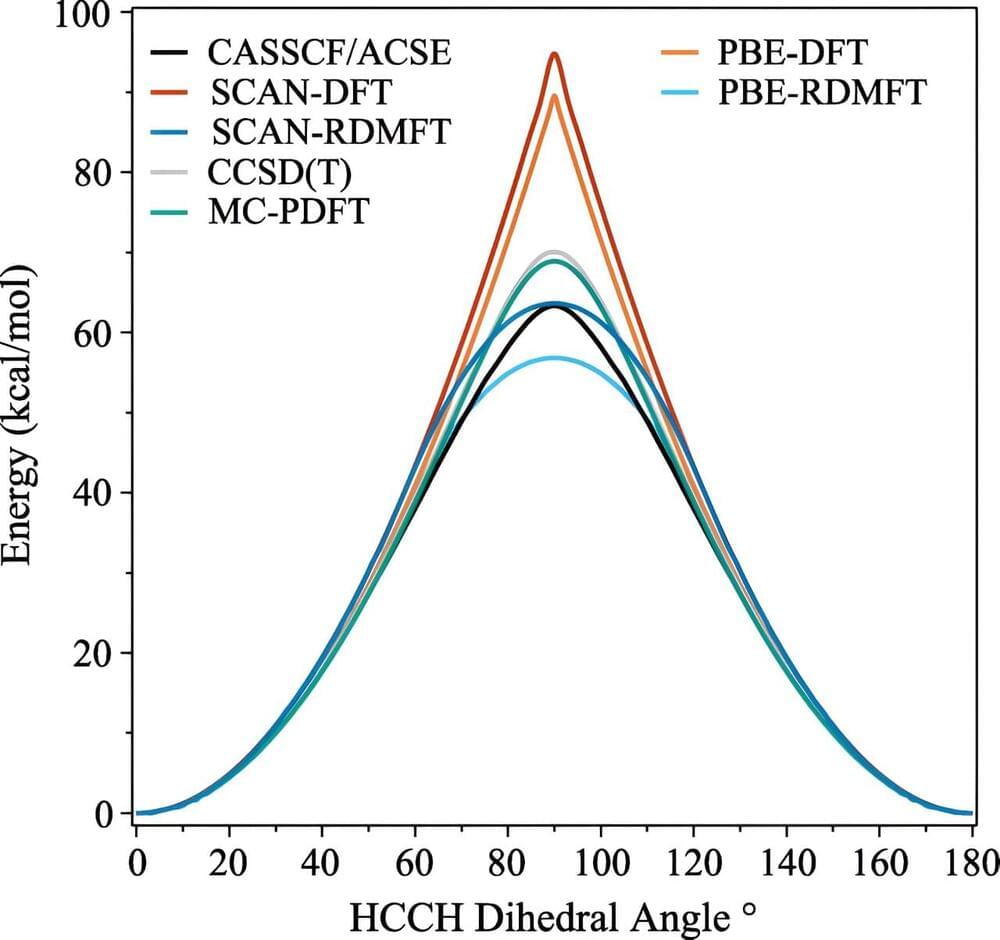
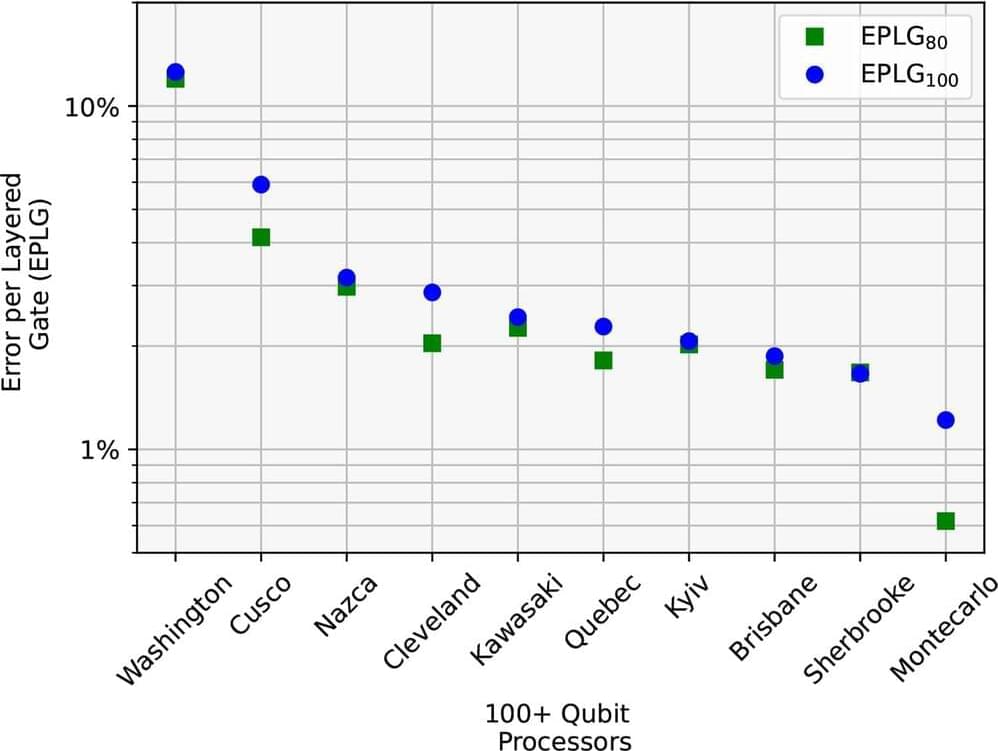
Much like the humans that created them, computers find physics hard, but quantum mechanics even harder. But a new technique created by three University of Chicago scientists allows computers to simulate certain challenging quantum mechanical effects in complex electronic materials with far less effort.
By making these simulations more accurate and efficient, the scientists hope the technique could help discover new molecules and materials, such as new types of solar cells or quantum computers.
“This advance holds immense potential for furthering our understanding of molecular phenomena, with significant implications for chemistry, material science, and related fields,” said scientist Daniel Gibney, a University of Chicago Ph.D. student in chemistry and first author on the paper, published Dec. 14 in Physical Review Letters.