Scientists in Osaka began clinical trials on proteins to enable children without permanent teeth to develop a third set of teeth by 2030.



A Kobe University team was able to edit the DNA of Lactobacillus strains directly without a template from other organisms. This technique is indistinguishable from natural variation and enabled the researchers to create a strain that doesn’t produce diabetes-aggravating chemicals.
Humans have improved the microorganisms we rely on for millennia, selecting variants that are better able to produce wine, yogurt, natto and many other products. More recently, direct genetic modification has emerged as a tool to exert more precise and efficient control over the improvement, but also has drawn much public criticism for often using DNA from unrelated organisms in these modifications. Kobe University bioengineer NISHIDA Keiji says, “As a consequence, using such transgenic techniques is not favorable for food products due to legislations being restrictive and social acceptance being low.”
Nishida and his team have developed a technique that gives even more precise control over the genetic content of a microorganism that does not rely on template DNA from other organisms. He says: “We have invented a DNA base editing technology named ‘Target-AID,’ which is superior to conventional techniques such as ‘CRISPR-Cas9’ in several aspects. For example, CRISPR-Cas9 induces DNA breaks and often causes cell death, while our Target-AID inserts precise point mutations without such breaks.”

Researchers at Amsterdam UMC have developed a new diagnostic test that can quickly and accurately diagnose bacterial meningitis. The test measures the CRP protein in cerebrospinal fluid, a protein that is already often tested in blood to detect bacterial infections. Currently, it often takes a long time before meningitis is diagnosed, which delays the start of adequate treatment.
The study is published in The Lancet Regional Health—Europe.
Bacterial meningitis is a life-threatening condition in which one in six patients die and half of the survivors have residual symptoms. Thus, prompt diagnosis and treatment are crucial.
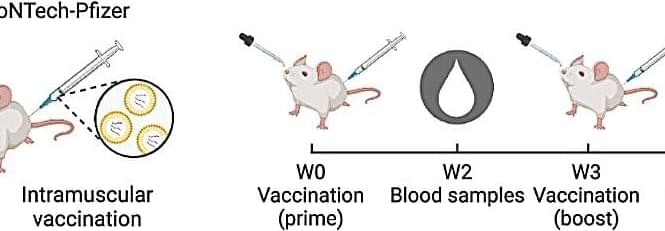
