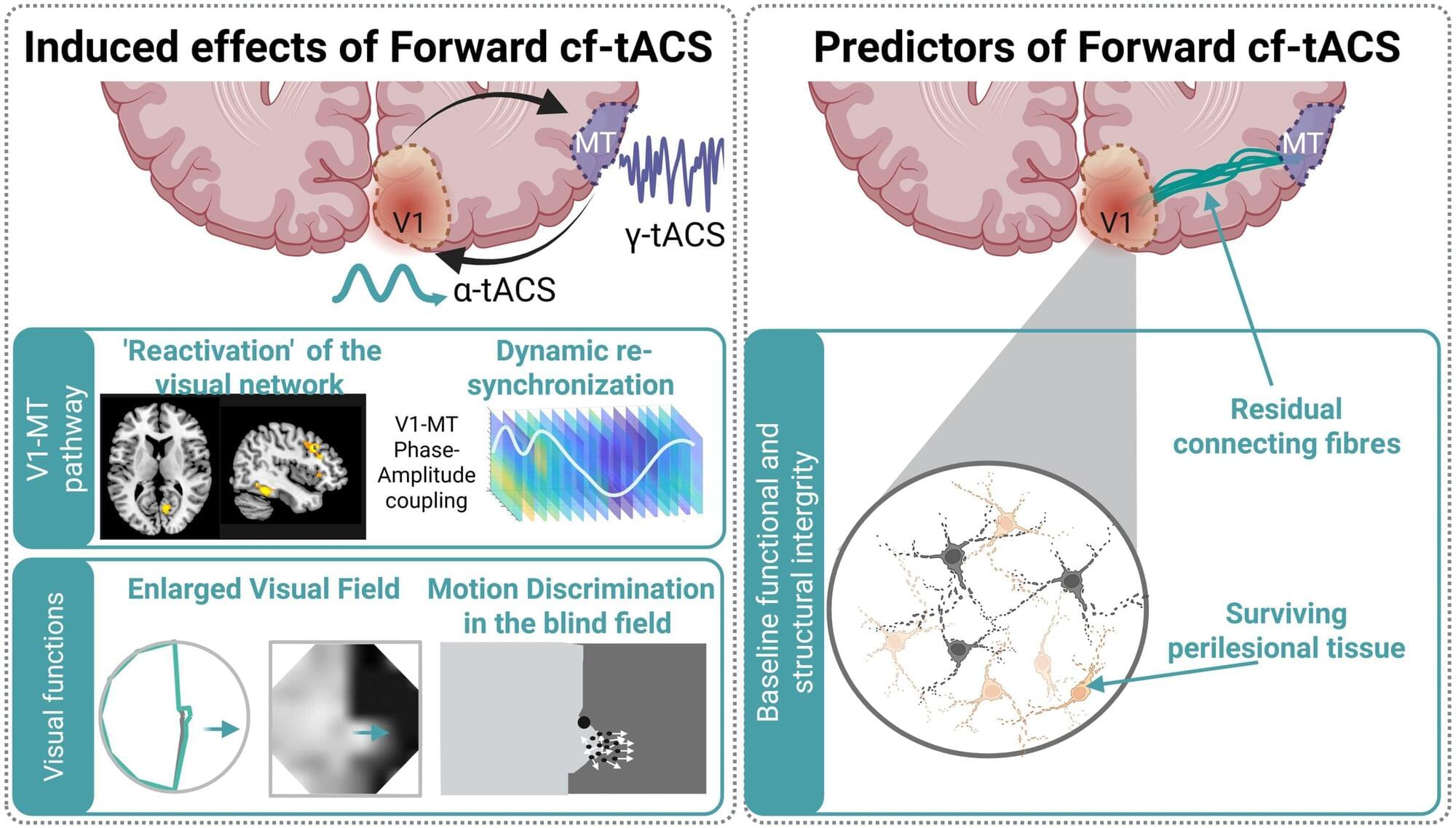
Scientists at EPFL have developed an innovative, non-invasive brain stimulation therapy to significantly improve visual function in stroke patients who have suffered vision loss following a stroke. The approach could offer a more efficient and faster way to regain visual function in such cases.
Each year, thousands of stroke survivors are left with hemianopia, a condition that causes loss of half of their visual field (the “vertical midline”). Hemianopia severely affects daily activities such as reading, driving, or just walking through a crowded space.
There are currently no treatments that can restore lost visual function in hemianopia satisfactorily. Most available options focus on teaching patients how to adapt to loss of vision rather than recovering it. To achieve some degree of recovery, months of intensive neurorehabilitative training are required for only moderate restoration at best.
SpaceKids Global; Inspiring students to excel in STEAM+ Environment education; with a focus on empowering young girls.

