In one-shot perceptual learning, what we see can be dramatically altered by a single past experience. Using psychophysics, fMRI, iEEG, and DNNs, the authors identify neural and computational mechanisms underlying this remarkable ability in humans.



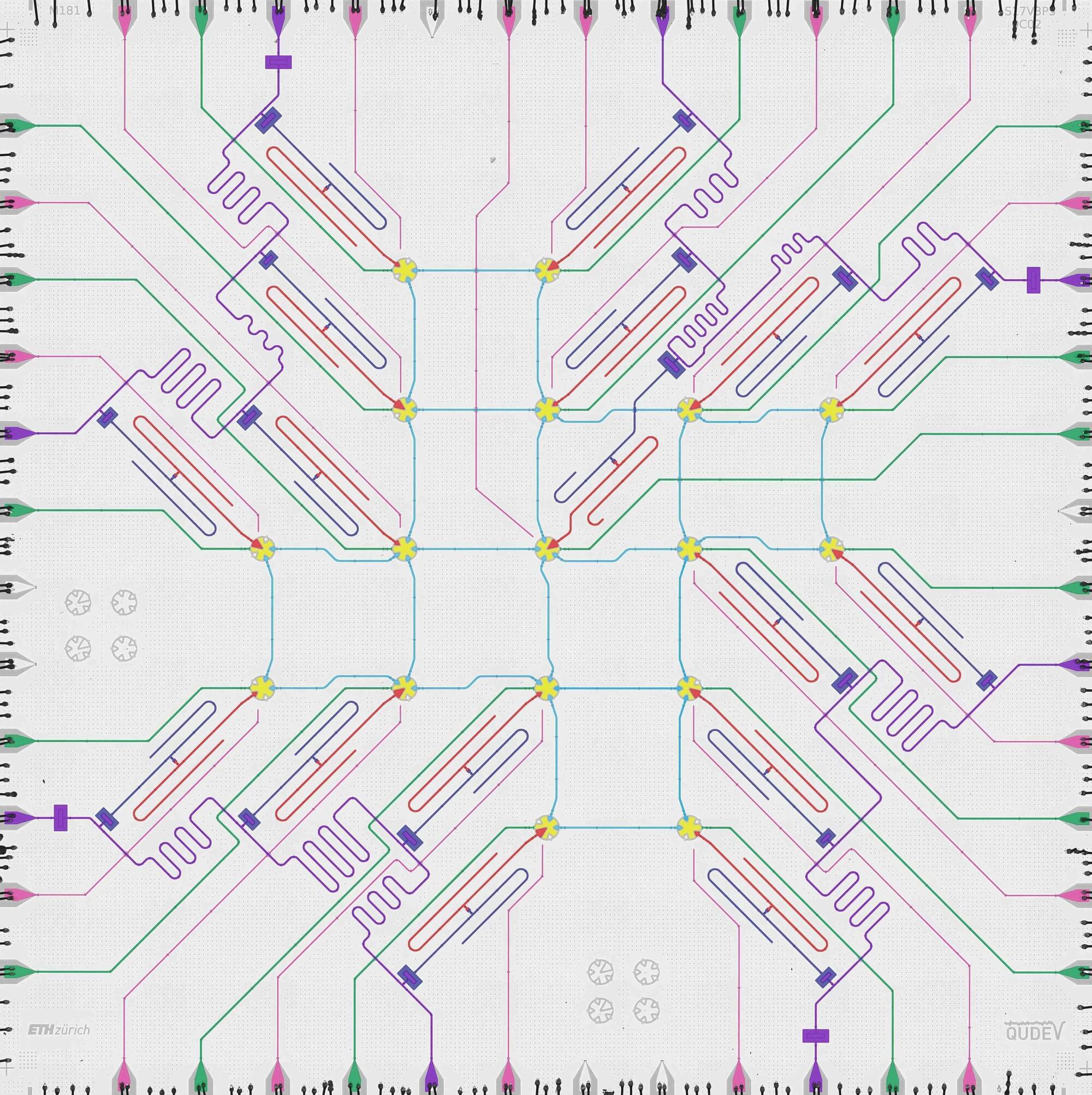
Mikhail Lukin’s team at Harvard presented a “universal” design for neutral-atom processors with robust error-correction capabilities using just 448 qubits, alongside a 3,000-qubit processor that can run for hours.
As Lukin notes: “These are really new kinds of instruments—by some measures, they’re not even computers… What’s really exciting is that these systems are now working already at a reasonable scale and we can start experimenting with them to figure out what we can do with them.”
A string of surprising advances suggests usable quantum computers could be here in a decade.
