Intel’s director of quantum hardware, Jim Clarke, explains the company’s two quantum computing technologies.
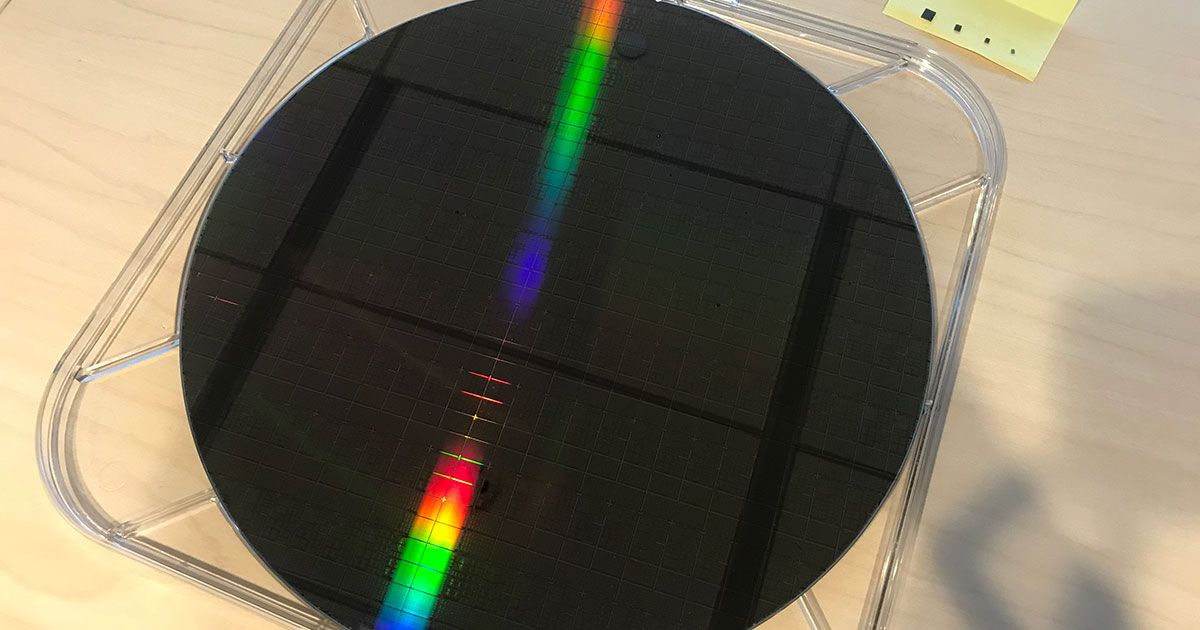

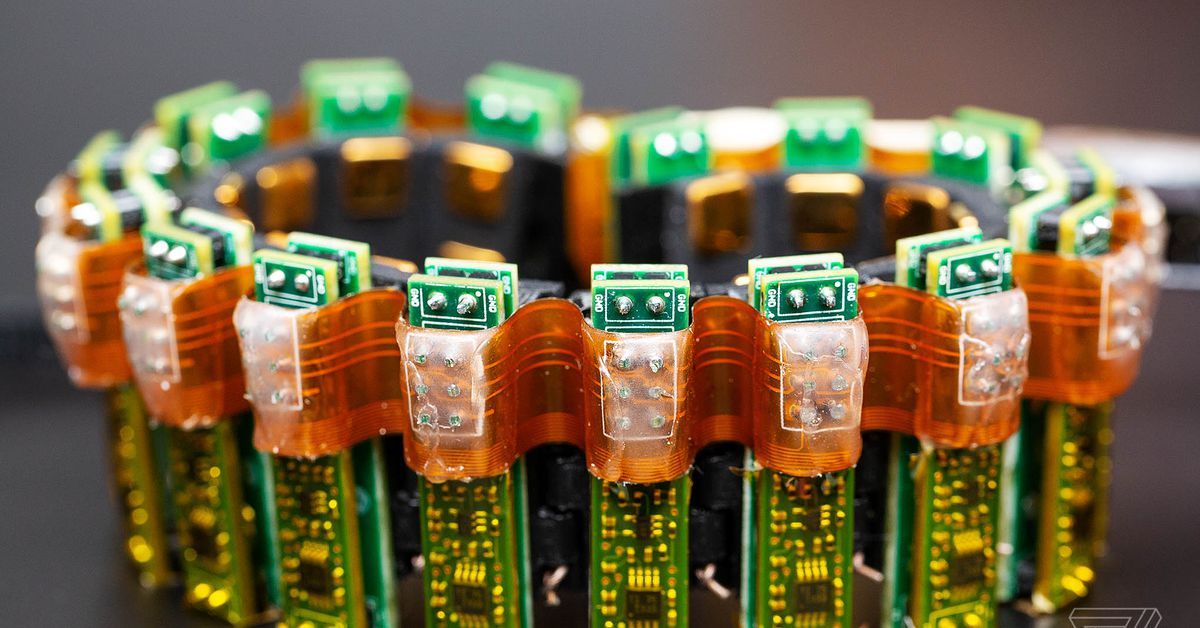
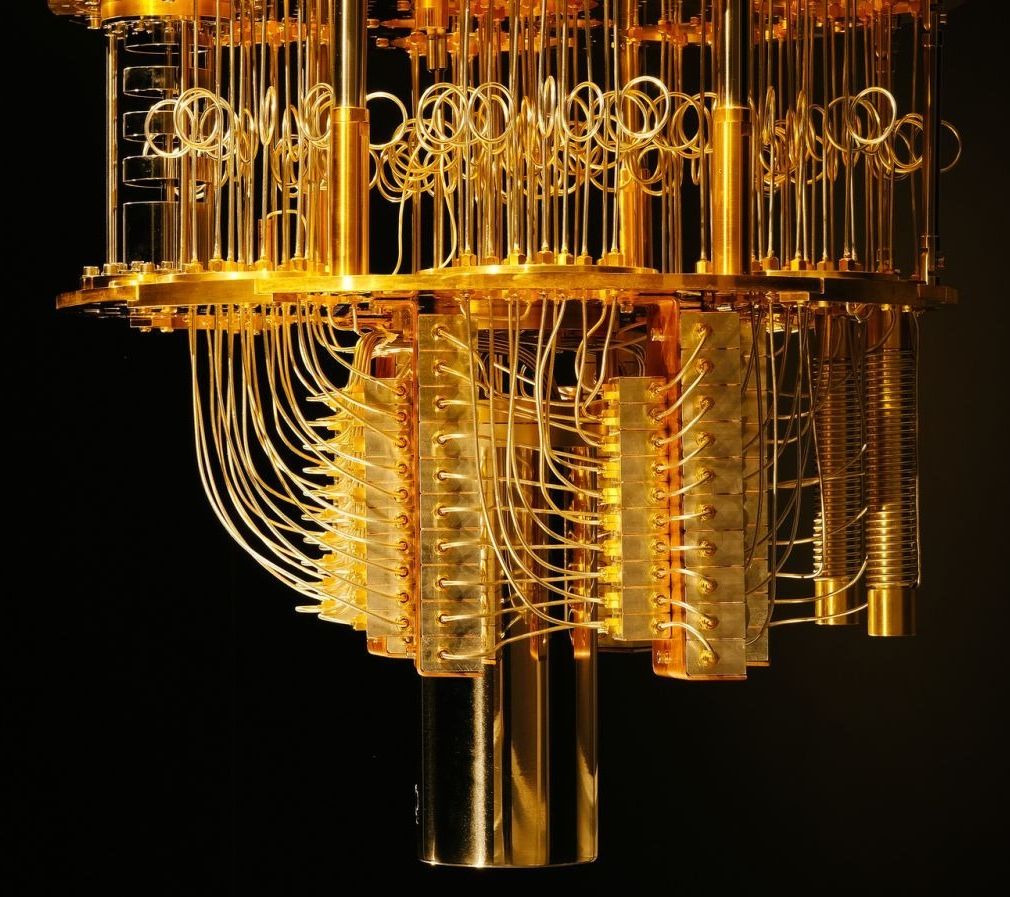
Quantum computing has made it to the United States Congress. If this field of quantum information is the new space race, the US doesn’t want to fall behind.
After all, China has funded a National Laboratory for Quantum Information Sciences, set to open in 2020, and has launched a satellite meant to test long-distance quantum secure information. Two new bills, one of which is still a draft, are meant to establish the US as a leader in the field.
“Quantum computing is the next technological frontier that will change the world, and we cannot afford to fall behind,” said Senator Kamala Harris (D-California) in a statement passed to Gizmodo. “We must act now to address the challenges we face in the development of this technology—our future depends on it.”
