We are urgently working to find new treatments and cures for ALS and are currently funding over 168 research projects in 12 countries. We work with many pharmaceutical companies that have attempted to bring new treatments to market.


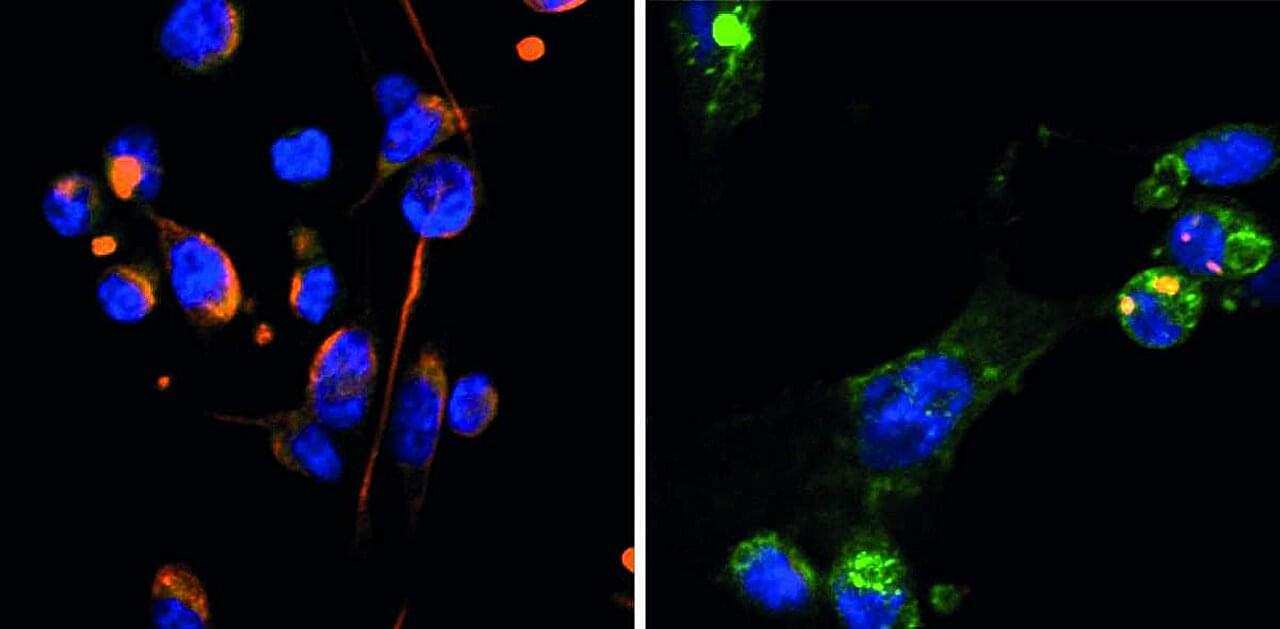
Breast cancer is becoming increasingly treatable, but in some cases the disease can resurface even decades after a patient has been declared cancer free. This is because of cells that detach from the original tumor and hide in a dormant state in the breast or other organs.
Little is known about the mechanisms responsible for dormancy in cancer cells, and even less is known about what causes these cells to suddenly wake up. A new study from the laboratory of Israel Prize laureate Prof. Yosef Yarden at the Weizmann Institute of Science, published in Science Signaling, reveals the mechanism that puts breast cancer cells to sleep, as well as the reason that they emerge from dormancy more aggressive than they were before they became dormant.
From the earliest stage of embryonic development, through sexual maturation to the production of breast milk during pregnancy and after childbirth, breast tissue changes throughout a woman’s life. These changes are made possible by the metamorphosis that breast tissue cells undergo, from the early developmental stage, known as mesenchymal, when the cells are round, highly mobile and dividing rapidly, to the more mature, epithelial stage, when they are somewhat cubical, less active and dividing slowly.
