Fabricating some structures using niobium instead of aluminum could lead to more resilient superconducting quantum computers.

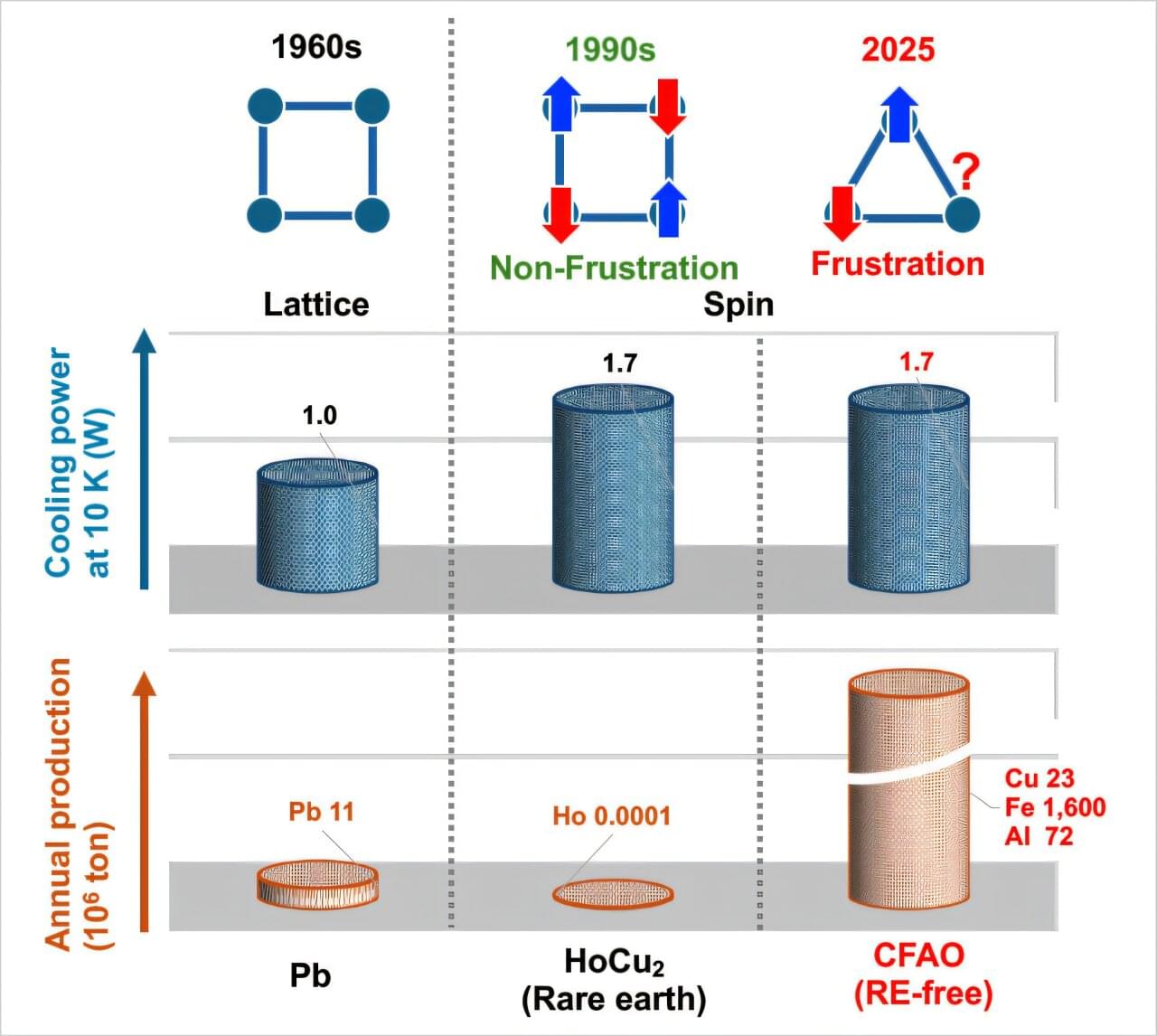
In collaboration with the National Institute of Technology (KOSEN), Oshima College, the National Institute for Materials Science (NIMS) succeeded in developing a new regenerator material composed solely of abundant elements, such as copper, iron, and aluminum, that can achieve cryogenic temperatures (approx. 4K = −269°C or below) without using any rare-earth metals or liquid helium.