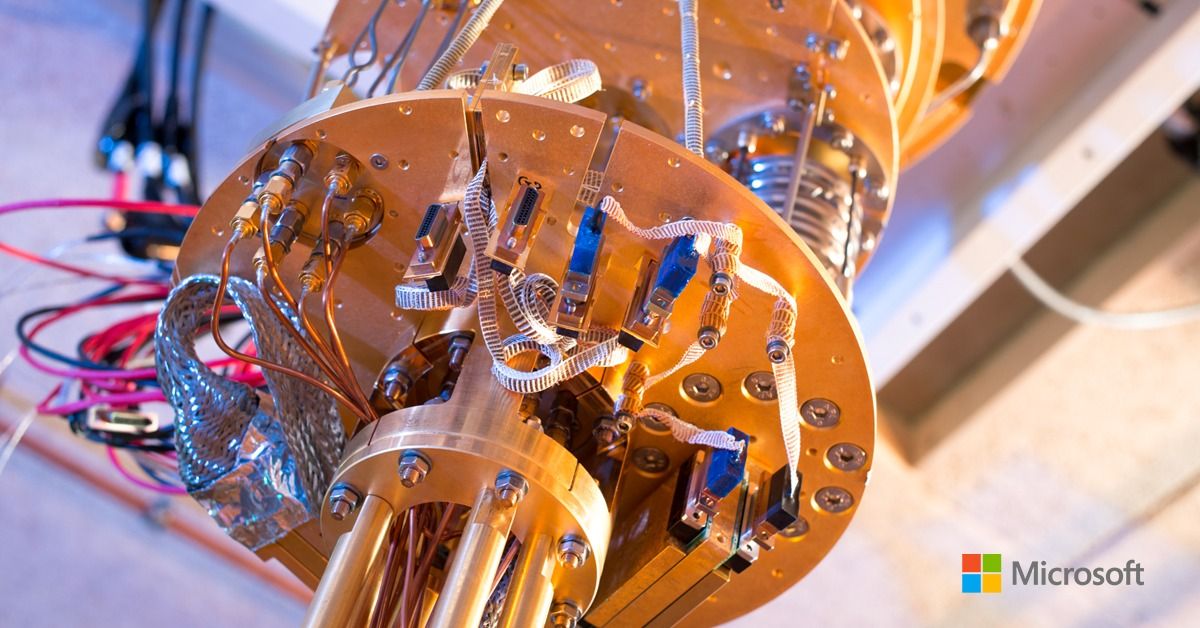
Together, this full quantum stack pairs with familiar tools to create an integrated, streamlined environment for quantum processing.
Scalability, from top to bottom
Quantum computers can help address some of the world’s toughest problems, provided the quantum computer has enough high-quality qubits to find the solution. While the quantum systems of today may be able to add a high number of qubits, the quality of the qubits is the key factor in creating useful scale. From the cooling system to qubits to algorithms, scalability is a fundamental part of the Microsoft vision for quantum computing.
MIT researchers, working with scientists from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, have developed a new way to power and communicate with devices implanted deep within the human body. Such devices could be used to deliver drugs, monitor conditions inside the body, or treat disease by stimulating the brain with electricity or light.
The implants are powered by radio frequency waves, which can safely pass through human tissues. In tests in animals, the researchers showed that the waves can power devices located 10 centimeters deep in tissue, from a distance of 1 meter.
“Even though these tiny implantable devices have no batteries, we can now communicate with them from a distance outside the body. This opens up entirely new types of medical applications,” says Fadel Adib, an assistant professor in MIT’s Media Lab and a senior author of the paper, which will be presented at the Association for Computing Machinery Special Interest Group on Data Communication (SIGCOMM) conference in August.
Using the physics equivalent of the strobe photography that captures every twitch of a cheetah in full sprint, researchers have used ultrafast spectroscopy to visualize electrons interacting as a hidden state of matter in a superconductive alloy.
It takes intense, single-cycle pulses of photons—flashes—hitting the cooled alloy at terahertz speed—trillions of cycles per second—to switch on this hidden state of matter by modifying quantum interactions down at the atomic and subatomic levels.
And then it takes a second terahertz light to trigger an ultrafast camera to take images of the state of matter that, when fully understood and tuned, could one day have implications for faster, heat-free, quantum computing, information storage and communication.

Although blockchain is traditionally seen as secure, it is vulnerable to attack from quantum computers. Now, a team of Russian researchers say they have developed a solution to the quantum-era blockchain challenge, using quantum key distribution (QKD).