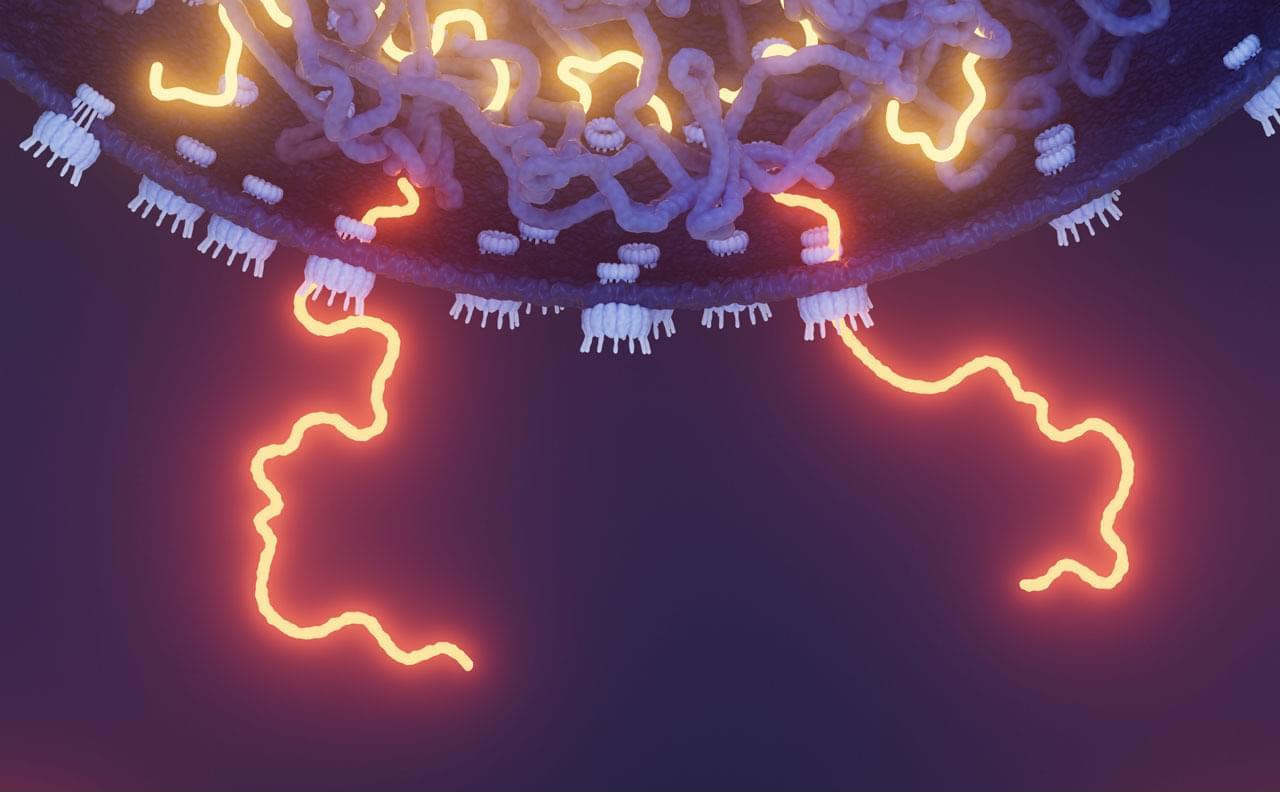

The pair decided to conduct a clinical trial that could be more compelling. In 12 people with early Alzheimer’s who took 3TC for 6 months, the drug didn’t boost cognitive abilities. But other indicators suggested some benefits, as Frost, Sullivan, and their colleagues revealed last month in npj Dementia. For instance, levels of one key neurodegeneration indicator dipped, suggesting 3TC protects patients’ brain cells. “That was the change I was most excited to see,” Frost says.
Their recent study was the first clinical test of an antitransposon strategy for Alzheimer’s to reach the finish line. But it’s just one of a growing number of trials launched by academic researchers and biotechs to gauge the effects of throttling transposons—so-called jumping genes. These vagrant sequences, some of which are relics of viruses that invaded cells long ago or may even be derived from symbiotic bacteria, make up more than 40% of the human genome but were once seen as largely harmless. However, a variety of evidence from human cell lines, lab animals, and epidemiological studies has implicated their antics in illnesses such as lupus, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), Parkinson’s disease, and cancer, as well as in aging.
Encouraging results are trickling in. In 2022, a phase 2 trial determined that 3TC halted tumor growth in some patients with colorectal cancer. Last year, Transposon Therapeutics revealed that a different drug that stymies replication of these sequences slowed one sign of physical decline in people with ALS or another neurodegenerative disease, frontotemporal dementia. “It’s really amazing how quickly the story has developed,” says John Sedivy, a molecular biologist at Brown and the company’s co-founder.
