Dr. Sui Huang, MD, PhD is a Professor at the Institute for Systems Biology ( ISB — https://isbscience.org/people/sui-huang-md-phd/?tab=biography ) where his…
Category: biotech/medical – Page 360
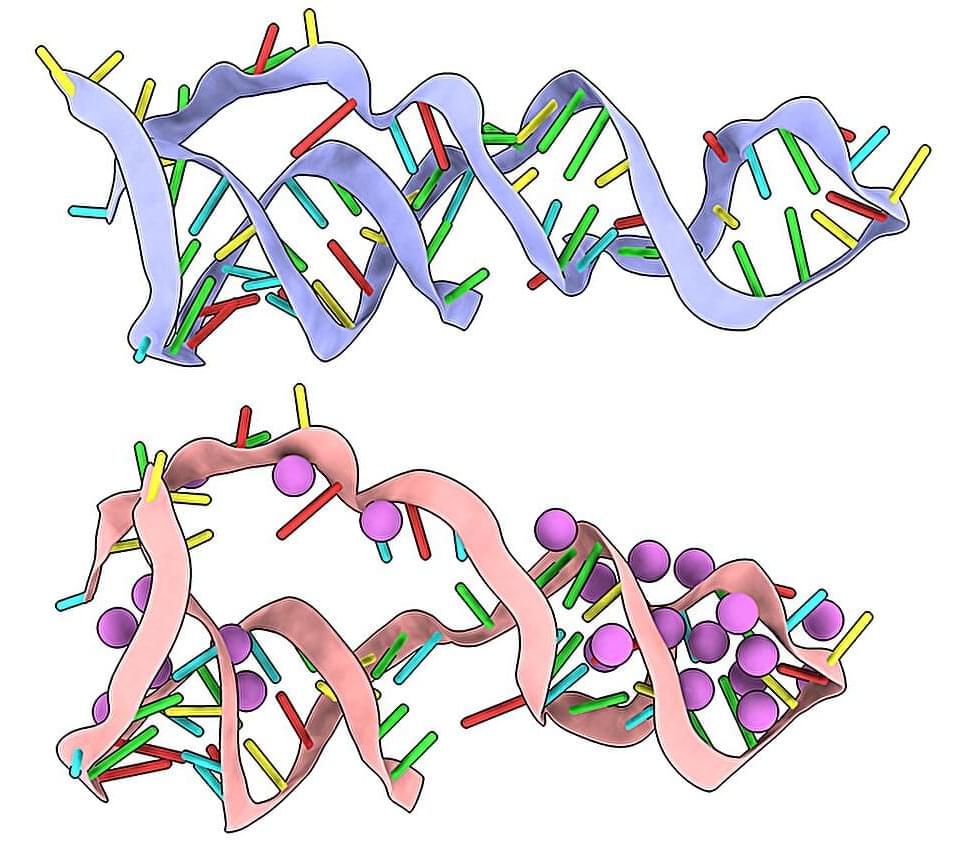
From sequence to structure: A fast track for RNA modeling
In Biology 101, we learn that RNA is a single, ribbon-like strand of base pairs that is copied from our DNA and then read like a recipe to build a protein. But there’s more to the story. Some RNA strands fold into complex shapes that allow them to drive cellular processes like gene regulation and protein synthesis, or catalyze biochemical reactions.
We know that these active molecules, called non-coding RNAs, are present in all life forms, yet we’re just starting to understand their many roles—and how they can be harnessed for applications in environmental science, agriculture, and medicine.
To study—and potentially modify—the functions of non-coding RNAs, we need to determine their structure. Scientists from Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) and the Hebrew University of Jerusalem have developed a streamlined process that predicts the structure of an RNA molecule down to the atomic level.
New study offers insights into designing safe, effective nasal vaccines
Most vaccines—and boosters—are injected directly into muscle tissue, usually in the upper arm, to kickstart the body’s immune system in the fight against disease. But for respiratory diseases like COVID-19, it can be important to have protection right where the virus enters: the respiratory tract.
