The study provides critical new insights into the African Humid Period, a time between 14,500 and 5,000 years ago when the Sahara desert was a green savanna, rich in water bodies that facilitated human habitation and the spread of pastoralism. Later aridification turned this region into the world’s largest desert. Due to the extreme aridity of the region today, DNA preservation is poor, making this pioneering ancient DNA study all the more significant.
Genomic analyses reveal that the ancestry of the Takarkori rock shelter individuals primarily derives from a North African lineage that diverged from sub-Saharan African populations at about the same time as the modern human lineages that spread outside of Africa around 50,000 years ago. The newly described lineage remained isolated, revealing deep genetic continuity in North Africa during the late Ice Age. While this lineage no longer exists in unadmixed form, this ancestry is still a central genetic component of present-day North African people, highlighting their unique heritage.
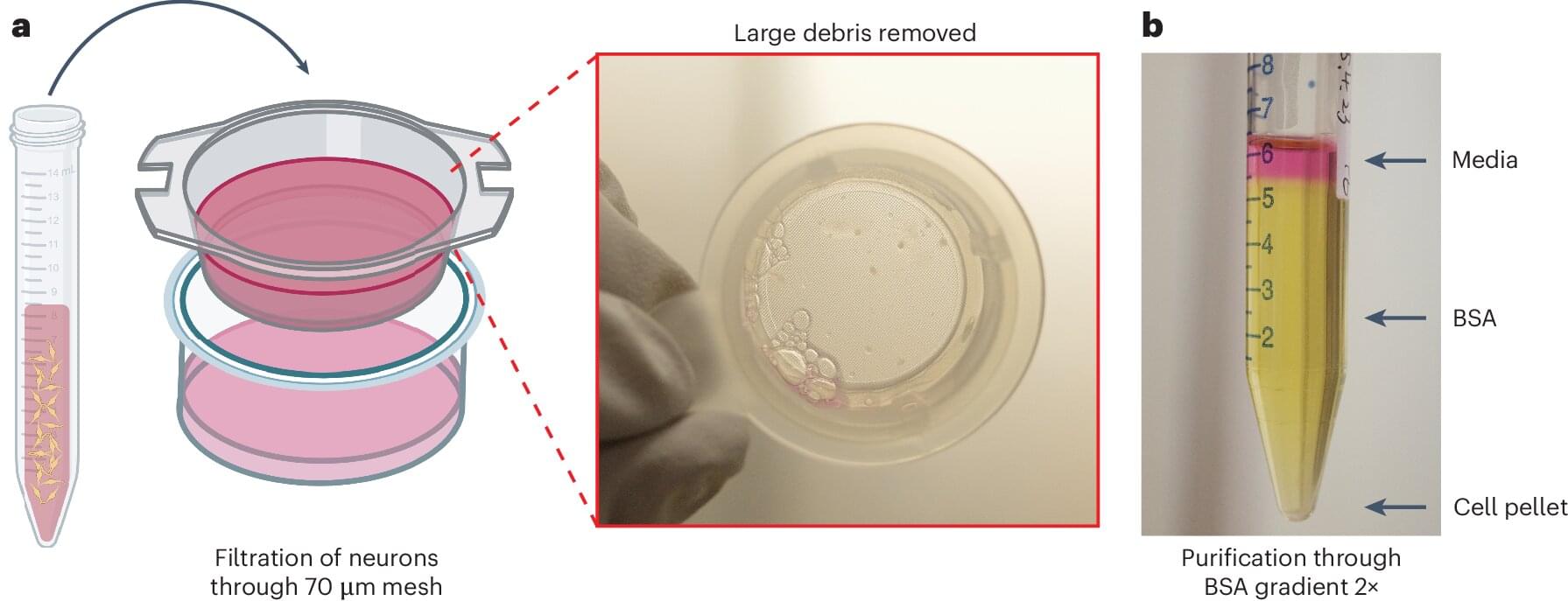
An international team led by researchers from the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology in Leipzig, Germany, has sequenced the first ancient genomes from the so-called Green Sahara, a period when the largest desert in the world temporarily turned into a humid savanna-like environment. By analyzing the DNA of two 7,000-year-old naturally mummified individuals excavated in the Takarkori rock shelter in southwestern Libya by the Archaeological Mission in the Sahara, Sapienza University of Rome, the team showed that they belonged to a long-isolated and now extinct North African human lineage. This group of cattle pastoralists has only a minor genetic component of non-African ancestry, suggesting that animal husbandry may have spread into the Green Sahara through cultural exchange rather than large-scale migrations.