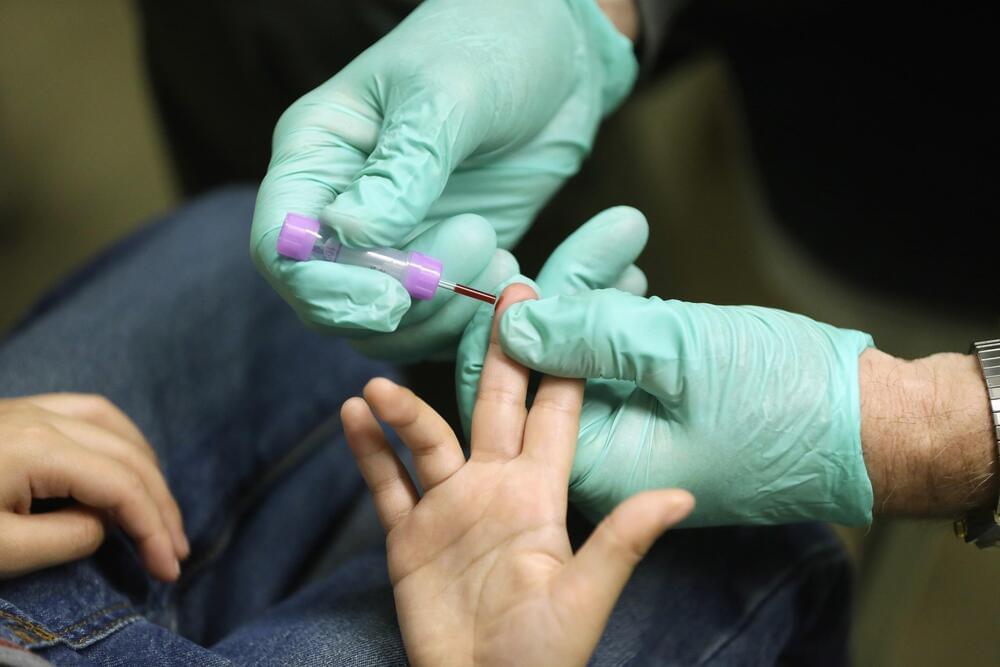
Few drugs are available to treat heavy metals that enter the body, either from lead poisoning or nuclear fallout. A UC Berkeley startup hopes to change that.
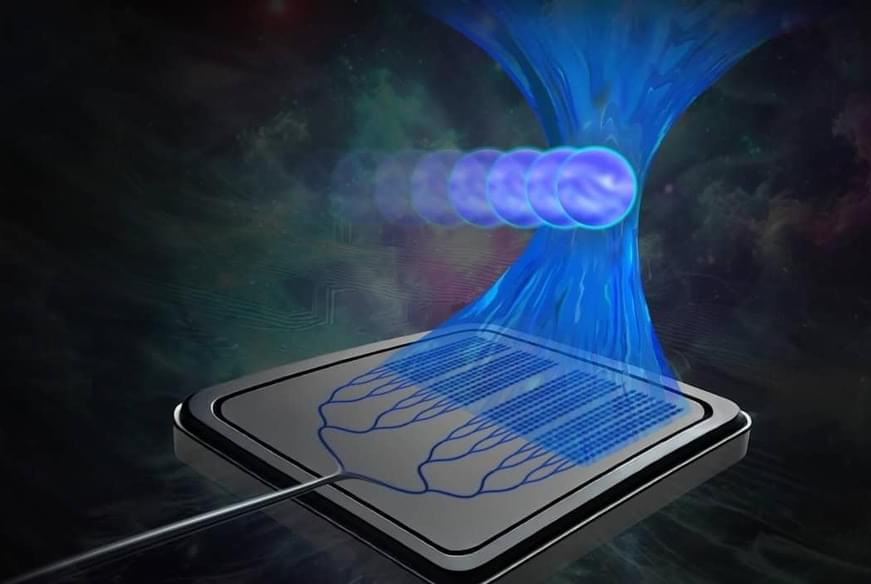