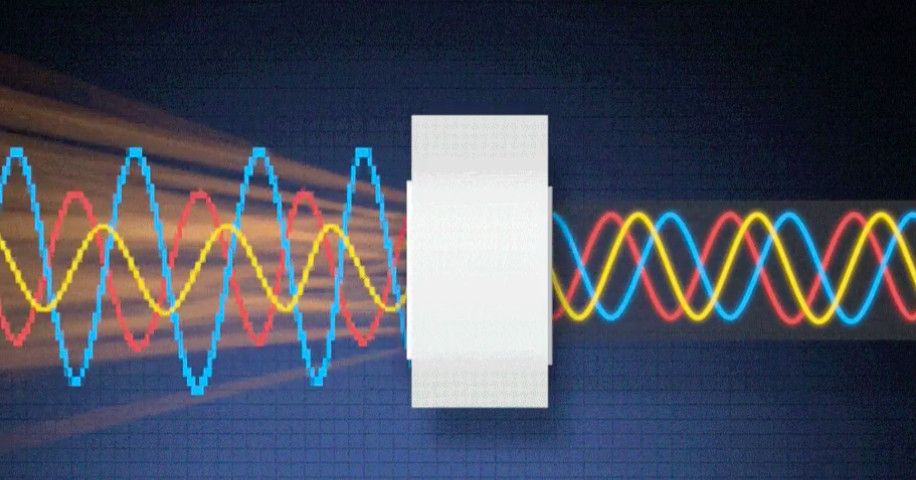
Quantum computers are different from binary digital electronic computers based on transistors. Whereas common digital computing requires that the data be encoded into binary digits (bits), each of which is always in one of two definite states (0 or 1), quantum computation uses quantum bits, which can have more by being in superpositions of states.
Writing in the journal Quantum Science and Technology, the researchers set out a quantum-safe blockchain platform that uses QKD to achieve secure authentication.
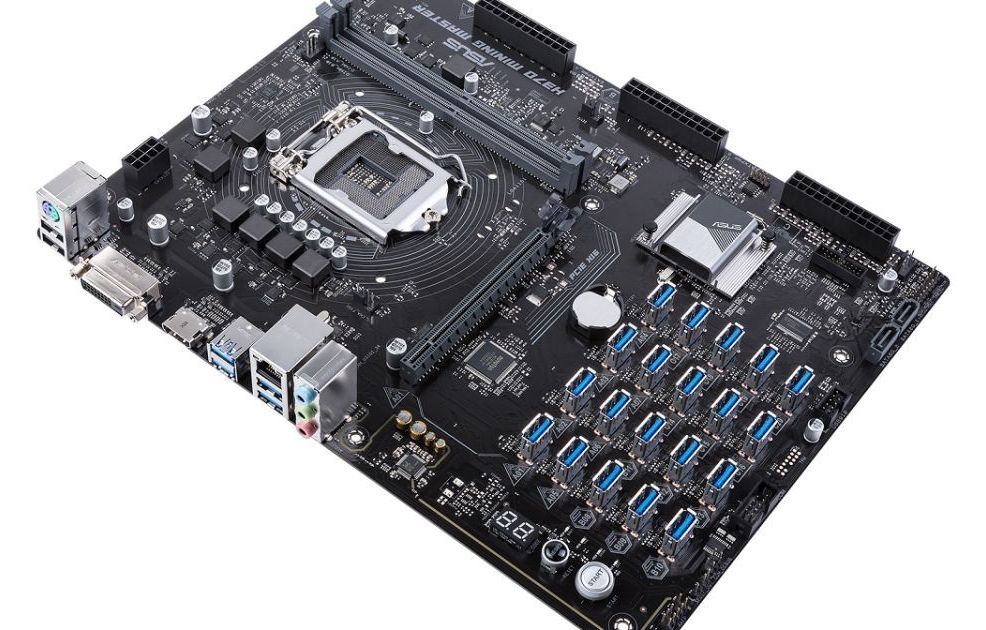

ASUS is moving further into the cryptocurrency hardware market with a motherboard that can support up to 20 graphics cards, which are typically used for mining. The H370 Mining Master uses PCIe-over-USB ports for what ASUS says is sturdier, simpler connectivity than other mining-focused motherboards.
You can manage each port and graphics card with on-board diagnostics. One feature scans your system when you boot up to determine the status of each port, while there are onboard LEDs that signify a problem with components such as memory or the processor (there’s space for an Intel 8th-gen Core CPU). ASUS has added some other features to optimize mining as well.
The H370 Mining Master follows last year’s B250 Mining Expert, which had room for 19 CPUs via PCIe ports. ASUS says that board had far more sales than it expected, which prompted the company to keep traveling down the crypto road and evolve its mining-tailored motherboards. The latest board will ship later this year, though ASUS has yet to announce pricing. You might need to fork over several Ethereum coins to buy enough graphics cards for all those spaces, though.