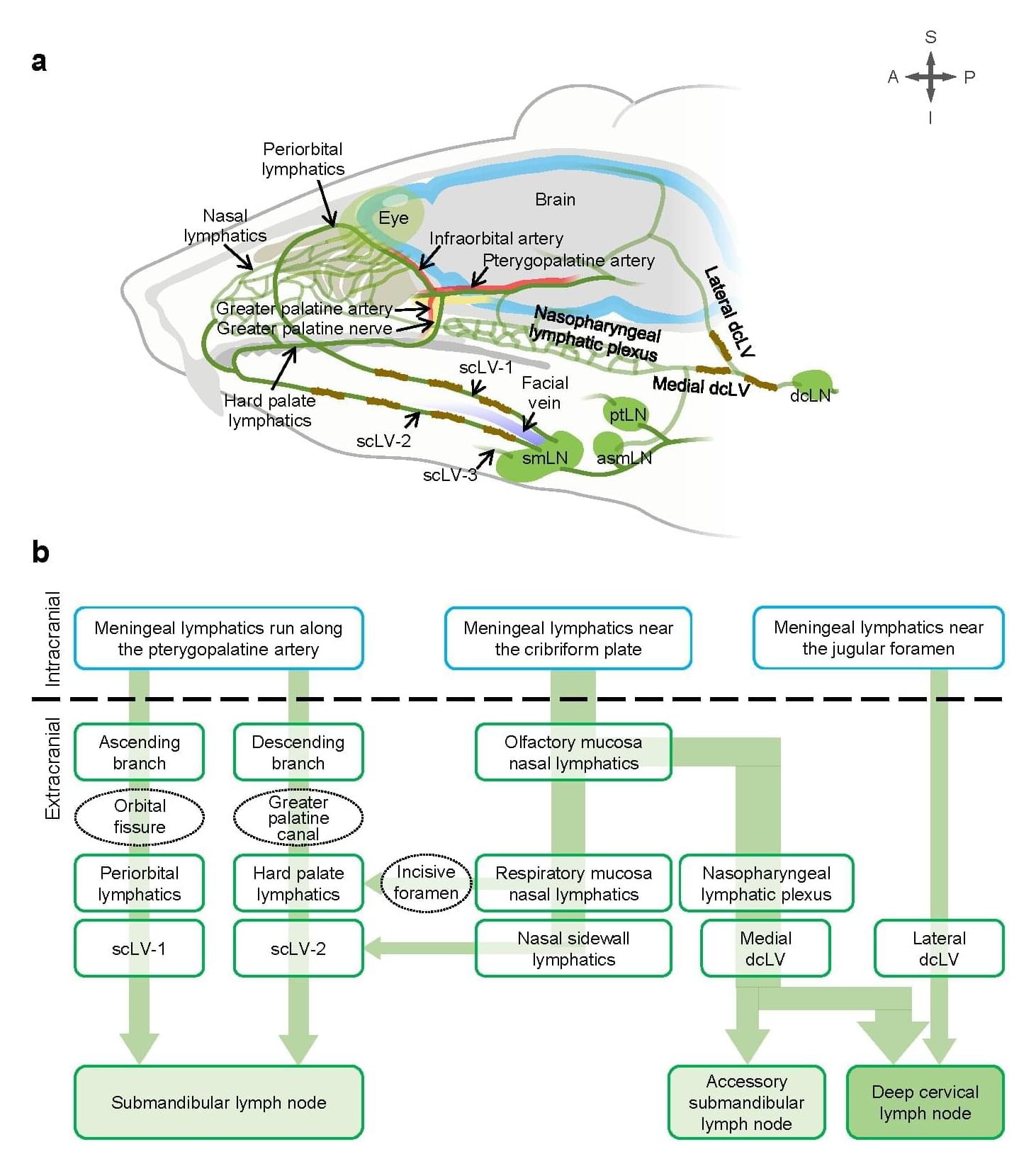
Scientists at the Institute for Basic Science (IBS) have uncovered a non-invasive method to boost the brain’s natural waste drainage system—a discovery that could open new avenues for tackling age-related neurological disorders.
In a study published in Nature, researchers from the IBS Center for Vascular Research, led by Director Koh Gou Young, along with senior researchers Jin Hokyung, Yoon Jin-Hui, and principal researcher Hong Seon Pyo, demonstrate that precisely stimulating the lymphatics under skin on the neck and face can significantly enhance the flow of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)—the liquid that cushions the brain and helps remove toxic waste —through lymphatic vessels.
This offers a new approach to clearing brain waste using safe, non-invasive mechanical stimulation, rather than relying on drugs or surgical interventions.