Although natural-killer-cell therapies are safer than T-cell therapies and offer other advantages, they require upgrades to overcome their limited lifespan and susceptibility to immunosuppression.


ABOVE: Researchers recapitulate electrical gradients in vitro to help guide stem cell differentiation for neural regeneration. ©istock, Cappan.
The dance of development is electric. Bioelectrical gradients choreograph embryonic growth, signaling to stem cells what cell types they should become, where they should travel, who their neighbors should be, and what structures they should form.1 The intensity and location of these signals serve as an electrical scaffold to map out anatomical features and guide development. Bioelectricity also shapes tissue regeneration.2 Tapping into these mechanisms is of special interest to researchers who grapple with the challenge of regenerating injured nerves.3
One such curious team from Stanford University and the University of Arizona recently reported a new approach using electrically conductive hydrogels to induce differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells into neurons and oligodendrocytes in vitro.4 Their findings, published in the Journal of Materials Chemistry B, provide important proof of principle for future studies of biocompatible materials to electrically augment transplanted and endogenous cells after injury.
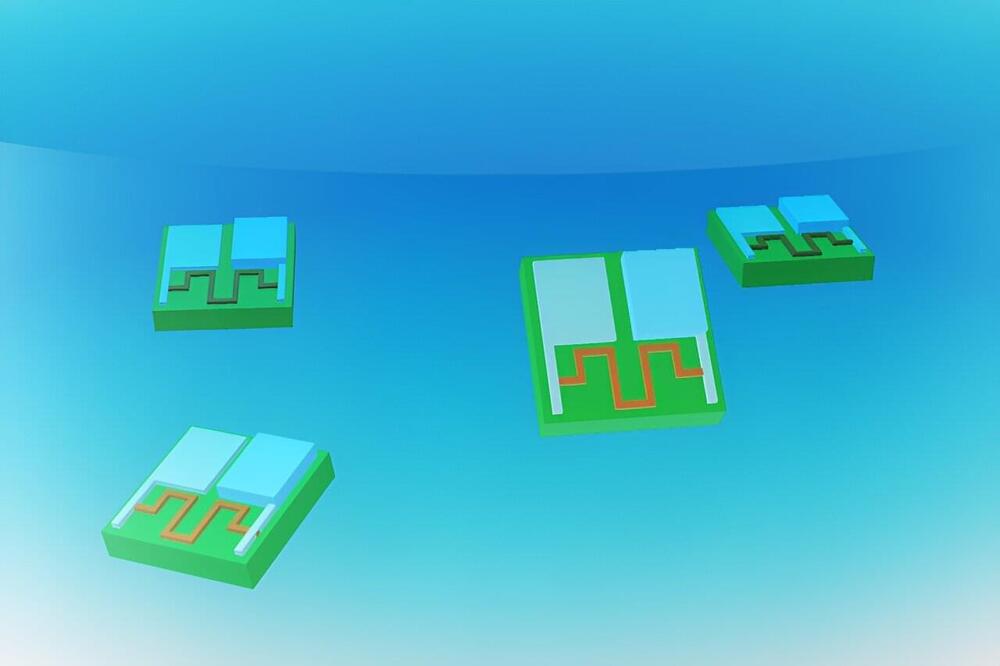
A tiny battery designed by MIT engineers could enable the deployment of cell-sized, autonomous robots for drug delivery within in the human body, as well as other applications such as locating leaks in gas pipelines.
The new battery, which is 0.1 millimeters long and 0.002 millimeters thick—roughly the thickness of a human hair—can capture oxygen from air and use it to oxidize zinc, creating a current of up to 1 volt. That is enough to power a small circuit, sensor, or actuator, the researchers showed.
“We think this is going to be very enabling for robotics,” says Michael Strano, the Carbon P. Dubbs Professor of Chemical Engineering at MIT and the senior author of the study. “We’re building robotic functions onto the battery and starting to put these components together into devices.”