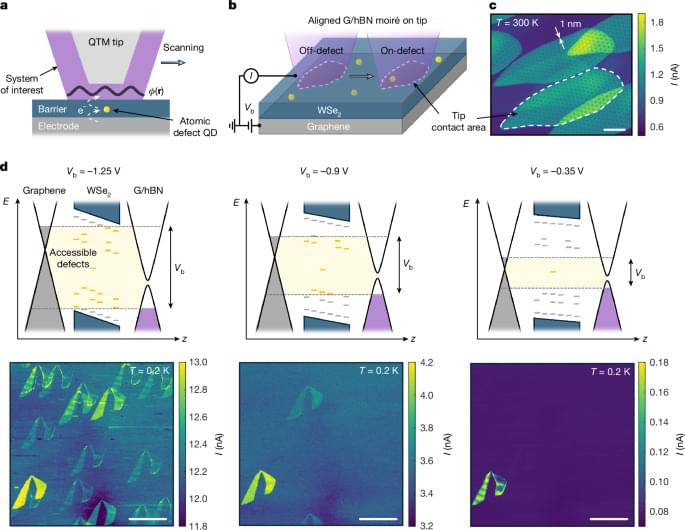
Quantum computers hold great promise for exciting applications in the future, but for now they keep presenting physicists and engineers with a series of challenges and conundrums. One of them relates to decoherence and the errors that result from it: bit flips and phase flips. Such errors mean that the logical unit of a quantum computer, the qubit, can suddenly and unpredictably change its state from “0” to “1,” or that the relative phase of a superposition state can jump from positive to negative.
These errors can be held at bay by building a logical qubit out of many physical qubits and constantly applying error correction protocols. This approach takes care of storing the quantum information relatively safely over time. However, at some point it becomes necessary to exit storage mode and do something useful with the qubit—like applying a quantum gate, which is the building block of quantum algorithms.
The research group led by D-PHYS Professor Andreas Wallraff, in collaboration with the Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI) and the theory team of Professor Markus Müller at RWTH Aachen University and Forschungszentrum Jülich, has now demonstrated a technique that makes it possible to perform a quantum operation between superconducting logical qubits while correcting for potential errors occurring during the operation. The researchers have just published their results in Nature Physics.
Today’s most powerful computers hit a wall when tackling certain problems, from designing new drugs to cracking encryption codes. Error-free quantum computers promise to overcome those challenges, but building them requires materials with exotic properties of topological superconductors that are incredibly difficult to produce. Now, researchers at the University of Chicago Pritzker School of Molecular Engineering (UChicago PME) and West Virginia University have found a way to tune these materials into existence by simply tweaking a chemical recipe, resulting in a change in many-electron interactions.
The team adjusted the ratio of two elements— tellurium and selenium —that are grown in ultra-thin films. By doing so, they found they could switch the material between different quantum phases, including a highly desirable state called a topological superconductor.
The findings, published in Nature Communications, reveal that as the ratio of tellurium and selenium changes, so too do the correlations between different electrons in the material—how strongly each electron is influenced by those around it. This can serve as a sensitive control knob for engineering exotic quantum phases.
What does it take to turn bold ideas into life-saving medicine?
In this episode of The Big Question, we sit down with @MIT’s Dr. Robert Langer, one of the founding figures of bioengineering and among the most cited scientists in the world, to explore how engineering has reshaped modern healthcare. From early failures and rejected grants to breakthroughs that changed medicine, Langer reflects on a career built around persistence and problem-solving. His work helped lay the foundation for technologies that deliver large biological molecules, like proteins and RNA, into the body, a challenge once thought impossible. Those advances now underpin everything from targeted cancer therapies to the mRNA vaccines that transformed the COVID-19 response.
The conversation looks forward as well as back, diving into the future of medicine through engineered solutions such as artificial skin for burn victims, FDA-approved synthetic blood vessels, and organs-on-chips that mimic human biology to speed up drug testing while reducing reliance on animal models. Langer explains how nanoparticles safely carry genetic instructions into cells, how mRNA vaccines train the immune system without altering DNA, and why engineering delivery, getting the right treatment to the right place in the body, remains one of medicine’s biggest challenges. From personalized cancer vaccines to tissue engineering and rapid drug development, this episode reveals how science, persistence, and engineering come together to push the boundaries of what medicine can do next.
#Science #Medicine #Biotech #Health #LifeSciences.
Chapters:
00:00 Engineering the Future of Medicine.
01:55 Failure, Persistence, and Scientific Breakthroughs.
05:30 From Chemical Engineering to Patient Care.
08:40 Solving the Drug Delivery Problem.
11:20 Delivering Proteins, RNA, and DNA
14:10 The Origins of mRNA Technology.
17:30 How mRNA Vaccines Work.
20:40 Speed and Scale in Vaccine Development.
23:30 What mRNA Makes Possible Next.
26:10 Trust, Misinformation, and Vaccine Science.