By utilizing a special property called “frustration” found in some magnetic materials, where the spins cannot simultaneously satisfy each other’s orientations in a triangular lattice, the team demonstrated a novel method that replaces the conventional rare-earth-dependent cryogenic cooling technology.
The developed material holds promise for responding to the lack of liquid helium as well as for stable cooling in medical magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and quantum computers, which are expected to see further growth in demand. The results are published in Scientific Reports.
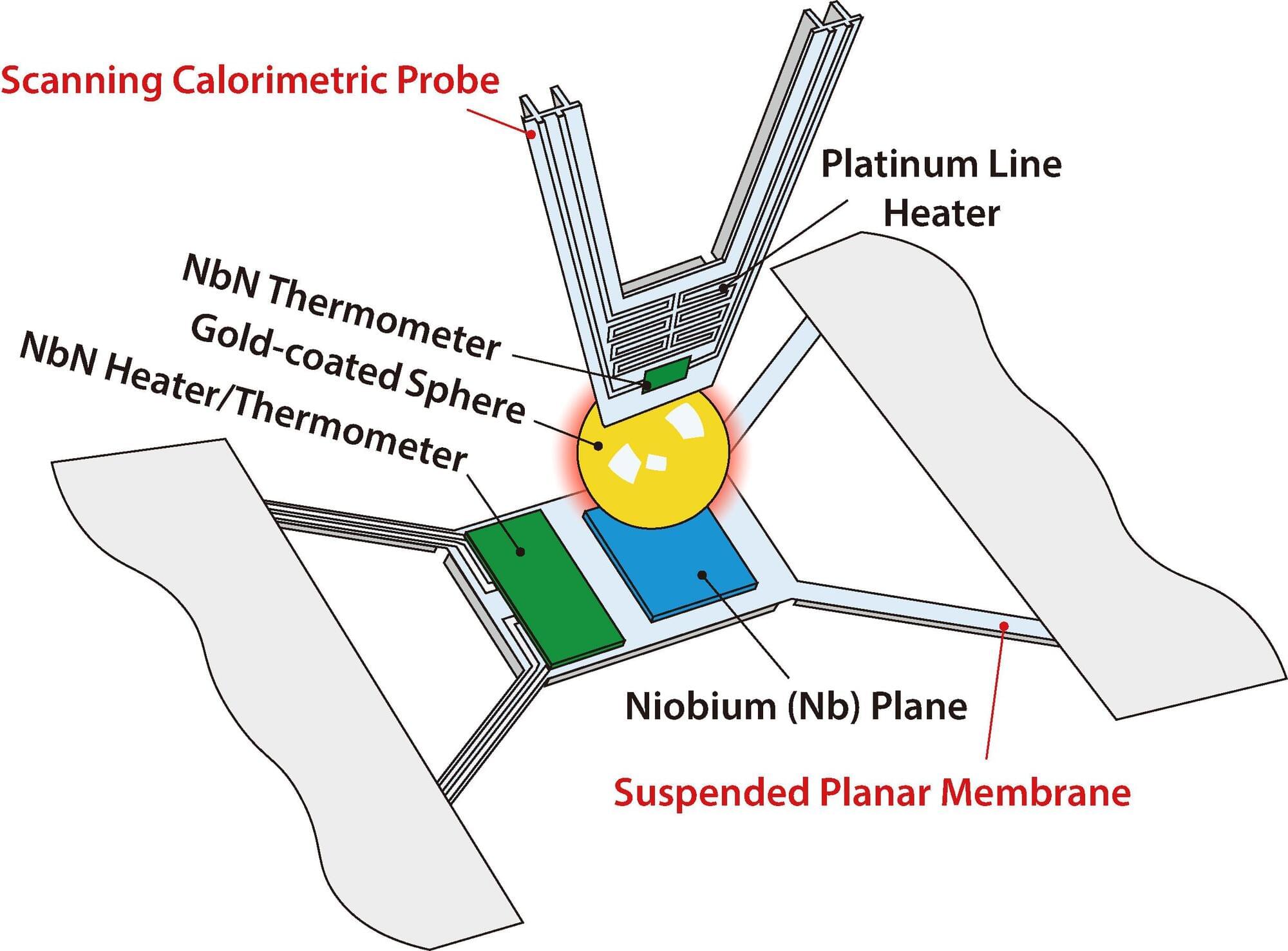
When cooled to its superconducting state, niobium blocks the radiative flow of heat 20 times better than when in its metallic state, according to a study led by a University of Michigan Engineering team. The experiment marks the first use of superconductivity—a quantum property characterized by zero electrical resistance—to control thermal radiation at the nanoscale.