Soft drink consumption is linked to an increased risk of major depressive disorder and greater depressive symptom severity, mediated by changes in gut microbiota, particularly Eggerthella abundance.
Question Is soft drink consumption related to depression diagnosis and severity, and is this association mediated by gut microbiome alteration?
Findings In this cohort study, soft drink consumption was significantly associated with diagnosis of major depressive disorder, as well as depression severity, across a single-study cohort of 932 clinically diagnosed patients and healthy controls. This association was significantly mediated by Eggerthela abundance in female patients and controls.
Meaning Education, prevention strategies, and policies aiming to reduce soft drink consumption are urgently required to mitigate depressive symptoms; in addition, interventions for depression targeting the microbiome composition appear promising.

This Neurology Education Teaching Neurovisual by Sutherland and Gummerson details the Head-Impulse-Nystagmus-Test-of-Skew (HINTS) exam, which uses special maneuvers to identify central etiologies of acute vestibular syndrome with greater sensitivity than hyperacute MRI.
Letters to the Editor.
The Letters section represents an opportunity for ongoing author debate and post-publication peer review. View our submission guidelines for Letters to the Editor before submitting your comment.

Join us, Dr Sal Consoli (University of Edinburgh) and Dr Samantha Curle (University of Bath) for a dynamic 60-minute webinar celebrating the inaugural volume in the series Elements in Research Methods in Education series.
We will interview the author of How to Use Generative AI in Educational Research — Dr Jasper Roe, to explore why he chose this specific topic, the writing process behind this book, and how he hopes it will influence educational researchers and practitioners.
Then we’ll open the floor to attendees interested in contributing to the series. We will provide a unique opportunity to ask questions about the commissioning process, editorial expectations, and how to develop a successful proposal.

In an MIT classroom, a professor lectures while students diligently write down notes they will reread later to study and internalize key information ahead of an exam.
Humans know how to learn new information, but large language models can’t do this in the same way. Once a fully trained LLM has been deployed, its “brain” is static and can’t permanently adapt itself to new knowledge.
This means that if a user tells an LLM something important today, it won’t remember that information the next time this person starts a new conversation with the chatbot.

About 68% of respondents said the pressure to publish their research is greater than it was two to three years ago and only 45% agreed that they have sufficient time for research (see ‘Researchers are feeling the pressure’). Another concern is uncertainty over funding — just 33% of respondents expect funding in their field to grow in the next 2–3 years. And that proportion fell to just 11% in North America, reflecting unprecedented cuts to US research funding this year.
“As a researcher based in Brazil, I strongly relate to the survey’s findings, particularly the growing pressure to publish despite limited time and resources,” says Claudia Suemoto, a gerontologist at the University of São Paulo Medical School. “The demand for productivity has indeed increased in recent years, yet opportunities for funding and access to qualified personnel remain constrained in Brazil and other low-and middle-income countries.”
Suemoto says this imbalance of high demands and restricted resources often forces researchers to do more with less, which could affect the quality and innovation of research. Comments researchers made as part of the survey indicate that the lack of time is down to factors including growing administrative and teaching demands and trying to identity and acquire funding.