With just a transistor and sensor coil, a new DIY motor achieves continuous motion without complex external electronics.
Category: computing – Page 2
Amaterasu Particle That Broke Physics Has Finally Been Explained
A mysterious, extremely energetic particle, known as the Amaterasu particle, was detected coming from a distant region of space, and scientists have proposed explanations for its origin, potentially tracing it back to a starburst galaxy like Messier 82 ##
## Questions to inspire discussion.
Understanding Ultra-High Energy Cosmic Rays.
🔬 Q: What makes the Amaterasu particle exceptionally powerful? A: The Amaterasu particle detected in Utah in 2021 carries energy 40 million times higher than anything produced on Earth, equivalent to a baseball traveling at 100 km/h compressed into a single subatomic particle, making it one of the most energetic particles ever detected.
Solving the Origin Mystery.
🎯 Q: Where did scientists determine the Amaterasu particle actually originated? A: A 2026 study by Max Planck Institute scientists using approximate Bayesian computation and 3D magnetic field simulations traced the particle’s origin to a starburst galaxy like Messier 82, located 12 million light-years away, rather than the initially suspected local void with only six known galaxies.

Twisted 2D magnet creates skyrmions for ultra dense data storage
As data keeps exploding worldwide, scientists are racing to pack more information into smaller and smaller spaces — and a team at the University of Stuttgart may have just unlocked a powerful new trick. By slightly twisting ultra-thin layers of a magnetic material called chromium iodide, researchers created an entirely new magnetic state that hosts tiny, stable structures known as skyrmions — some of the smallest and toughest information carriers ever observed.

A microfluidic chip for one-step detection of PFAS and other pollutants
Environmental pollutant analysis typically requires complex sample pretreatment steps such as filtration, separation, and preconcentration. When solid materials such as sand, soil, or food residues are present in water samples, analytical accuracy often decreases, and filtration can unintentionally remove trace-level target pollutants along with the solids.