Leveraging this effect, the researchers also experimentally demonstrated a cryogenic thermal diode that rectifies the flow of heat (i.e., the heat flow exhibits a directional preference) by as much as 70%.
“This work is exciting because it experimentally shows, for the very first time, how nanoscale heat transfer can be tuned by superconductors with potential applications for quantum computing,” said Pramod Sangi Reddy, a professor of mechanical engineering and materials science and engineering at U-M and co-corresponding author of the study published in Nature Nanotechnology.
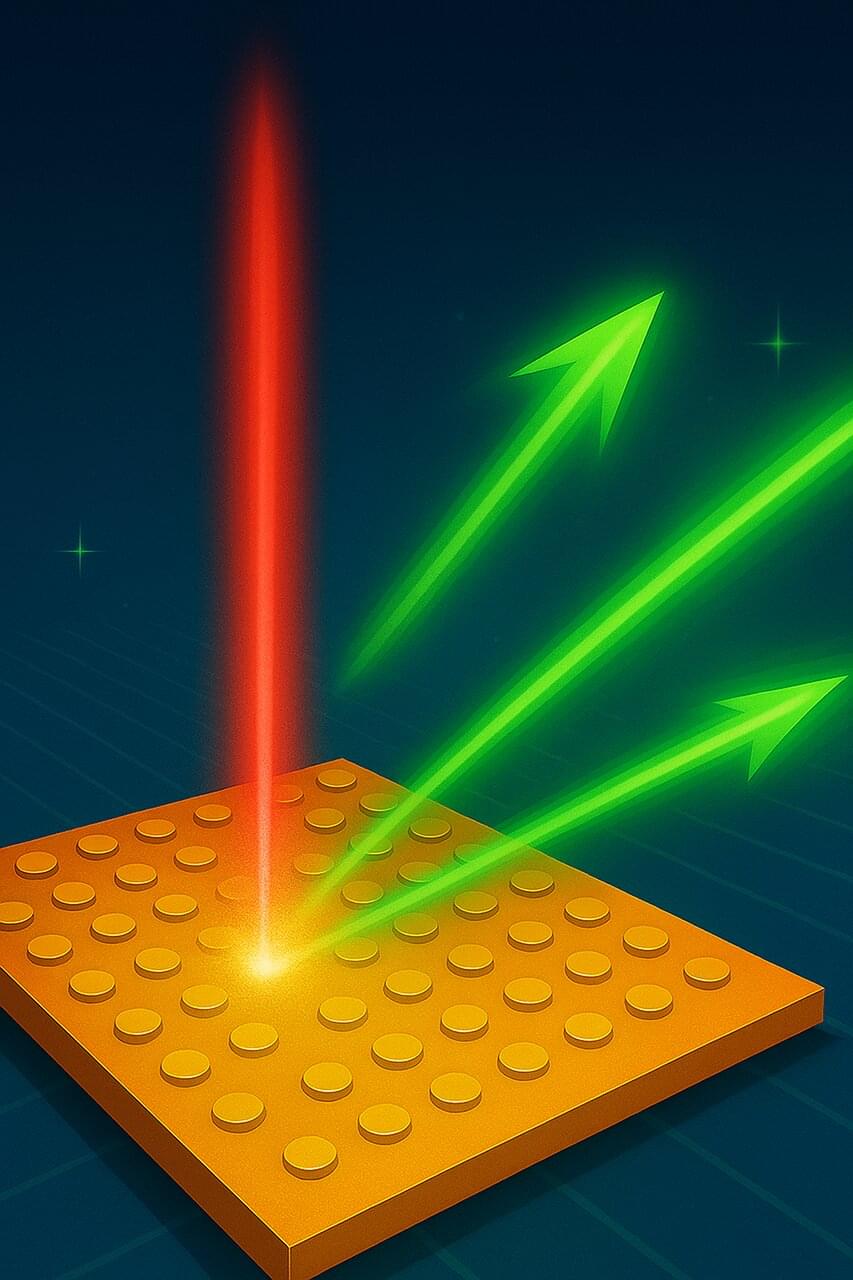
The invention of tiny devices capable of precisely controlling the direction and behavior of light is essential to the development of advanced technologies. Researchers at the Advanced Science Research Center at the CUNY Graduate Center (CUNY ASRC) have taken a significant step forward with the development of a metasurface that can turn invisible infrared light into visible light and aim it in different directions—without any moving parts. The details of their work are explained in a paper published in the journal eLight.
