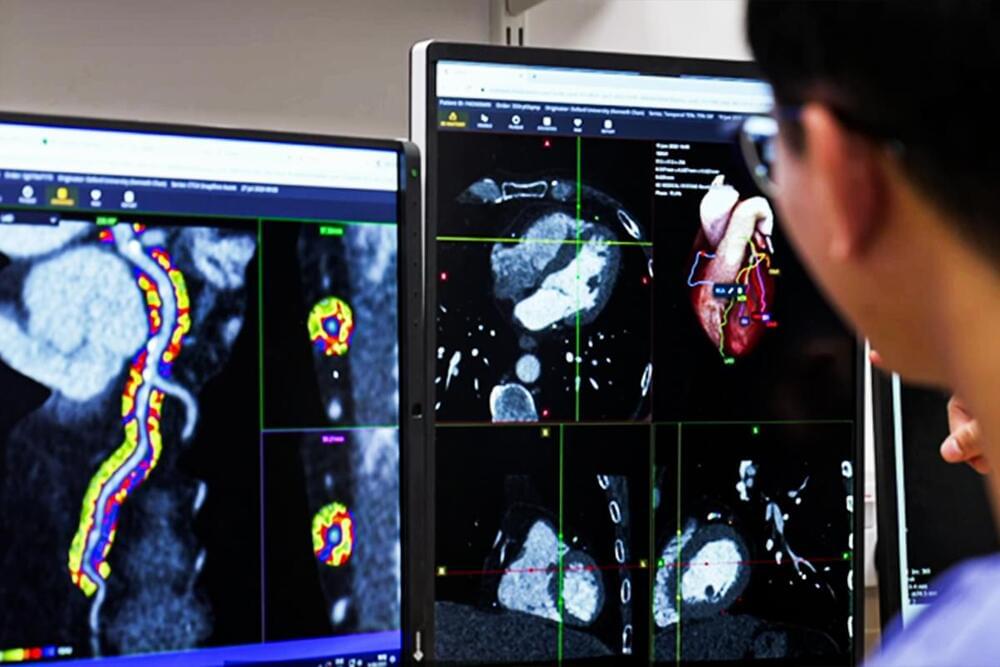
By contrast, information on coronary inflammation can provide crucial early warning signs of a cardiac event. Yet traditional diagnostic methods of measuring inflammation are not specific for cardiovascular diseases. Inflammation is invisible to CT scans, for instance. And biomarkers such as hsCRP (High-sensitivity C-reactive Protein) measure systemic inflammation, rather than cardiovascular inflammation, so the test may show up high in the case of inflammation driven by non-heart organs.
CaRi-Heart leverages AI tech to detect and quantify coronary inflammation, giving it an edge over traditional diagnostic methods. Cheng explains that while it is important to find patients who already have significantly narrowed coronary arteries, and obviously need immediate treatment, cardiologists often end up archiving many cases of patients with no visible signs of disease but who potentially have high coronary inflammation. This inflammation, driven by cholesterol, or smoking, or diabetes and other risk factors, ultimately causes the wall of the artery to become thickened and narrowed.
Caristo’s CaRi-Heart technology is a non-invasive cloud-based solution that utilizes AI to analyse CT scans, overcoming the limitations of traditional diagnostic methods, offering a more sensitive and specific approach to detecting and quantifying coronary inflammation, says Cheng. CaRi-Heart is the only commercially available technology that can detect and measure coronary inflammation on routine cardiac CT scans, and it has been cleared for clinical use in the UK, EU and Australia.