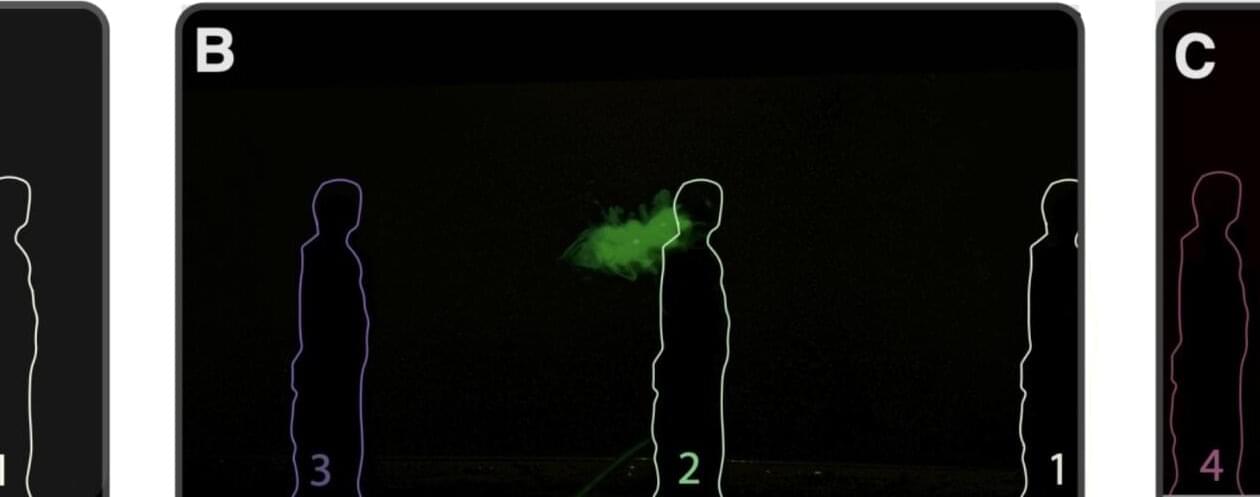
We all remember the advice frequently repeated during the COVID pandemic: maintain six feet of distance from every other human when waiting in a line to avoid transmitting the virus. While reasonable, the advice did not take into account the complicated fluid dynamics governing how the airborne particles actually travel through the air if people are also walking and stopping. Now, a team of researchers led by two undergraduate physics majors at the University of Massachusetts Amherst has modeled how aerosol plumes spread when people are waiting and walking in a line.
The results, published recently in Science Advances, grew out of a question that many of us may have asked ourselves when standing in marked locations six-feet apart while waiting for a vaccine, to pay for groceries or to get a cup of coffee: what’s the science behind six-feet of separation? If you are a physicist, you might even have asked yourself, “What is happening physically to the aerosol plumes we’re all breathing out while waiting in a line, and is the six-foot guideline the best way to design a queue?”
To find answers to these questions, two UMass Amherst undergrads, Ruixi Lou and Milo Van Mooy, took the lead.