The novel metasurface is constructed of an ultra-thin chip patterned with tiny structures smaller than the wavelength of light. When hit with an infrared laser, the chip converts the incoming light to a higher color (or frequency) and sends the new light out as a narrow beam that can be steered simply by changing how the incoming light is polarized.
In their experiments, the team converted infrared light around 1,530 nanometers—similar to the light used in fiber-optic communications—into visible green light near 510 nanometers and steered it to chosen angles.
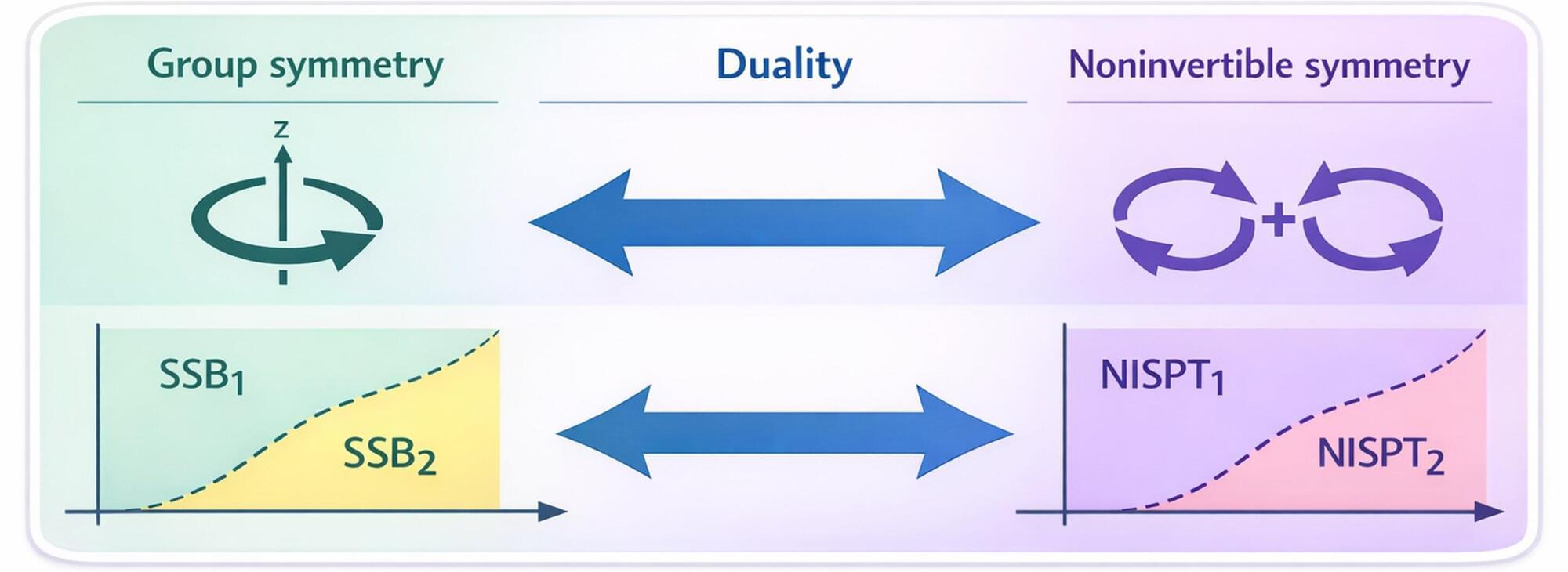
A team of theoretical researchers has found duality can unveil non-invertible symmetry protected topological phases, which can lead to researchers understanding more about the properties of these phases, and uncover new quantum phases. Their study is published in Physical Review Letters.
