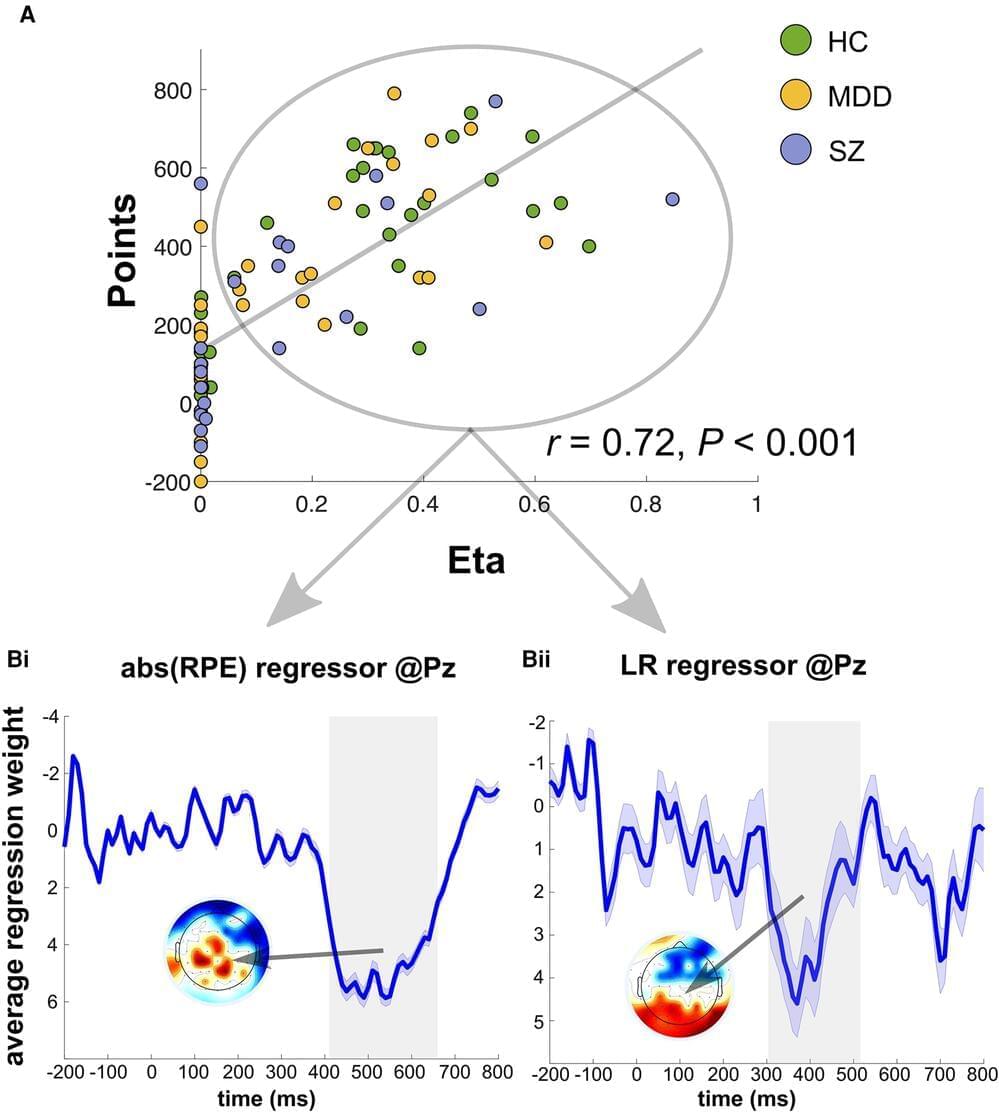
When learning, patients with schizophrenia or depression have difficulty making optimal use of information that is new to them. In the learning process, both groups of patients give greater weight to less important information and, as a result, make less than ideal decisions.
This was the finding of a several-months-long study conducted by a team led by neuroscientist Professor Dr. med. Markus Ullsperger from the Institute of Psychology at Otto von Guericke University Magdeburg in collaboration with colleagues from the University Clinic for Psychiatry & Psychotherapy and the German Center for Mental Health.
By using electroencephalography (EEG) and complex mathematical computer modeling, the team of researchers discovered that learning deficits in depressive and schizophrenic patients are caused by diminished/reduced flexibility in the use of new information.