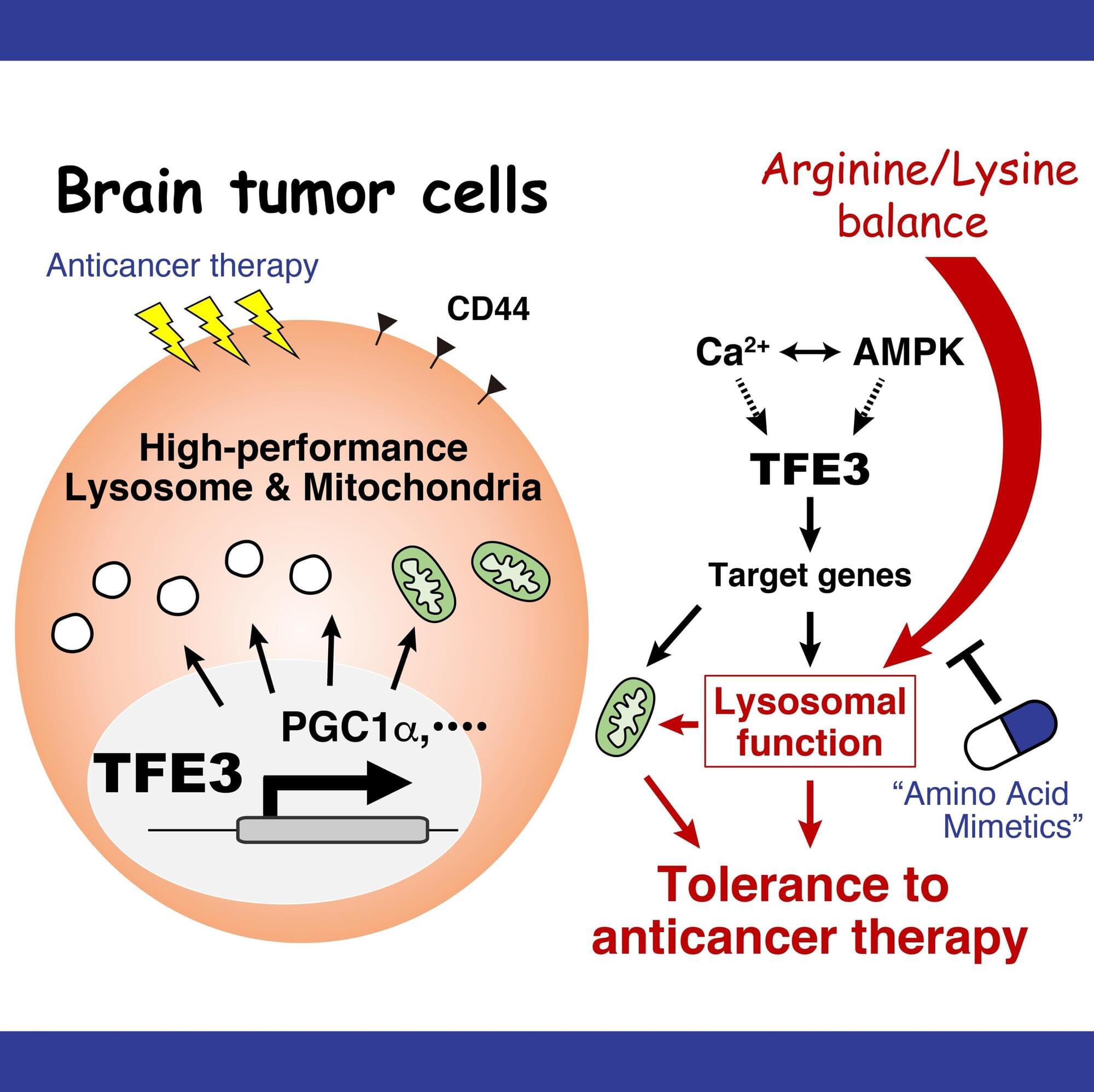
Researchers at Nano Life Science Institute (WPI-NanoLSI), Kanazawa University, report in Nature Communications on how the targeted suppression of lysosome function may lead to brain cancer therapy.
Glioblastoma is a type of brain cancer with a very poor prognosis of survival. Causes of glioblastoma are not known, and there is no method for preventing the cancer. Traditional treatment includes the drug temozolomide (TMZ). In many cases, TMZ kills glioblastoma cells, but a significant portion of patients show resistance to the drug.
Changes in the levels of metabolites—small molecules playing key roles in metabolic processes in living organisms—have been observed in TMZ-resistant glioblastoma cells, pointing to the importance of understanding and targeting metabolic pathways in the context of cancer therapy.