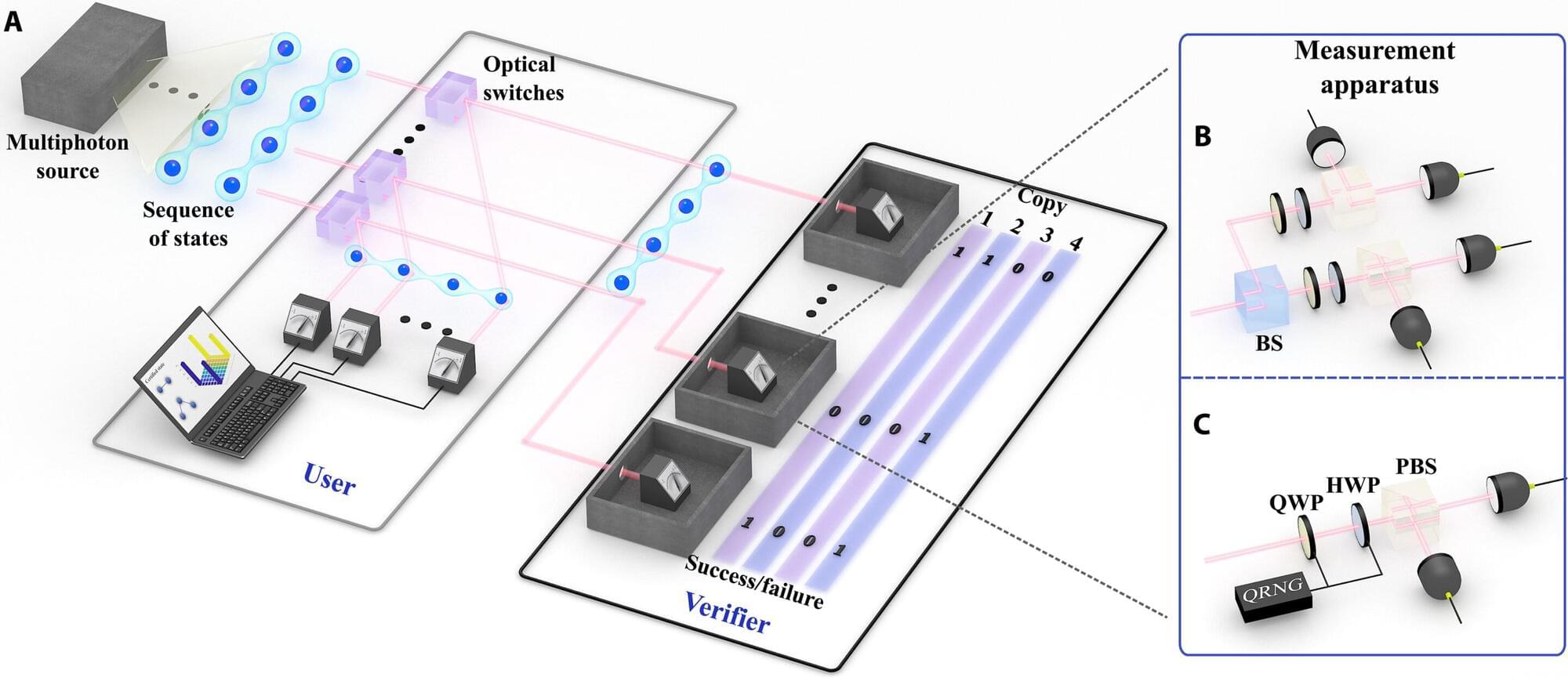
The fragility and laws of quantum physics generally make the characterization of quantum systems time‑consuming. Furthermore, when a quantum system is measured, it is destroyed in the process. A breakthrough by researchers at the University of Vienna demonstrates a novel method for quantum state certification that efficiently verifies entangled quantum states in real time without destroying all available states—a decisive step forward in the development of robust quantum computers and quantum networks.
The work was carried out in Philip Walther’s laboratories at the Faculty of Physics and the Vienna Center for Quantum Science and Technology (VCQ) and published in the journal Science Advances.
Entangled quantum states are the fundamental building blocks of many new quantum technologies, from ultra‑secure communication to powerful quantum computing. However, before these delicate states can be used, they must be rigorously verified to ensure their quality and integrity.