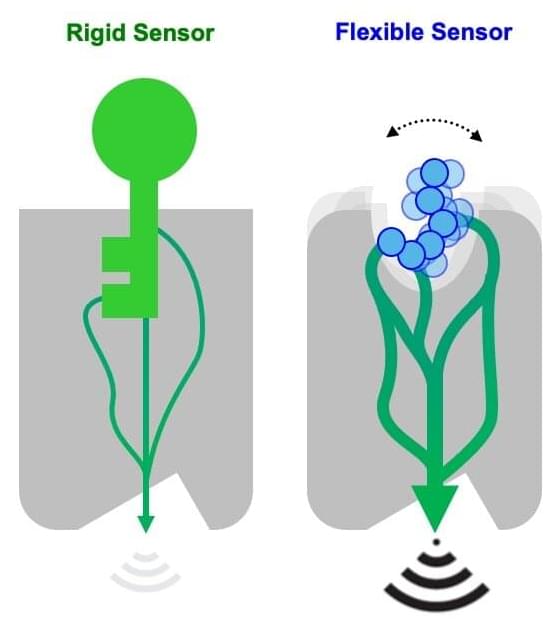
Biosensors are artificial molecular complexes designed to detect the presence of target chemicals or even biomolecules. Consequently, biosensors have become important in diagnostics and synthetic cell biology. However, typical methods for engineering biosensors focus on optimizing the interactions between static binding surfaces, and current biosensor designs can only recognize structurally well-defined molecules, which can be too rigid for “real-life” biology.
“We developed a novel computational approach for designing protein-peptide ligand binding and applied it to engineer cell-surface chemotactic receptors that reprogrammed cell migration,” says EPFL professor Patrick Barth. “We think that our work could broadly impact the design of protein binding and cell engineering applications.”
The new biosensors developed by Barth’s group can sense flexible compounds and trigger complex cellular responses, which open up new possibilities for biosensor applications. The researchers created a computational framework, which is a computer-based system, for designing protein complexes that can change their shape and function dynamically—as opposed to the conventional static approaches. The framework can look at previously unexplored protein sequences to come up with new ways for the protein’s groups to be activated, even in ways that are different to their natural function.