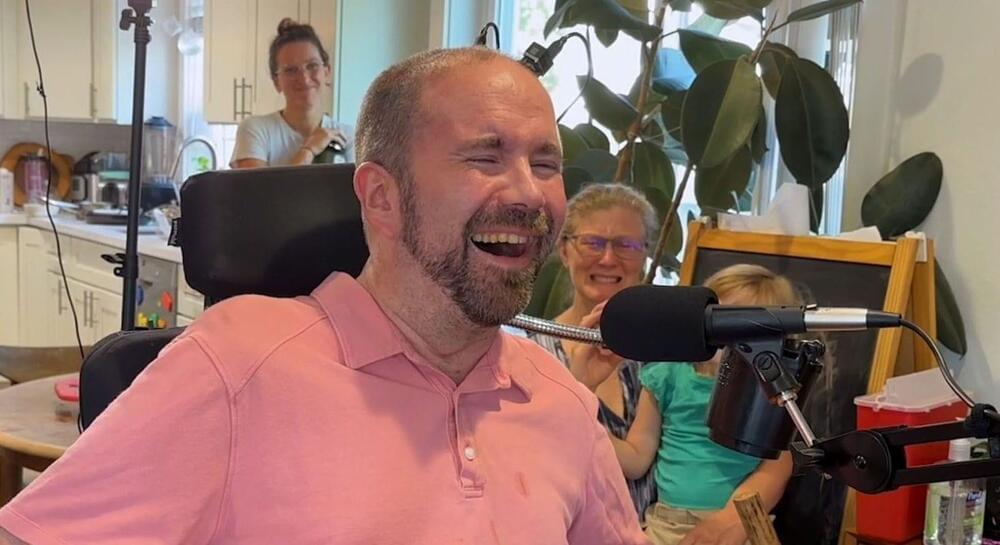

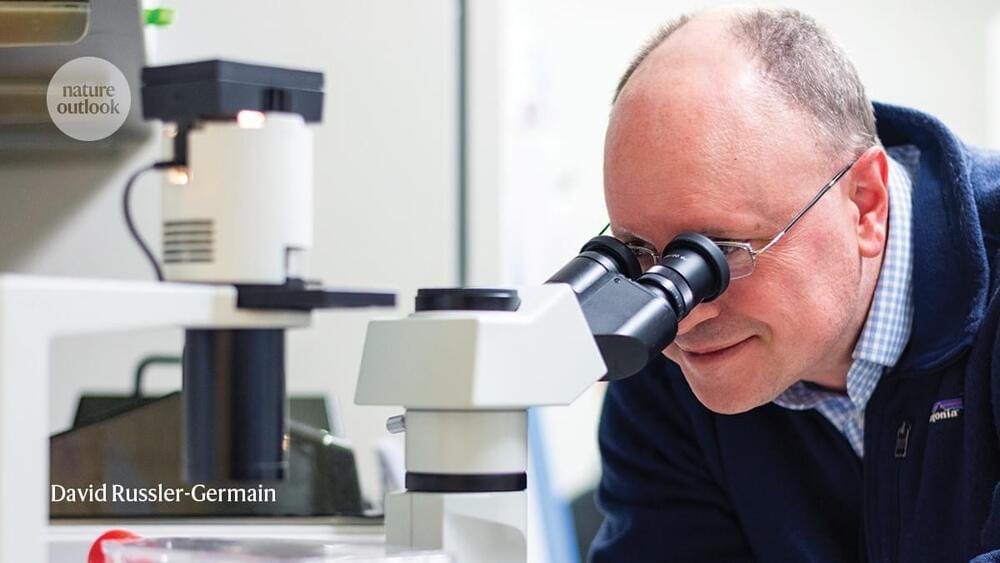
“Not being able to communicate is so frustrating and demoralizing. It is like you are trapped,” Harrell said. “Something like this technology will help people back into life and society.”
For the researchers involved, seeing the impact of their work on Harrell’s life has been deeply rewarding. “It has been immensely rewarding to see Casey regain his ability to speak with his family and friends through this technology,” said the study’s lead author, Nicholas Card, a postdoctoral scholar in the UC Davis Department of Neurological Surgery.
