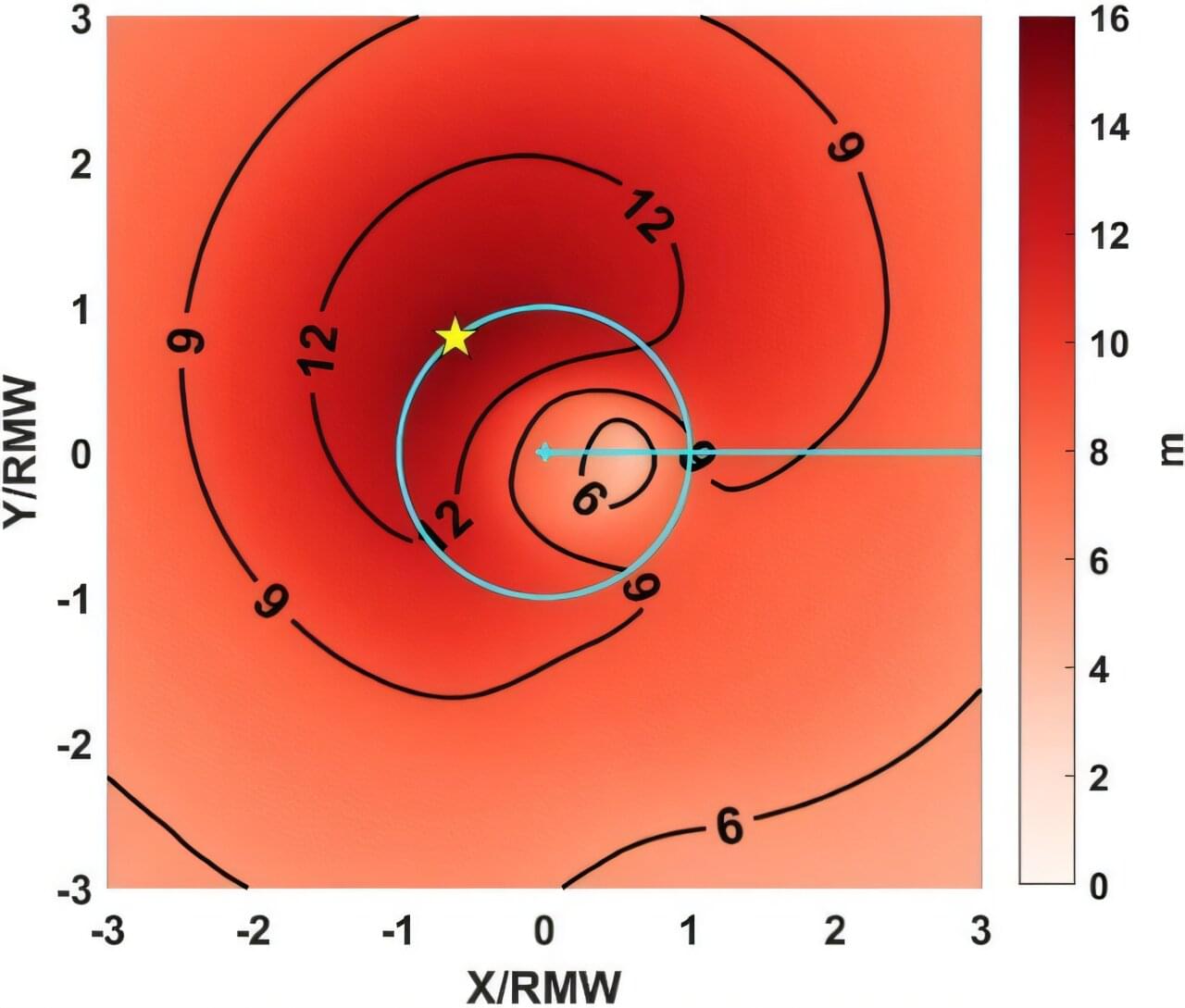
Using advanced computer simulations, researchers from the University of Rhode Island’s Graduate School of Oceanography (GSO) have concluded how and why strong ocean currents modify surface waves. “Our primary finding is that hurricane-generated ocean currents can substantially reduce both the height and the dominant period of hurricane waves,” said Isaac Ginis, URI professor of oceanography. “The magnitude of wave reduction depends strongly on how accurately ocean currents are predicted. This highlights the importance of using fully coupled wave-ocean models when forecasting hurricane waves.”
Ginis conducted the research with URI Professor Tetsu Hara and Angelos Papandreou, who earned his Ph.D. in oceanography from URI in December 2025. Their results were published in a peer-reviewed article in the Journal of Physical Oceanography in January 2026.
According to Ginis, waves are most strongly reduced by currents on the front right of the storm, where winds, waves, and currents are typically strongest.