To address this challenge, a joint research team led by Dr. Ju Hyeon Kim at the Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology (KRICT), in collaboration with Professor Jae Bem You’s group at Chungnam National University, has developed a microfluidic-based analytical device that enables direct extraction and analysis of pollutants from solid-containing samples without any pretreatment. The study was published in ACS Sensors
Water, food, and environmental samples encountered in daily life may contain trace amounts of hazardous contaminants that are invisible to the naked eye.
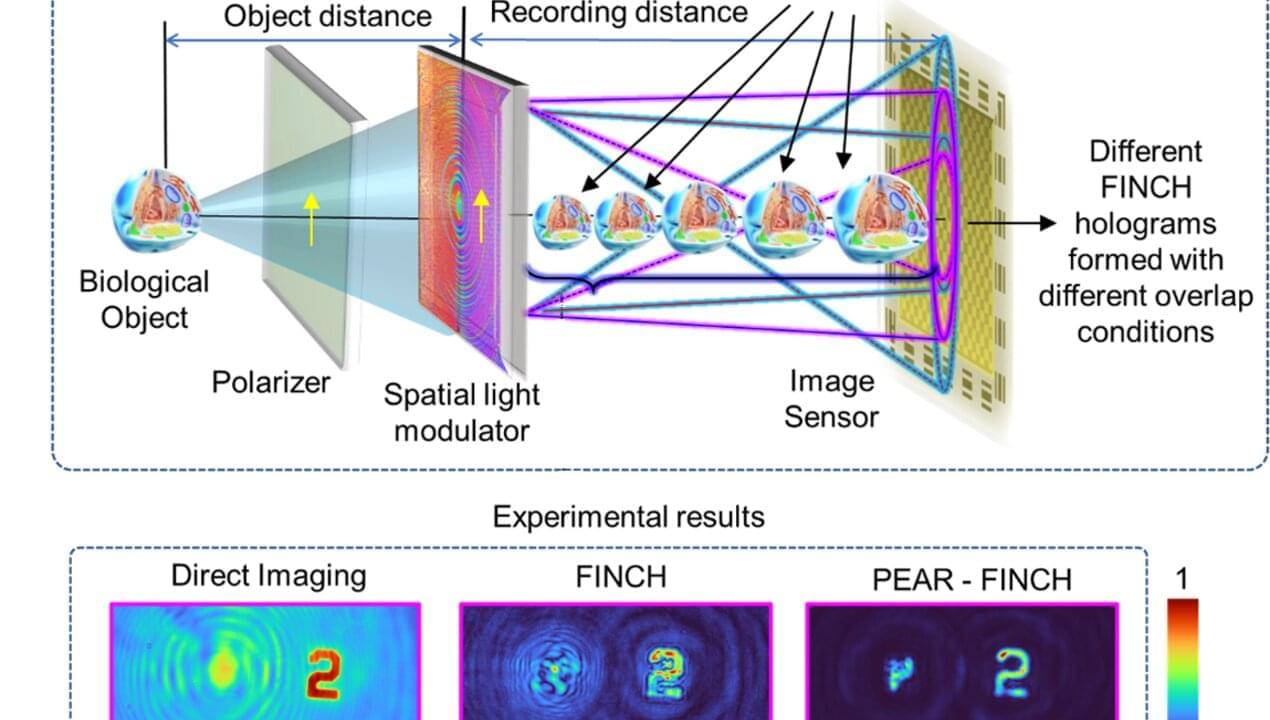
Hologram processing method boosts 3D image depth of focus fivefold
Researchers from the University of Tartu Institute of Physics have developed a novel method for enhancing the quality of three-dimensional images by increasing the depth of focus in holograms fivefold after recording, using computational imaging techniques. The technology enables improved performance of 3D holographic microscopy under challenging imaging conditions and facilitates the study of complex biological structures.
The research results were published in the Journal of Physics: Photonics in the article “Axial resolution post-processing engineering in Fresnel incoherent correlation holography.”
One of the main limitations of conventional microscopes and 3D imaging systems is that, once an image or hologram has been recorded, its imaging properties cannot be altered. To overcome this limitation, Shivasubramanian Gopinath, a Junior Research Fellow at the University of Tartu Institute of Physics, and his colleagues have developed a new method that enables to capture a set of holograms with different focal distances at the time of acquisition, instead of a single image. These can then be computationally combined to produce a synthetic hologram that offers a much greater depth of focus than conventional approaches, and allows for post-processing of the recorded image.

Quantum research in two ways: From proving someone’s location to simulating financial markets
Quantum physics may sound abstract, but Ph.D. candidates Kirsten Kanneworff and David Dechant show that quantum research can also be very concrete. Together, they are investigating how quantum technology can change the world. While Kanneworff worked in the lab to study how quantum optics can be used to prove someone’s location, Dechant focused on quantum computing for dynamic systems, such as the financial world. The two researchers are defending their doctoral theses this week.