Typhoid fever might be rare in developed countries, but this ancient threat, thought to have been around for millennia, is still very much a danger in our modern world.
According to research published in 2022, the bacterium that causes typhoid fever is evolving extensive drug resistance, and it’s rapidly replacing strains that aren’t resistant.
Currently, antibiotics are the only way to effectively treat typhoid, which is caused by the bacterium Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi (S Typhi). Yet over the past three decades, the bacterium’s resistance to oral antibiotics has been growing and spreading.
Nanobots aren’t just microscopic machines—they could come in countless shapes and sizes, each designed for a unique purpose. From medical nanobots that repair cells to swarming micro-robots that build structures at the atomic level, the future of nanotechnology is limitless. Could these tiny machines revolutionize medicine, industry, and even space exploration? #Nanotech #Nanobots #FutureTech #Science #Innovation …
Measles cases are going up—and a federal scientist has warned that case counts have probably been underreported. Another vaccine-preventable illness, whooping cough, sees a troubling increase in cases. Ancient humans found sun-protection solutions when Earth’s magnetic poles wandered. A colossal squid has been captured on video in its natural habitat for the first time. Plus, we discuss evidence that Mars once had a carbon cycle and a planet that is orbiting a pair of brown dwarfs.
Episode Transcript: https://www.scientificamerican.com/po… reading: This Is the First Colossal Squid Filmed in the Deep Sea—And It’s a Baby! • See the first colossal squid ever cau… RFK, Jr., Is Wrong about Cause of Rising Autism Rates, Scientists Say https://www.scientificamerican.com/ar… How to Talk about Vaccines in an Era of Scientific Mistrust https://www.scientificamerican.com/ar… E-mail us at [email protected] if you have any questions, comments or ideas for stories we should cover! Discover something new every day: subscribe to Scientific American: https://www.scientificamerican.com/ge… And sign up for Today in Science, our daily newsletter: https://www.scientificamerican.com/ac… Science Quickly is produced by Rachel Feltman, Fonda Mwangi, Kelso Harper, Naeem Amarsy and Jeff DelViscio. This episode was hosted by Rachel Feltman. Our show is edited by Alex Sugiura with fact-checking by Shayna Posses and Aaron Shattuck. The theme music was composed by Dominic Smith.
Recommended reading:
This Is the First Colossal Squid Filmed in the Deep Sea—And It’s a Baby! • See the first colossal squid ever cau…
RFK, Jr., Is Wrong about Cause of Rising Autism Rates, Scientists Say https://www.scientificamerican.com/ar…
How to Talk about Vaccines in an Era of Scientific Mistrust https://www.scientificamerican.com/ar…
E-mail us at [email protected] if you have any questions, comments or ideas for stories we should cover!
Discover something new every day: subscribe to Scientific American: https://www.scientificamerican.com/ge…


Psychedelic drugs are seeing a surge of interest from mainstream medicine, and initial results suggest that psychedelic-therapy can be a safe and effective treatment for some mental health conditions. However, the side-effect profile is still incompletely understood. In particular, the use of psychedelics has been posited to carry a risk of triggering latent psychotic disorders or persistent visual hallucinations, known as hallucinogen persisting perception disorder (HPPD).
In order to better understand the prevalence and risk factors of such side-effects, Katie Zhou and colleagues surveyed 654 people online who were planning to take psychedelics through their own initiative. The findings are published in the journal PNAS Nexus.
Of the 654 people surveyed, 315 people were resurveyed two weeks after their experience and 212 people were resurveyed again four weeks after their experience. The sample was 74% male, and 77% university-educated. About one-third had been diagnosed with at least one psychiatric condition.

Acquired resistance is a common occurrence among patients with oncogene-driven non-small-cell lung cancer receiving targeted therapies. Monitoring of circulating tumour DNA in liquid biopsy samples provides an appealing, minimally invasive method of monitoring for acquired resistance in this setting. However, research into detecting mechanisms of acquired resistance in liquid biopsy samples has thus far been limited by various challenges. In this Perspective, the authors describe the available data on detecting mechanisms of acquired resistance to targeted therapies in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer, as well as the various challenges to progress, such as a lack of a consensus definition of acquired resistance, and other inconsistencies in the approach to detecting and investigating these alterations.