Leigh Hochberg, a neurologist and neuroscientist involved in the BrainGate trial, praised Harrell and other participants for their contributions to this groundbreaking research. “Casey and our other BrainGate participants are truly extraordinary. They deserve tremendous credit for joining these early clinical trials,” Hochberg said. “They do this not because they’re hoping to gain any personal benefit, but to help us develop a system that will restore communication and mobility for other people with paralysis.”
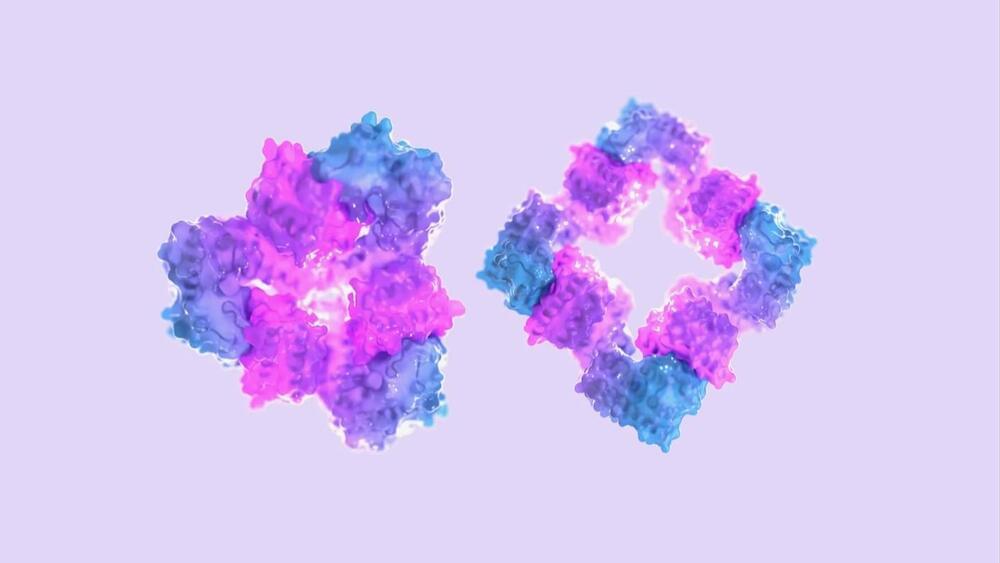

This type of molecular collaboration has inspired scientists for nearly a century. Here, oxygen is the effector. It flips a protein switch, helping proteins better carry oxygen through the body. In other words, it may be possible to optimize protein functions with an alternative effector drug.
The problem? The original inspiration is wonky. Sometimes hemoglobin proteins carry oxygen. Other times they don’t. In 1965, a French and American collaboration found out why. Each protein alternates between two three-dimensional shapes—one that carries oxygen and another that doesn’t. The shapes can’t coexist in the assembled protein to carry oxygen: It’s all-or-none, depending on the presence and amount of the effector.
The new study built on these lessons to guide their AI-designed proteins.


Fermented foods have been used for several years all over the world, due to their unique nutritional characteristics and because fermentation promotes conservation and food security. Moreover, fermented foods and beverages have a strong impact on human gut microbiota. Papaya is the fruit of the Carica papaya plant, traditionally used as a medicinal fruit, but there are also references to the use of the fermented form of this fruit. The main purpose of this review is to provide an improved understanding of fermented papaya nutritional and health applications. A literature search was conducted in the PubMed and Google Scholar databases. Both in vitro and in vivo studies were included. According to the retrieved studies, fermented papaya has proven to be an excellent antioxidant and an excellent nutraceutical adjuvant in combined therapies against several diseases, such as Alzheimer’s disease, allergic reactions, anticancer activity, and anemias. Therefore, it is concluded that fermented papaya has many benefits for human health and can be used as prevention or aid in the treatment of various diseases.
Keywords: fermented food, fermented papaya, health benefits, oxidative stress.