Symmetry is one of the most fundamental concepts for understanding phases of matter in modern physics—in particular, symmetry-protected topological (SPT) phases, whose quantum mechanical properties are protected by symmetries, with possible applications in quantum computing and other fields.
Over the past few years, non-invertible symmetries, which extend the framework of conventional symmetries, have attracted significant attention in high energy physics and condensed matter physics. However, their complex mathematical structures have made it difficult to understand their corresponding phases of matter, or SPT phases.
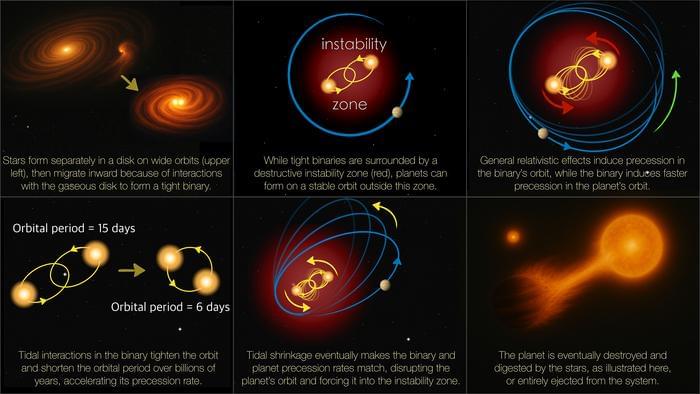
“Two things can happen: Either the planet gets very, very close to the binary, suffering tidal disruption or being engulfed by one of the stars, or its orbit gets significantly perturbed by the binary to be eventually ejected from the system,” said Dr. Mohammad Farhat.
Why is it so rare to find exoplanets orbiting two stars, also called circumbinary planets (CBPs)? This is what a recent study published in The Astrophysical Journal Letters hopes to address as a team of researchers investigated the celestial processes responsible for the formation and evolution of CBPs. This study has the potential to help scientists better understand solar system and planetary formation and evolution, which could narrow the search for life beyond Earth.
For the study, the researchers used a combination of computer models and Einstein’s theory of relativity to simulate the formation and evolution of CBPs. For example, the researchers explored the interaction between the CBP and its binary star, resulting in one of three outcomes: stable orbit, ejection, or consumption by the binary star. The reason Einstein’s theory of relativity was used as part of the study was because it calls for objects to have their orbit perturbed the closer they orbit to a larger object, like a star.
A common example that’s used for the theory is of a trampoline with objects falling inward when a large body is in the middle of it. Essentially, stars have “instability zones” where planets get consumed if they orbit too close. In the case of CBPs, the astronomers found that of the 14 known CBPs out of more than 6,000 confirmed exoplanets, 12 orbit just beyond the instability zone and none of the 14 have orbits less than seven days. The researchers concluded that a common phenomenon in astronomy called the three-body problem is responsible for the lack of CBPs.

