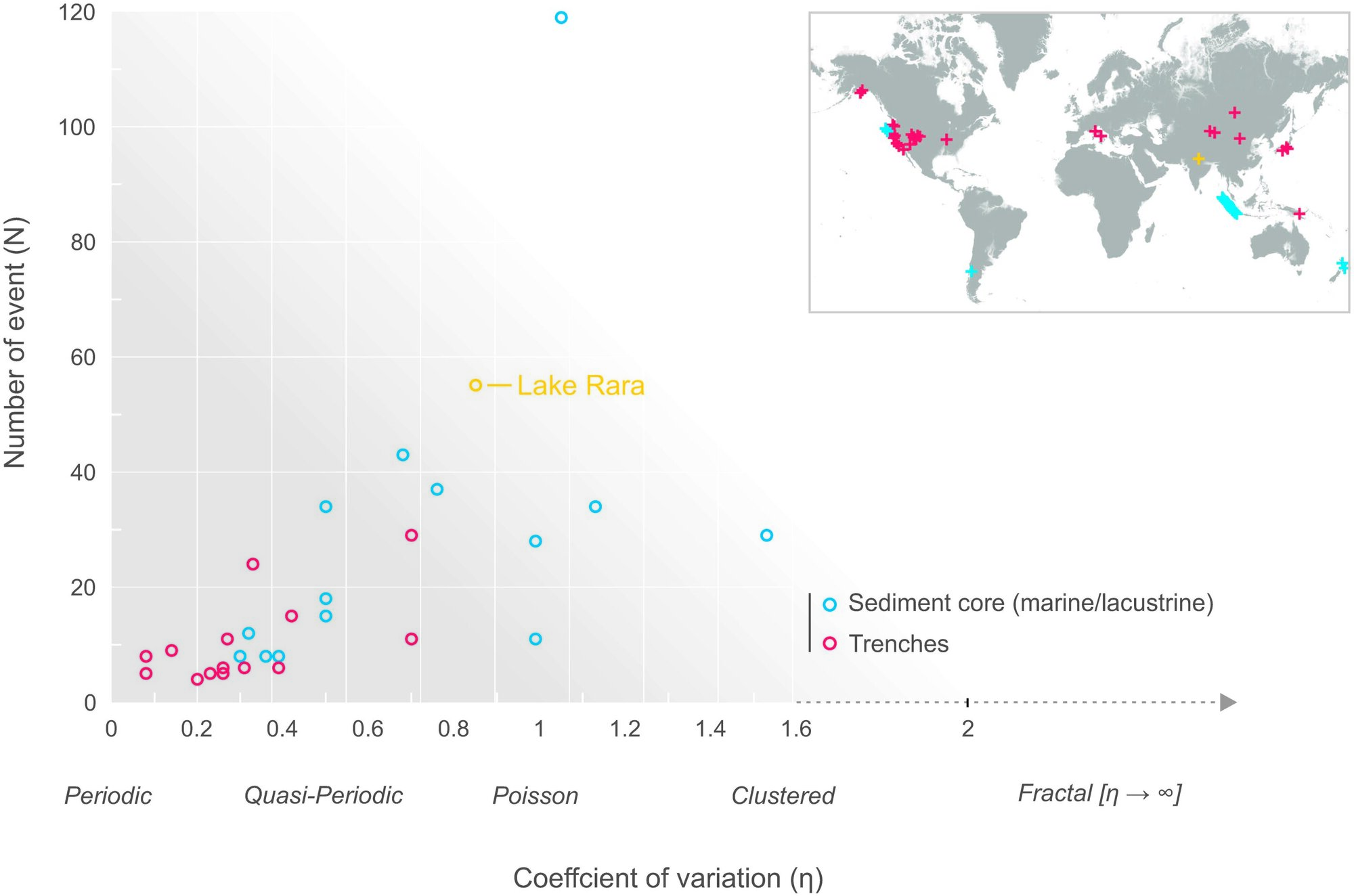
For obvious reasons, it would be useful to predict when an earthquake is going to occur. It has long been suspected that large quakes in the Himalayas follow a fairly predictable cycle, but nature, as it turns out, is not so accommodating. A new study published in the journal Science Advances shows that massive earthquakes are just as random as small ones. A team of researchers led by Zakaria Ghazoui-Schaus at the British Antarctic Survey reached this conclusion after analyzing sediments from Lake Rara in Western Nepal.
The team extracted a 4-meter-long tube from the bottom of the lake and identified 50 sediment layers spanning 6,000 years. Whenever a major quake shakes the region, underwater landslides create layers of sediment called turbidites. These deposits are characterized by coarse materials that settle first, followed by sand, then silt and finally clay. Each layer is essentially a snapshot of an individual earthquake, although they can also result from floods and slope failures.
To confirm that these layers were caused by quakes, the team compared them with modern records and computer models. They concluded that only a quake of magnitude 6.5 or higher could trigger underwater landslides. Radiocarbon dating of organic material within each layer revealed roughly when each of the major quakes occurred.