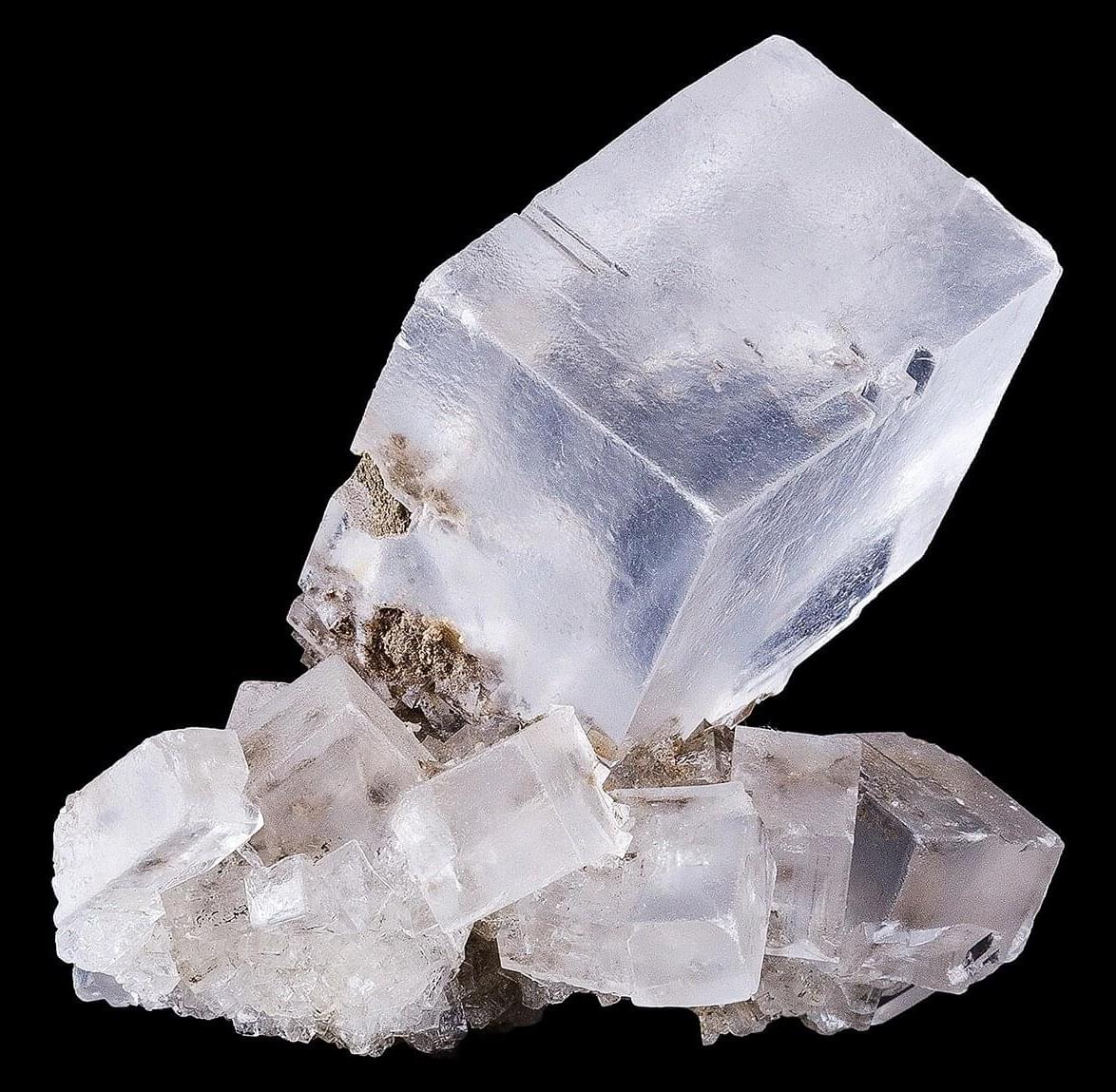
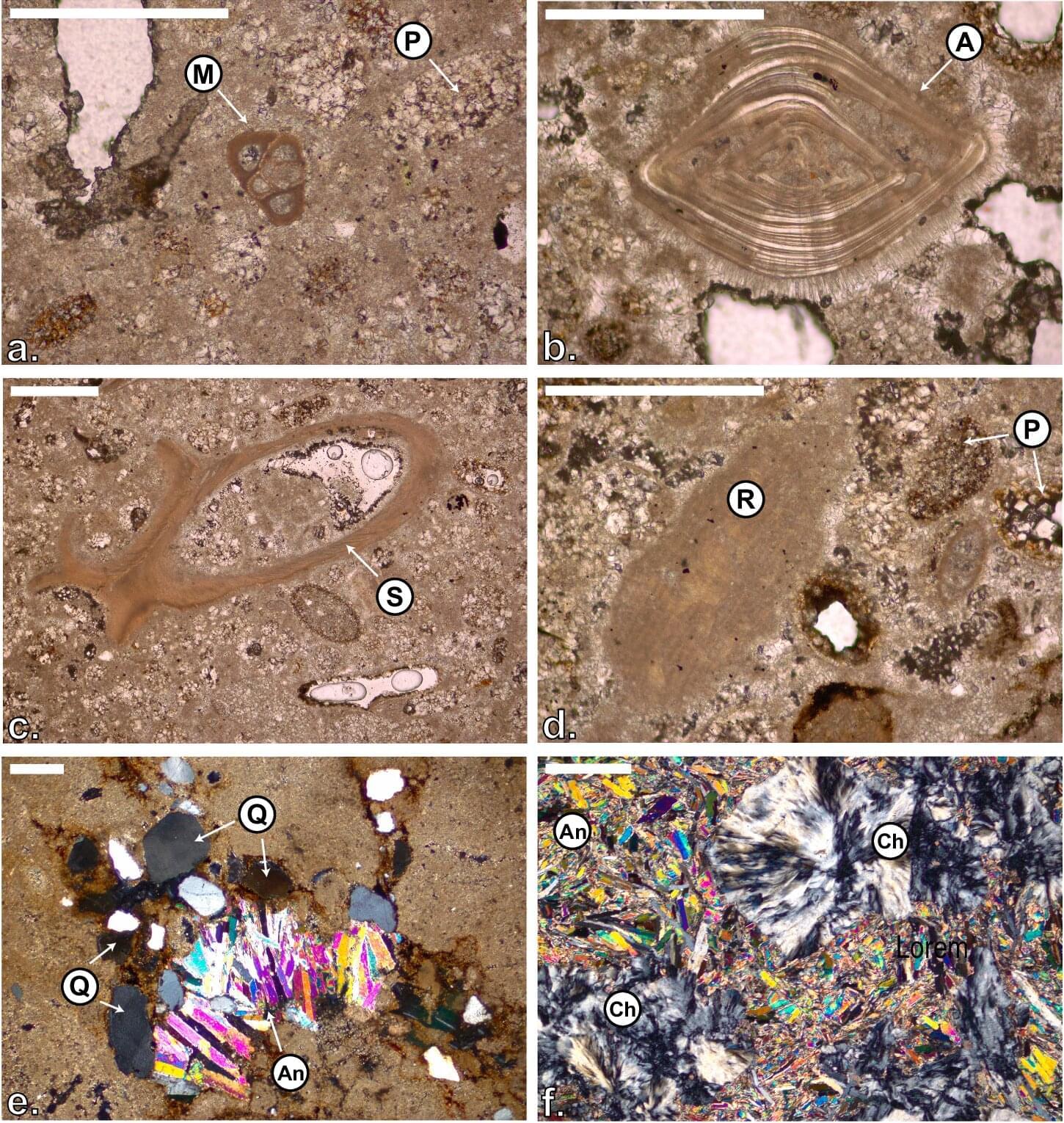
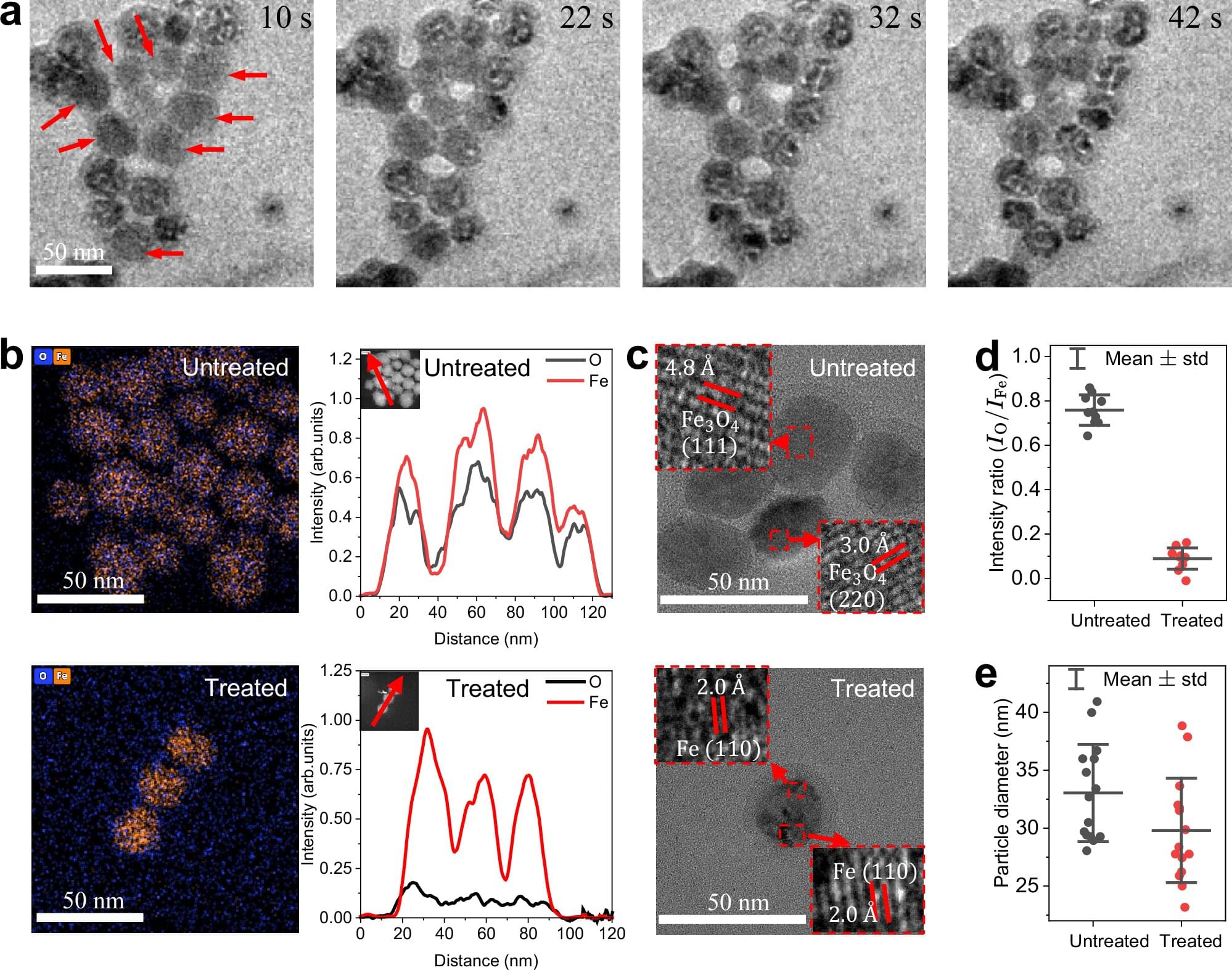
Scientists at King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST) have provided conclusive evidence that the Red Sea completely dried out about 6.2 million years ago, before being suddenly refilled by a catastrophic flood from the Indian Ocean. The findings put a definitive time on a dramatic event that changed the Red Sea.
Using seismic imaging, microfossil evidence, and geochemical dating techniques, the KAUST researchers showed that a massive change happened in about 100,000 years—a blink of an eye for a major geological event. The Red Sea went from connecting with the Mediterranean Sea to an empty, salt-filled basin. Then, a massive flood burst through volcanic barriers to open the Bab el-Mandab strait and reconnect the Red Sea with the world’s oceans.
The work is published in the journal Communications Earth & Environment.