Vaccines save millions of lives every year, but there is still an urgent need for more efficient vaccines. Strategies to combat serious outbreaks of viral infections are particularly important. Such infections are initiated at mucosal surfaces, where there is a close association between polarized epithelial cells and immune effector cells. However, vaccines are usually given intramuscularly or subcutaneously, and often do not provide sufficient protection at the actual site of infection.
In Nature Communications, the laboratory of Professor Jan Terje Andersen and collaborators report on a novel vaccine technology platform, in which the subunit antigen is genetically fused to albumin.
Albumin was chosen as a carrier as it is actively transported across the mucosal barrier by FcRn, a receptor found on mucosal epithelial cells.
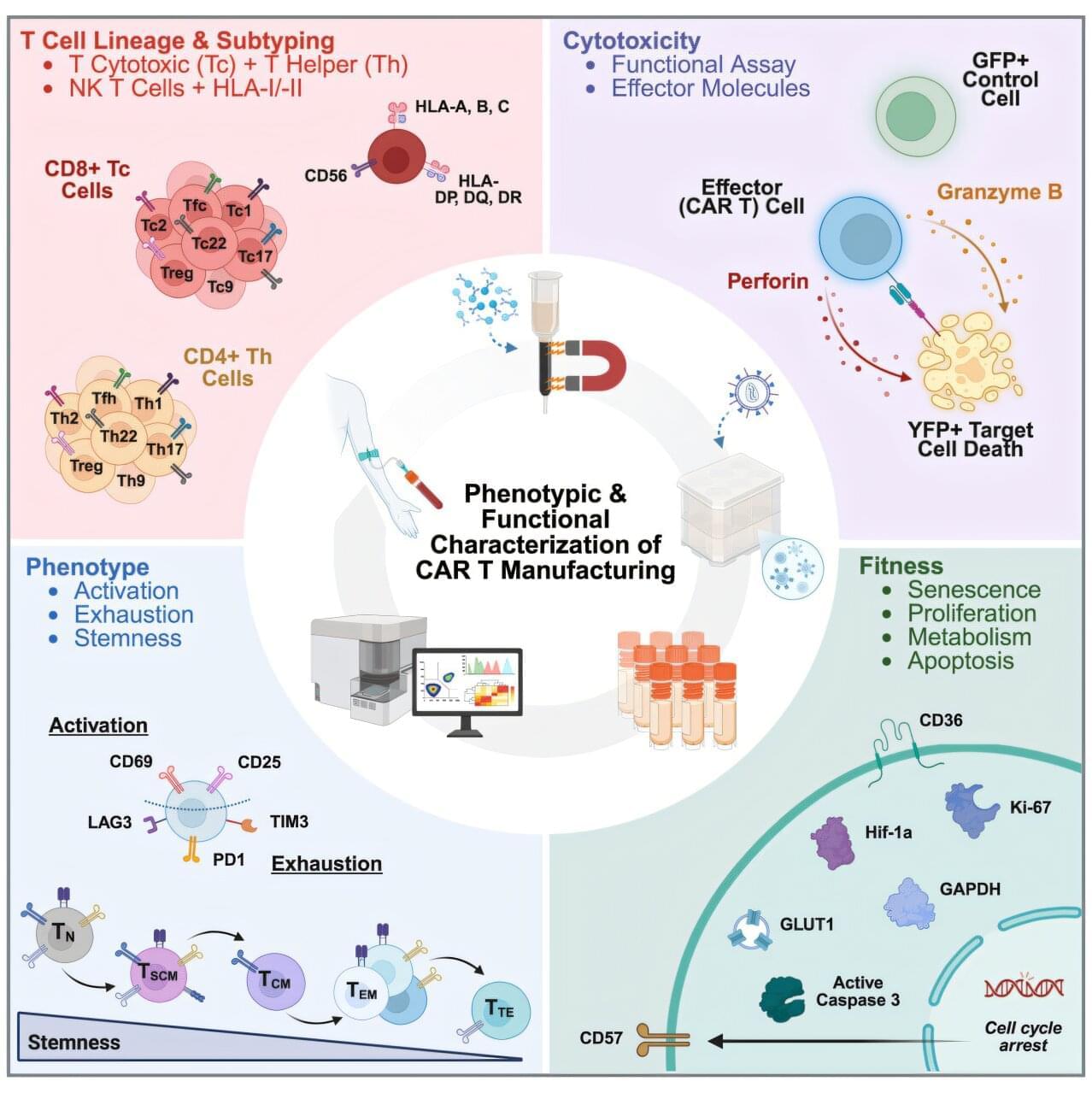
A team of researchers from the Keck School of Medicine of USC has developed an advanced tool for analyzing chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells, including how they evolve during manufacturing and which ones are most effective at killing cancer. Using the platform, which leverages a laser-based technology known as spectral flow cytometry, researchers have already found one key insight: CAR T cells are better equipped to fight cancer after a shorter five-day expansion process than at the 10-day mark.
The study was just published in the 25th anniversary special issue of Molecular Therapy.
CAR T cell therapies, which reprogram a patient’s own immune cells to recognize and attack cancer, represent a major advance in treating blood cancers such as leukemia and lymphoma. But not all patients respond equally well, and researchers believe one key to optimizing treatment is to understand how various T-cell features relate to patient outcomes down the line.

Scientists looking to tackle our ongoing obesity crisis have made an important discovery: Intermittent calorie restriction leads to significant changes both in the gut and the brain, which may open up new options for maintaining a healthy weight.
Researchers from China studied 25 volunteers classed as obese over a period of 62 days, during which they took part in an intermittent energy restriction (IER) program – a regime that involves careful control of calorie intake and relative fasting on some days.
Not only did the participants in the study lose weight – 7.6 kilograms (16.8 pounds) or 7.8 percent of their body weight on average – there was also evidence of shifts in the activity of obesity-related regions of the brain, and in the make-up of gut bacteria.