In a new study, Yale researchers have found that nasal vaccine boosters can trigger strong immune defenses in the respiratory tract, even without the help of immune-boosting ingredients known as adjuvants. The findings, researchers suggest, may offer critical insights into developing safer, more effective nasal vaccines in the future.
“Our study shows how a simple viral protein antigen can boost respiratory tract immune responses against viruses,” said Akiko Iwasaki, Sterling Professor of Immunobiology at Yale School of Medicine (YSM) and senior author of the study. “These data imply that viral proteins in nasal spray may be used as a safe way to promote antiviral immunity at the site of viral entry.”
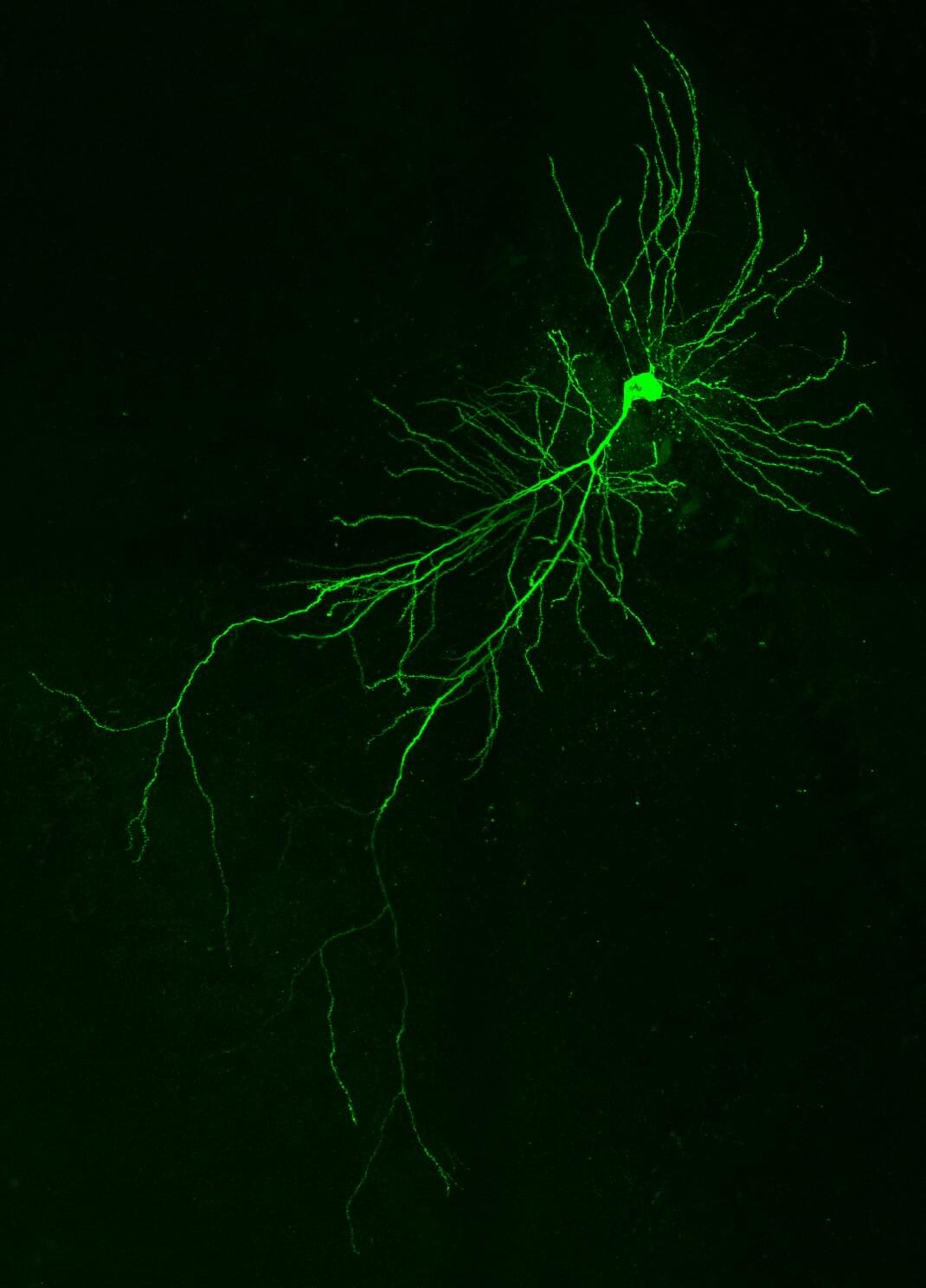
Mouse memory hinges on a nine-letter protein fragment exclusive to neurons
Cells have a trick called splicing. They can cut a gene’s message into pieces and decide which fragments to keep. By mixing and matching these fragments, a single gene can produce many different proteins, giving tissues and organs more options to thrive and evolve. Out of all tissues, splicing is most prevalent in the brain.
