Epilepsy is characterized by recurrent seizures and neurological consequences, which may be associated with impaired myelin and glial integrity, and exacerbated by environmental neurotoxicants. Environmental neurotoxicants, such as Cypermethrin (CPM), may heighten these impairments, worsening seizure outcomes. This study investigates the effects of Cypermethrin (CPM) on Pentylenetetrazole (PTZ)-induced seizures and the Vitamin E (Vit E) and valproate (VAP) co-interventions on myelin and glial integrity.
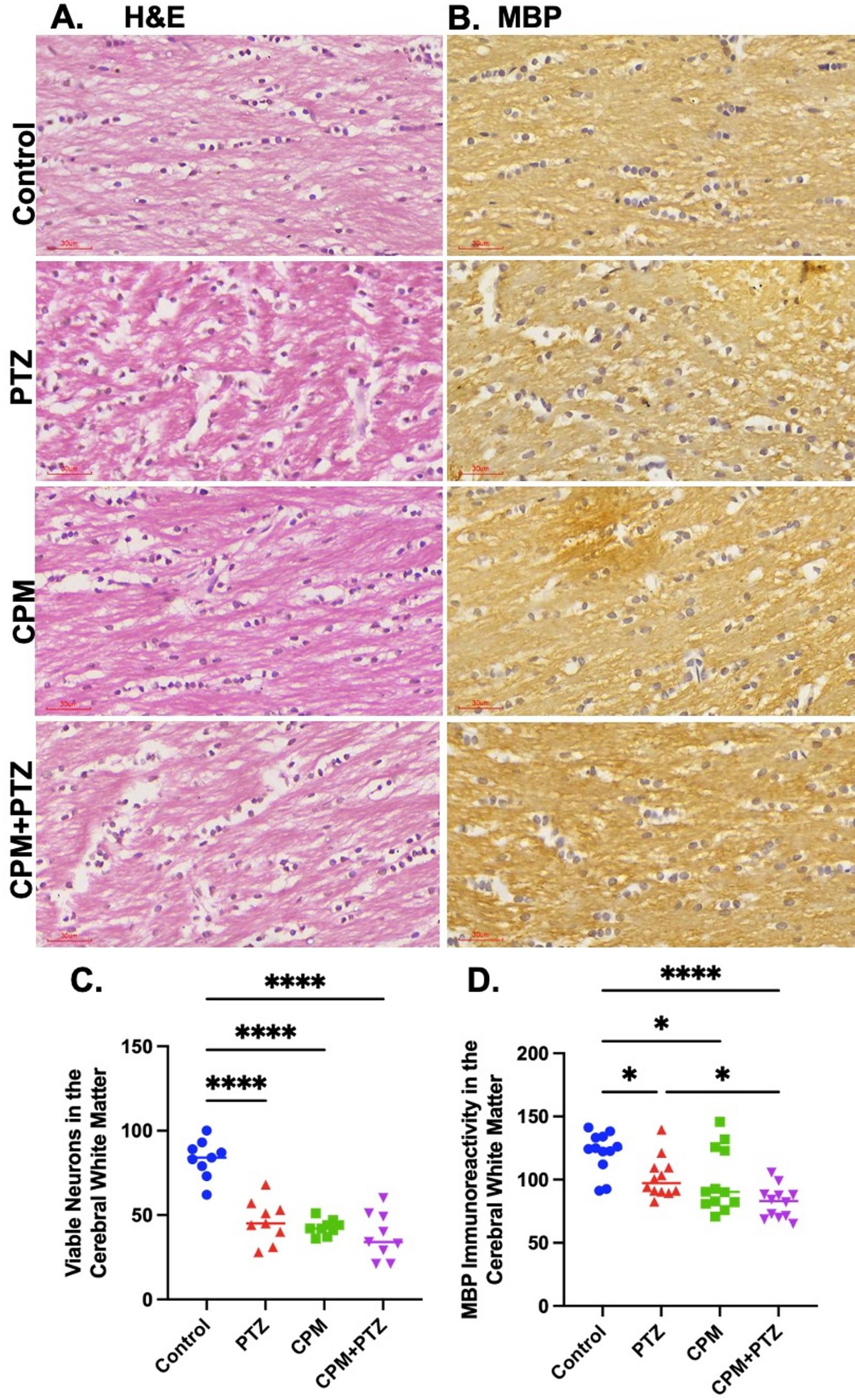
Histochemical and immunohistochemical analyses for hematoxylin and eosin (H&E), myelin basic protein (MBP), ionized calcium-binding adaptor molecule 1 (IBA1), glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), and oligodendrocyte transcription factor 2 (OLIG-2) were conducted on cerebral white matter and corpus callosum tissues. The density of stained cells and immunoreactivity obtained with ImageJ was subjected to one-way analysis of variance.
Immunohistochemistry revealed that cypermethrin exposure in PTZ-induced seizure rats led to marked neuronal, oligodendroglial, and myelin loss, accompanied by substantial glial activation in both cerebral white matter and corpus callosum. Interventional ingestions of VAP and Vit E, especially when combined, substantially reduced both microglial activation and reactive astrogliosis, thereby consequently preventing oligodendrocyte and neuronal loss, thus preserving both cerebral white matter and callosal myelin.