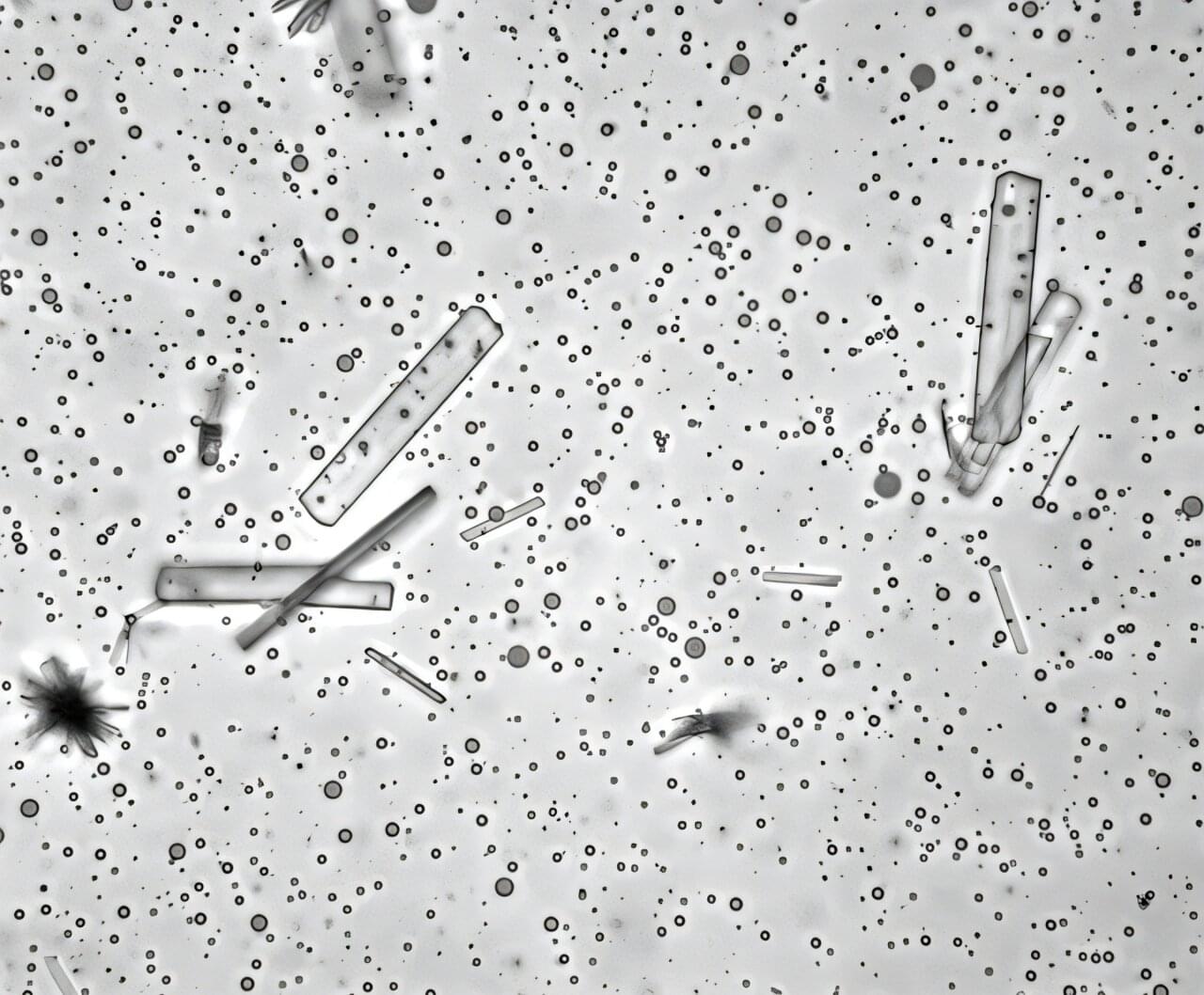
A new study led by researchers at the Earth-Life Science Institute (ELSI) at the Institute of Science, Tokyo, has uncovered a surprising role for calcium in shaping life’s earliest molecular structures. Their findings suggest that calcium ions can selectively influence how primitive polymers form, shedding light on a long-standing mystery: how life’s molecules came to prefer a single “handedness” (chirality).
The study is published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Like our left and right hands, many molecules exist in two mirror-image forms. Yet life on Earth has a striking preference: DNA’s sugars are right-handed, while proteins are built from left-handed amino acids. This phenomenon, called homochirality, is essential for life as we know it—but how it first emerged remains a major puzzle in origins of life research.