Chip-based tractor beam Integrated optical tweezers use an intensely focused beam of light to capture and manipulate biological particles without damaging the cells.
Optical manipulation techniques are garnering increased interest for biological applications.
Optical manipulation techniques are garnering increased interest for biological applications. Researchers from Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) have now developed a miniature, chip-based optical trap that acts as a “tractor beam” for studying DNA, classifying cells and investigating disease mechanisms. The device – which is small enough to fit in your hand – is made from a silicon-photonics chip and can manipulate particles up to 5 mm away from the chip surface, while maintaining a sterile environment for cells.
The promise of integrated optical tweezers
Integrated optical trapping provides a compact route to accessible optical manipulation compared with bulk optical tweezers, and has already been demonstrated using planar waveguides, optical resonators and plasmonic devices. However, many such tweezers can only trap particles directly on (or within several microns of) the chip’s surface and only offer passive trapping.
This clip is from the following episode: https://youtu.be/xqS5PDYbTsE
Recorded on Oct 18th, 2024
Views are my own thoughts; not Financial, Medical, or Legal Advice.
In this episode, Ray and Peter discuss 2025 predictions, Job loss in the coming years, and Ray’s thoughts on nanotech taking over the world.
Ray Kurzweil is a world-class inventor, thinker, and futurist, with a thirty-five-year track record of accurate predictions. He has been a leading developer in artificial intelligence for 61 years – longer than any other living person. He was the principal inventor of the first CCD flat-bed scanner, omni-font optical character recognition, print-to-speech reading machine for the blind, text-to-speech synthesizer, music synthesizer capable of recreating the grand piano and other orchestral instruments, and commercially marketed large-vocabulary speech recognition software. Ray received a Grammy Award for outstanding achievement in music technology; he is the recipient of the National Medal of Technology, was inducted into the National Inventors Hall of Fame, and holds twenty-one honorary Doctorates. He has written five best-selling books including The Singularity Is Near and How To Create A Mind, both New York Times bestsellers, and Danielle: Chronicles of a Superheroine, winner of multiple young adult fiction awards. His new book, The Singularity Is Nearer was released on June 25th and debuted at #4 on the New York Times Best Seller list. He is a Principal Researcher and AI Visionary at Google.
I send weekly emails with the latest insights and trends on today’s and tomorrow’s exponential technologies. Stay ahead of the curve, and sign up now: https://www.diamandis.com/subscribe.
Connect with Peter:
Anirban Datta, Head of Discovery Biology at Verseon International Corporation, details how recent breakthroughs are bringing once-distant possibilities, such as testing drugs more efficiently and restoring lost organ function through implantation, closer to reality.
Imagine being able to create an in vitro replica of a diseased organ to study the molecular mechanism underlying the illness. Now take a step further: envision testing drugs in these organoids to identify the ones that can treat disease safely and effectively without needing to run expensive clinical trials first. Further still, think about implanting these mini organs into the patient to restore lost function. With multiple breakthroughs in recent decades, these goals are now much closer to reality.


Generative AI is changing medicine, and it’s happening fast. HMS is getting a jump on this shift by training future doctors with skills in data and machine learning.
Harvard Medical School is building artificial intelligence into the curriculum to train the next generation of doctors.


“Al-determined tumor volume has the potential to advance precision medicine for patients with prostate cancer by improving our ability to understand the aggressiveness of a patient’s cancer and therefore recommend the most optimal treatment,” said Dr. David D. Yang, MD.
How can artificial intelligence (AI) help medical professionals identify, diagnose, and treat prostate cancer? This is what a recent study published in Radiology hopes to address as a team of researchers developed an AI model designed to identify prostate cancer lesions, which holds the potential to help medical professionals and patients make the best-informed decisions regarding diagnoses and treatment options.
For the study, which was conducted between January 2021 to August 2023, the researchers had their AI model examine MRI scans from 732 patients, including 438 patients who underwent radiation therapy (RT) and 294 patients who underwent radical prostatectomy (RP). The goal was to compare a potential success rate of the AI model identifying tumors compared to patient treatment between 5 to 10 years after being diagnosed.
In the end, the AI model demonstrated an 85 percent accuracy in identifying cancerous lesions. Additionally, the AI model identified the larger volume lesions that resulted in failed treatment and metastasis, which is when cancer tumors spread beyond the original location within the body. Finally, the AI model determined that RT patients were at a decreased risk of metastasis based on their tumor volumes.