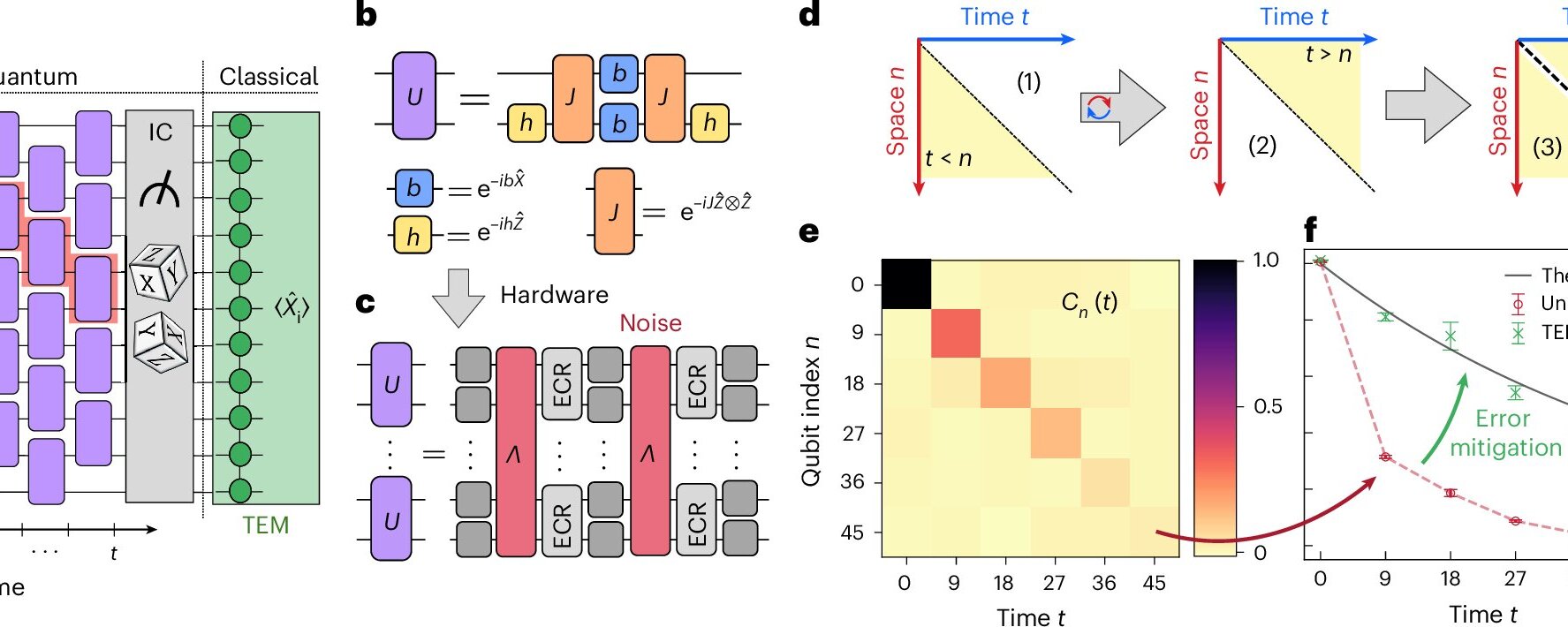
Quantum chaos describes chaotic classical dynamical systems in terms of quantum theory, but simulations of these systems are limited by computational resources. However, one team seems to have found a way by leveraging error mitigation and specialized circuits on a 91-qubit superconducting quantum processor. Their results are published in Nature Physics.
While useful quantum simulations require an ability to eliminate errors, full quantum error correction requires large overheads in qubits and control. Previous work has gotten around this problem by simulating limited quantum many-body systems mostly at smaller scales or with integrable—or less chaotic—models.
The research team involved in the new study opted for a different method. Instead, they used error mitigation, which accepts noise and then corrects errors later, saving computational resources in the process.