Researchers at the Center for Genomic Regulation (CRG) have discovered that one such fragment, a “microexon” just nine amino acids long, is inserted into the DAAM1 protein exclusively in neurons and nowhere else in the body. The inclusion of the microexon is critical for healthy neuronal development, with effects rippling all the way up to memory function. The findings are published in Nature Communications.
DAAM1 makes a protein that helps cells maintain their shape and enables their movement. When the team deleted the nine-letter microexon in mice, the animals were healthy at birth, but their adult brain cells had half of the usual “learning spines,” protrusions known to be important for learning and retrieval of memories.

Distinct neuron populations in the hypothalamus encode states associated with predator-related threats
The ability to detect imminent threats and execute behaviors aimed at protecting oneself, such as hiding, running away or defending oneself, is central to the survival of most animal species. A region of the mammalian brain known to play a key role in threat response is the hypothalamus, which also regulates the release of hormones and other vital bodily functions.
Researchers at California Institute of Technology (Caltech) and Howard Hughes Medical Institute recently carried out a study aimed at better understanding how a specific group of neurons in the mouse ventromedial hypothalamus dorsomedial subdivision (VMHdm), which are identified by the presence of the steroidogenic factor 1 (SF1) gene, contribute to the coding of predator imminence.
Their findings, published in Neuron, show that distinct subsets of VMHdmSF1 neurons encode multiple internal states that are evoked by the imminence of predators.
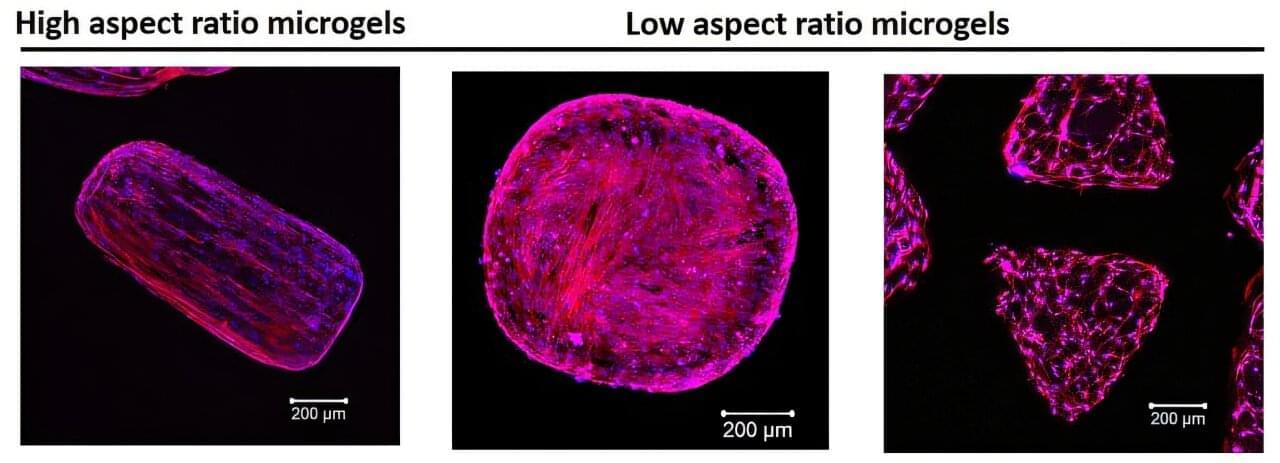
3D printed hydrogels guide cell growth to form functional tissue structures
Researchers at the Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation (TIBI) have developed a technique that could help advance treatments in tissue engineering. The study, published in the journal Small, introduces a technique for producing tissues with precise cellular organization designed to mimic the natural structure of human tissue.