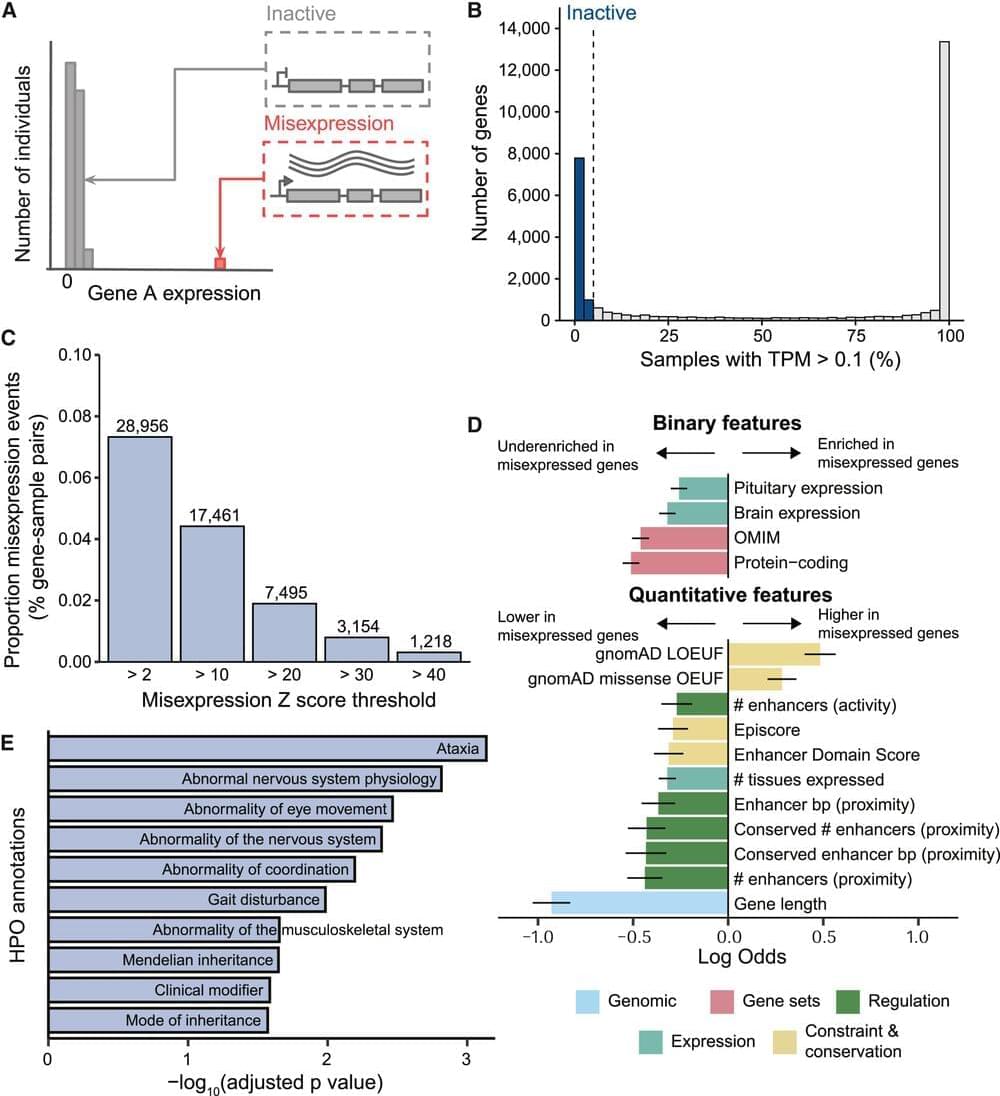
New insights into the prevalence and mechanisms of gene misexpression in a healthy population could help in diagnosing and developing treatments for complex diseases.
Scientists have uncovered that ‘gene misbehaviour’ – where genes are active when they were expected to be switched off – is a surprisingly common phenomenon in the healthy human population.
The team also identify several mechanisms behind these gene activity errors. This may help inform precision medicine approaches and enable the development of targeted therapies to correct expression.
A new Australian study has identified why a diet rich in magnesium is so important for our health, reducing the risk of DNA damage and chronic degenerative disorders.
Scientists from the University of South Australia measured blood samples from 172 middle aged adults, finding a strong link between low magnesium levels and high amounts of a genotoxic amino acid called homocysteine.
This toxic combination damages the body’s genes, making people more susceptible to Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease, gastrointestinal diseases, a range of cancers, and diabetes.