Imagine that you receive an email from someone posing as your bank, asking you to enter your personal details on a website. How can you verify the sender’s identity?
Kanneworff investigated a smart way to check whether someone is really in a certain place: quantum position verification. “The idea for this project came about during my master’s degree,” she says. “I found it an interesting subject. The combination of optics and quantum communication really appealed to me, especially since it has a clear application.”
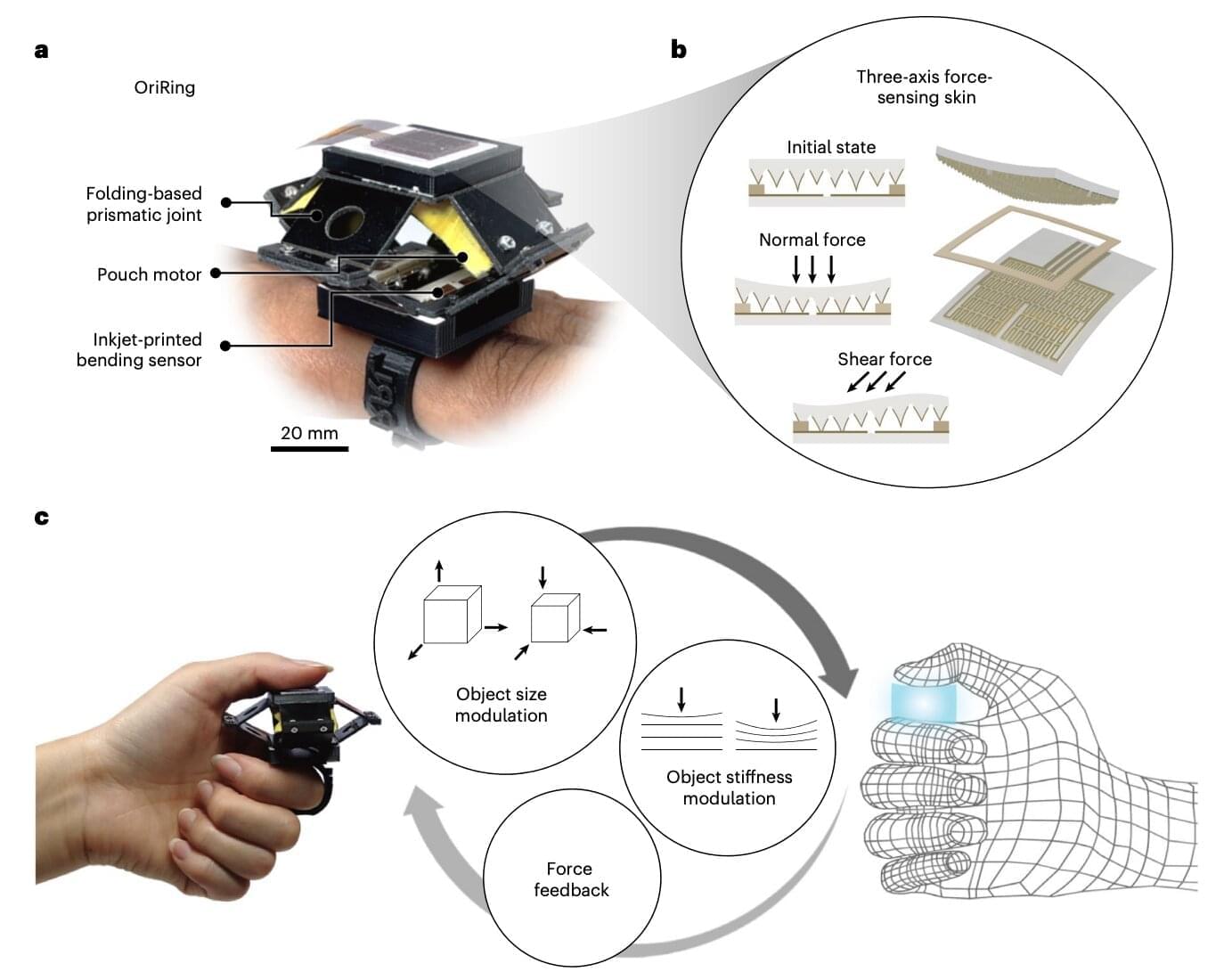
Origami-inspired ring lets users ‘feel’ virtual worlds
Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) are technologies that allow users to immerse themselves in digital worlds or enhance their surroundings with computer-generated filters or images, respectively. Both these technologies are now widely used worldwide, whether to experience video games and media content in more engaging ways or improve specific training and assist professionals in their daily tasks.
To date, VR and AR have primarily focused on what users see and hear, primarily improving the quality of digital experiences from a visual and auditory standpoint. The sense of touch, on the other hand, has been in great part overlooked.
Researchers at Sungkyunkwan University, École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne and Istanbul Technical University recently developed a new wearable device that could allow users to also realistically “feel” tactile sensations aligned with what they are experiencing in a virtual world. This device, introduced in a paper published in Nature Electronics, is an origami-inspired ring that measures forces on a user’s skin, pushing back onto the finger to produce specific sensations.

Quantum Calculations Boosted By Doubling Computational Space For Complex Molecules
Researchers have developed a new computational method, DOCI-QSCI-AFQMC, which accurately simulates complex molecular systems by effectively doubling the number of orbitals considered in standard quantum simulations and overcoming limitations of existing single-reference techniques, as demonstrated through successful modelling of chemical bonds and reactions.