Using a simple light-based 3D printing method, the team created microgels with controlled internal architectures. These structures help guide how cells behave and grow, mimicking the way cells naturally behave in the body.
By adjusting properties of light as it interacts with hydrogels, the team modified the internal structure of these microgels, enabling precise control of cell organization in 3D space. This breakthrough addresses a major challenge in creating realistic, functional tissue environments critical for tissue repair and regeneration.

3D printed smart fabrics maintain flexibility and sensing ability after repeated washes
Imagine a T-shirt that could monitor your heart rate or blood pressure. Or a pair of socks that could provide feedback on your running stride. It may be closer than you think, with new research from Washington State University demonstrating a particular 3D ink printing method for so-called smart fabrics that continue to perform well after repeated washings and abrasion tests. The research, published in the journal ACS Omega, represents a breakthrough in smart fabric comfort and durability, as well as using a process that is more environmentally friendly.
Hang Liu, a textile researcher at WSU and the corresponding author of the paper, said that the bulk of research in the field so far has focused on building technological functions into fabrics, without attention to the way fabrics might feel, fit, and endure through regular use and maintenance, such as washing.
“The materials used, or the technology used, generally produce very rigid or stiff fabrics,” said Liu, an associate professor in the Department of Apparel, Merchandising, Design and Textiles. “If you are wearing a T-shirt with 3D printed material, for example, for sensing purposes, you want this shirt to fit snugly on your body, and be flexible and soft. If it is stiff, it will not be comfortable and the sensing performance will be compromised.”

Daily mindfulness practice can reduce anxiety for autistic adults
Just 10 to 15 minutes of mindfulness practice a day led to reduced stress and anxiety for autistic adults who participated in a study led by scientists at MIT’s McGovern Institute for Brain Research. Participants in the study used a free smartphone app to guide their practice, giving them the flexibility to practice when and where they chose.
Mindfulness is a state in which the mind is focused only on the present moment. It is a way of thinking that can be cultivated with practice, often through meditation or breathing exercises—and evidence is accumulating that practicing mindfulness has positive effects on mental health. The open-access study, reported April 8 in the journal Mindfulness, adds to that evidence, demonstrating clear benefits for autistic adults.
“Everything you want from this on behalf of somebody you care about happened: reduced reports of anxiety, reduced reports of stress, reduced reports of negative emotions, and increased reports of positive emotions,” says McGovern investigator and MIT Professor John Gabrieli, who led the research with Liron Rozenkrantz, an investigator at the Azrieli Faculty of Medicine at Bar-Ilan University in Israel and a research affiliate in Gabrieli’s lab.

Current biomarkers may be ineffective for evaluating heart failure risk post-pregnancy
Biomarkers used to predict heart failure risk in the general population may be ineffective for assessing risk after pregnancies complicated by hypertension or diabetes, according to a study published in JAMA Cardiology.
Several adverse pregnancy outcomes, including preeclampsia and gestational diabetes, have been linked to long-term heart health risks for pregnant women, said Priya Freaney, MD, ‘22 GME, assistant professor of Medicine in the Division of Cardiology, who was first author of the study.
“We know that features of complicated pregnancies can impact a woman’s heart disease risk decades later,” Freaney said. “It’s important for us to have some way to track and screen the patients that have pregnancy complications to further clarify if someone’s on a high-risk path toward heart disease and help bring their risk down with aggressive screening, prevention or early implementation of therapies.”