28:50 Engineering Tissues and Organs.
31:20 Artificial Skin and Synthetic Blood Vessels.
33:40 Organs on Chips and Drug Testing.
36:10 Why Science Always Moves Forward.
The Big Question with the Museum of Science:
A group of researchers has built a computer chip in a flexible fiber thinner than an average human hair. The team from Fudan University in Shanghai says that their Fiber Integrated Circuit (FIC) design can process information like a computer, yet is durable enough to be “stretched, twisted, and woven into everyday clothing.” Use cases touted by the authors of the paper include advancements in the fields of brain-computer interfaces, VR devices, and smart textiles. This cutting-edge FIC design was apparently inspired by the construction of the humble sushi roll.
Flexible electronics have come a long way in recent years, with malleable components for power, sensing, and display readily available. However, so-called flexible electronic devices and the wearables made from them still usually contain components fabricated from rigid silicon wafers, limiting their applications and comfort. The Fudan team says that their FIC can remove the last vestiges of electronic rigidity “by creating a fiber integrated circuit (FIC) with unprecedented microdevice density and multimodal processing capacity.”

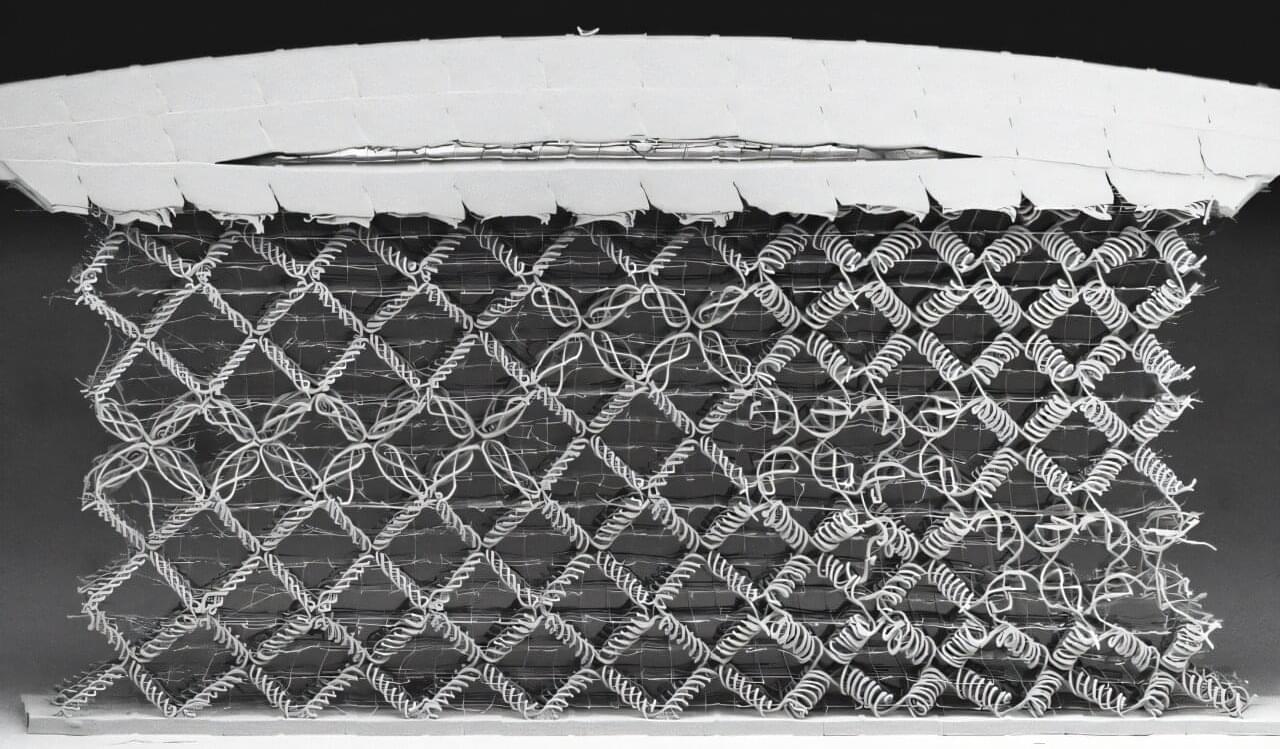
Metamaterials—materials whose properties are primarily dictated by their internal microstructure, and not their chemical makeup—have been redefining the engineering materials space for the last decade. To date, however, most metamaterials have been lightweight options designed for stiffness and strength.
New research from the MIT Department of Mechanical Engineering introduces a computational design framework to support the creation of a new class of soft, compliant, and deformable metamaterials. These metamaterials, termed 3D woven metamaterials, consist of building blocks that are composed of intertwined fibers that self-contact and entangle to endow the material with unique properties.