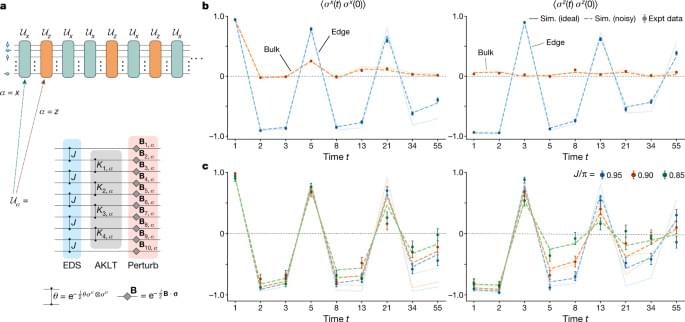
Basically the fibonacci sequence stabilized the quantum computers internal processes better essentially. This may fall into the theory of everything that supersymmetry and the fibonacci sequence can get us closer to a theory of everything even in quantum computers.
A dynamical topological phase with edge qubits that are dynamically protected from control errors, cross-talk and stray fields, is demonstrated in a quasiperiodically driven array of ten 171Yb+ hyperfine qubits in a model trapped-ion quantum processor.