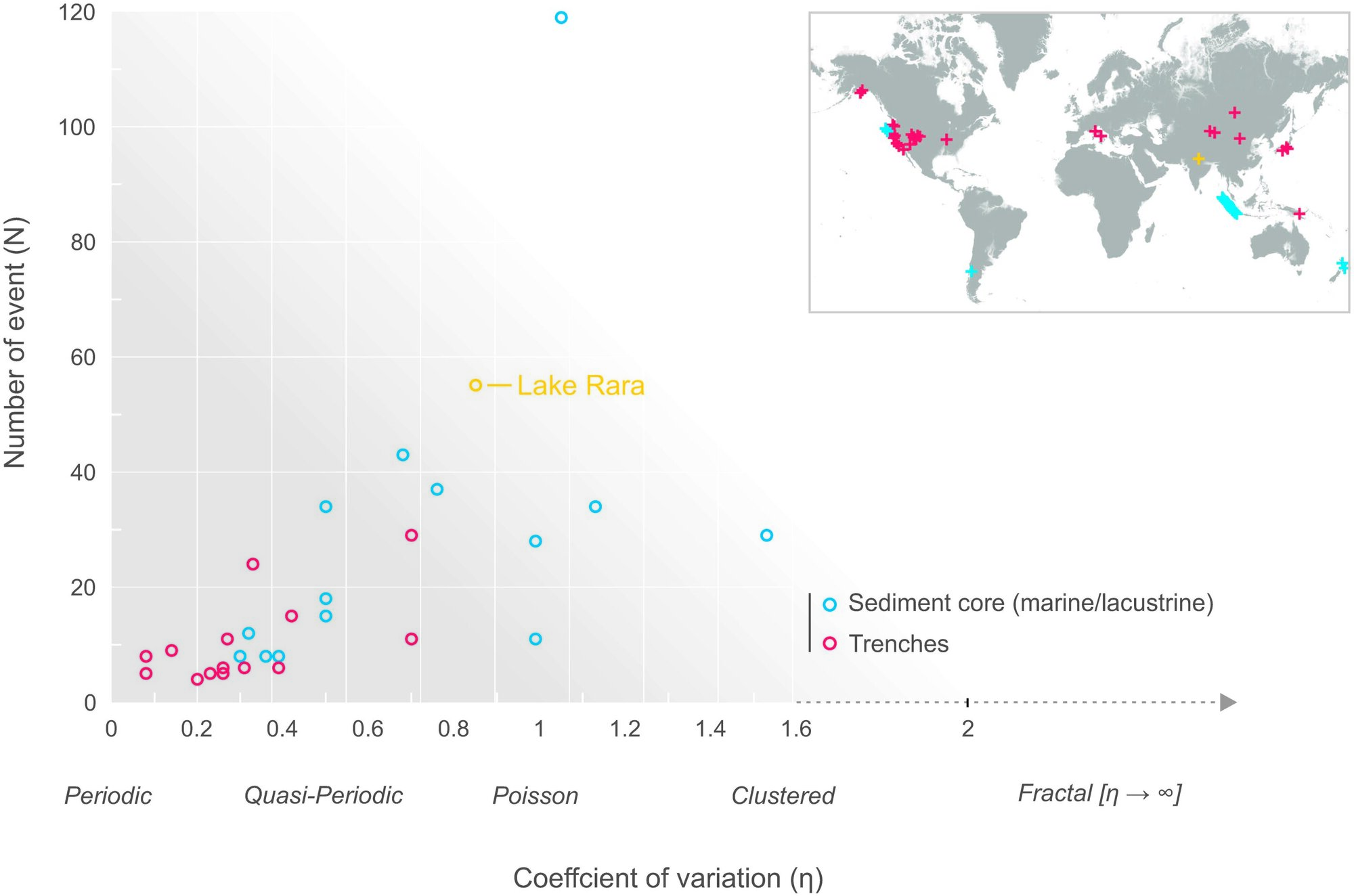
Major earthquakes are just as random as smaller ones
For obvious reasons, it would be useful to predict when an earthquake is going to occur. It has long been suspected that large quakes in the Himalayas follow a fairly predictable cycle, but nature, as it turns out, is not so accommodating. A new study published in the journal Science Advances shows that massive earthquakes are just as random as small ones. A team of researchers led by Zakaria Ghazoui-Schaus at the British Antarctic Survey reached this conclusion after analyzing sediments from Lake Rara in Western Nepal.
The team extracted a 4-meter-long tube from the bottom of the lake and identified 50 sediment layers spanning 6,000 years. Whenever a major quake shakes the region, underwater landslides create layers of sediment called turbidites. These deposits are characterized by coarse materials that settle first, followed by sand, then silt and finally clay. Each layer is essentially a snapshot of an individual earthquake, although they can also result from floods and slope failures.
To confirm that these layers were caused by quakes, the team compared them with modern records and computer models. They concluded that only a quake of magnitude 6.5 or higher could trigger underwater landslides. Radiocarbon dating of organic material within each layer revealed roughly when each of the major quakes occurred.