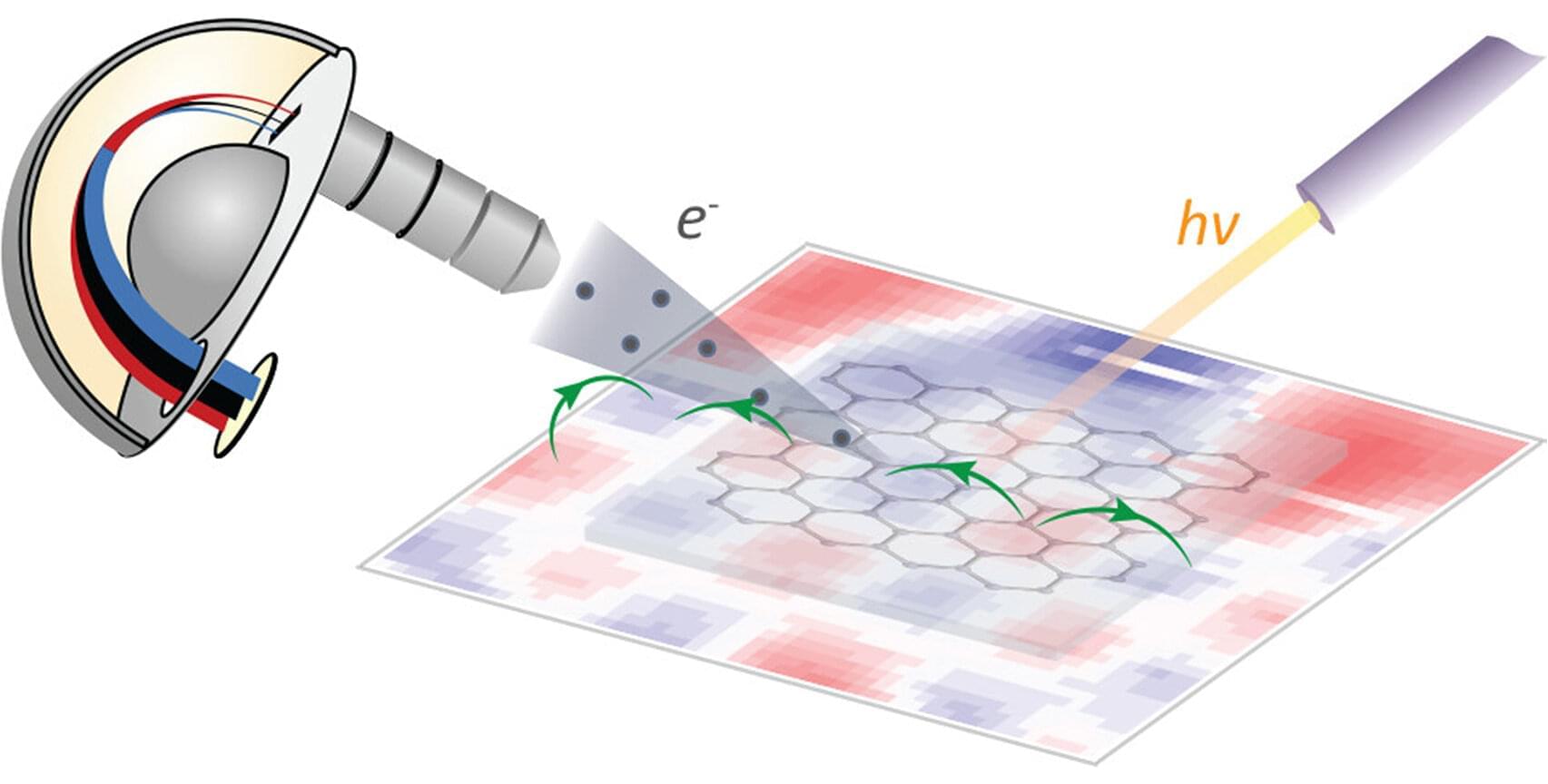
With an advanced technology known as angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy (ARPES), scientists are able to map out a material’s electron energy-momentum relationship, which encodes the material’s electrical, optical, magnetic and thermal properties like an electronic DNA. But the technology has its limitations; it doesn’t work well under a magnetic field. This is a major drawback for scientists who want to study materials that are deployed under or even actuated by magnetic fields.
Inspired by refrigerator magnets, a team of Yale researchers may have found a solution. Their study was featured recently on the cover of The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters.
Quantum materials —such as unconventional superconductors or topological materials—are considered critical to advancing quantum computing, high-efficiency electronics, nuclear fusion, and other fields. But many of them need to be used in the presence of a magnetic field, or even only become activated by magnetic fields. Being able to directly study the electronic structure of these materials in magnetic fields would be a huge help in better understanding how they work.