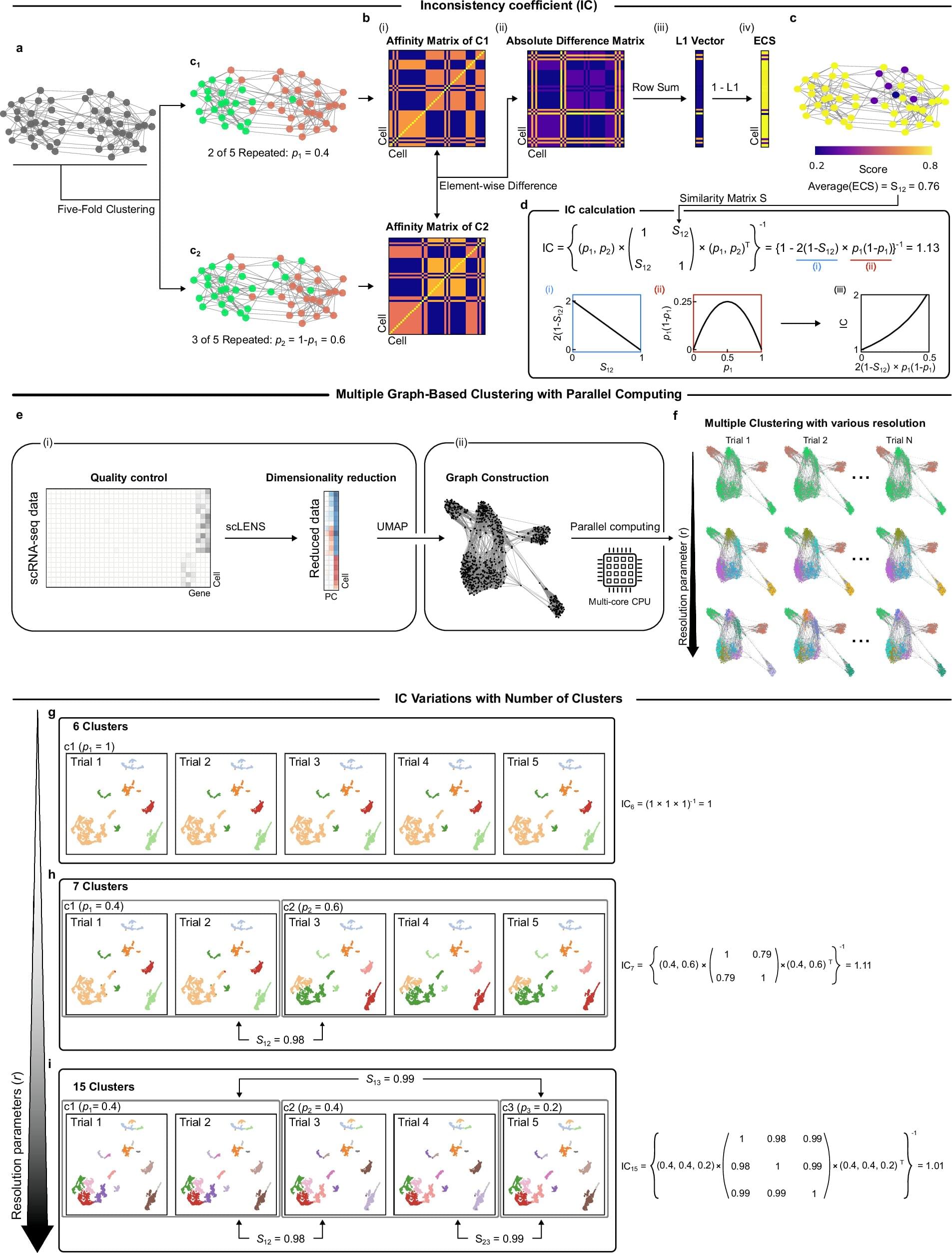
Lung macrophages play a pivotal role in diseases like idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Two types of macrophages—the white blood cells that defend the body by killing microbes, removing dead cells and stimulating immune responses—are found in the lung. They are tissue resident macrophages, which are present from birth, and monocyte-derived macrophages that enter the lungs for a short time in response to damage or infection.
Recently these monocyte-derived alveolar macrophages, or Mo-AMs, were identified as key drivers of lung fibrosis disease progression. However, the mechanisms of their pro-fibrotic behavior and survival in the lungs remained unclear, so clinicians continue to lack effective therapies.
In a study published in the journal Nature Communications, Gang Liu, M.D., Ph.D., Huachun Cui, Ph.D., and their University of Alabama at Birmingham colleagues show that TREM2, a cell surface receptor protein on Mo-AM cells, is a critical regulator of macrophage-mediated lung fibrosis. This makes it a promising therapeutic target for intervention, says Gang, a professor in the UAB Department of Medicine Division of Pulmonary, Allergy and Critical Care Medicine.