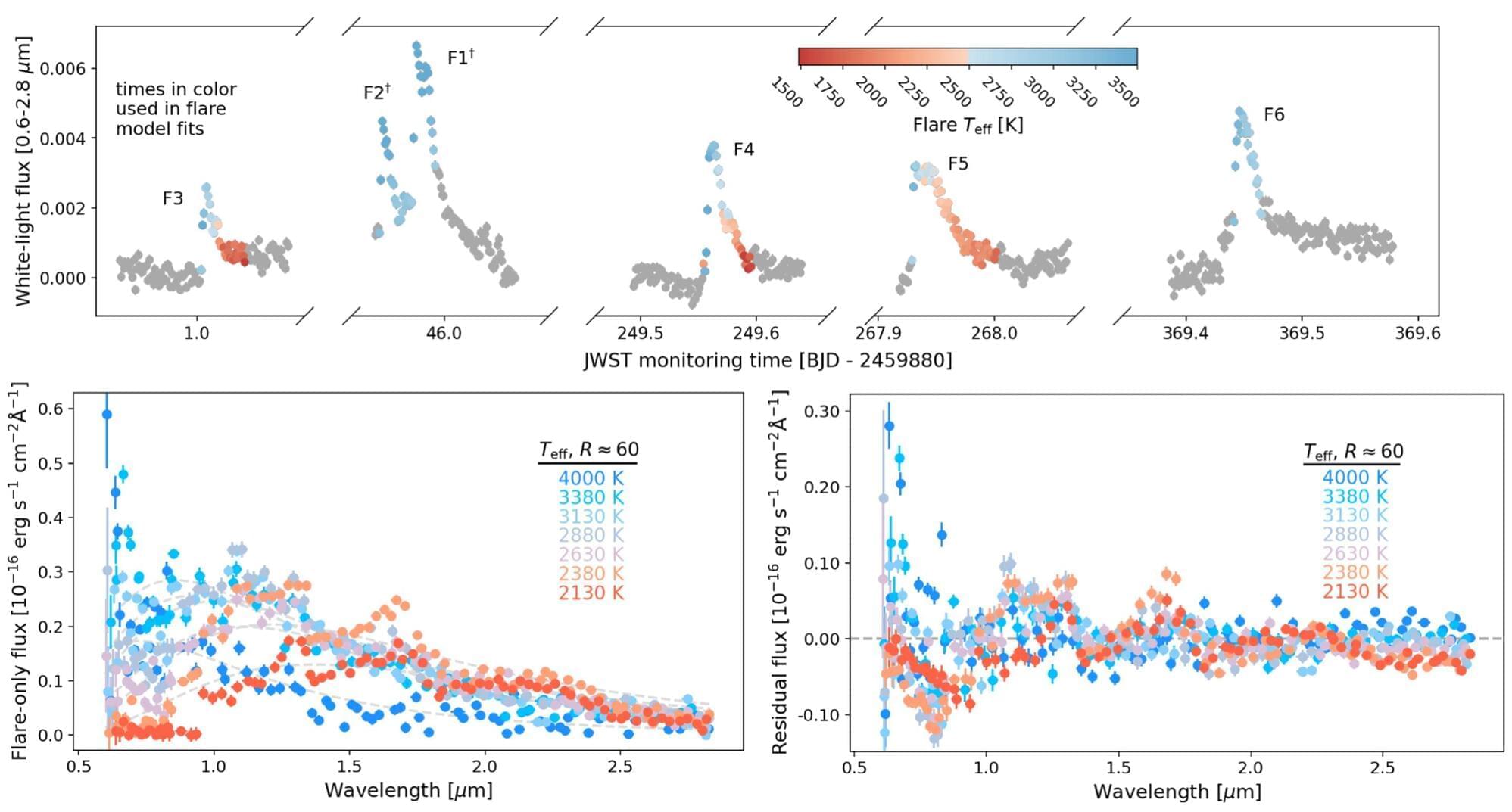
Like a toddler right before naptime, TRAPPIST-1 is a small yet moody star. This little star, which sits in the constellation Aquarius about 40 light-years from Earth, spits out bursts of energy known as “flares” about six times a day.
New research led by the University of Colorado Boulder takes the deepest look yet at the physics behind TRAPPIST-1’s celestial temper tantrums. The team’s findings could help scientists search for habitable planets beyond Earth’s solar system.
The researchers used observations from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope and computer simulations (models) to understand how TRAPPIST-1 produces its flares—first building up magnetic energy, then releasing it to kick off a chain of events that launches radiation deep into space. The results could help scientists unravel how the star has shaped its nearby planets, potentially in drastic ways.