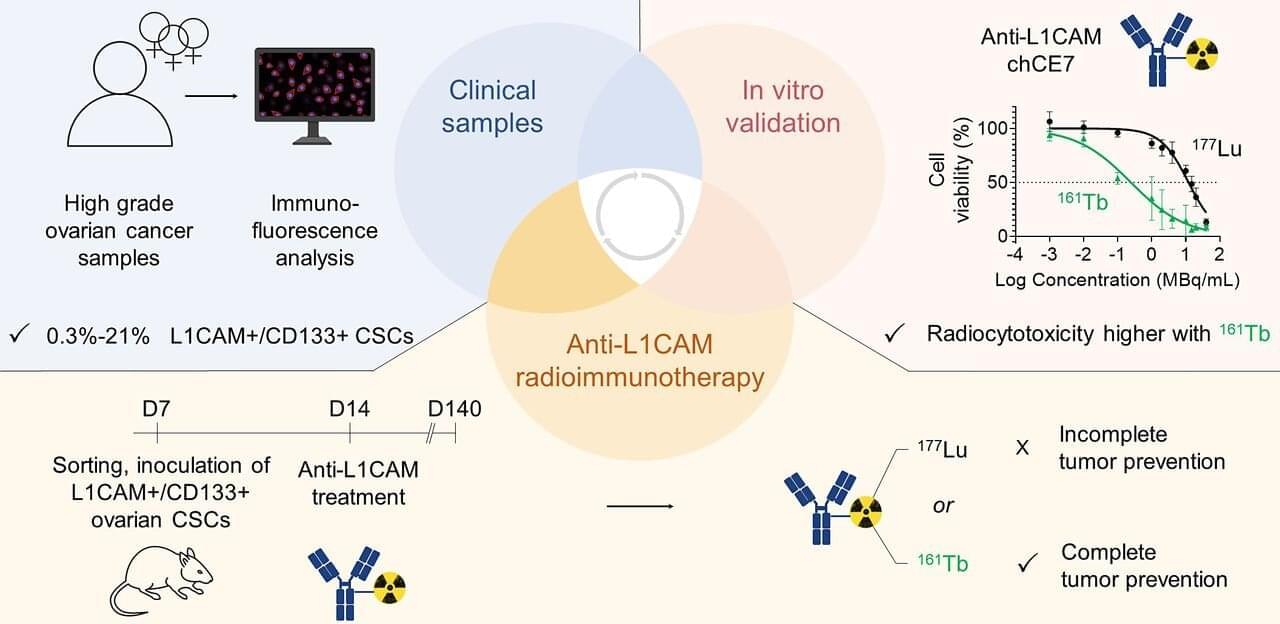
A new artificial intelligence (AI) tool could make it much easier—and cheaper—for doctors and researchers to train medical imaging software, even when only a small number of patient scans are available.
The AI tool improves upon a process called medical image segmentation, where every pixel in an image is labeled based on what it represents—cancerous or normal tissue, for example. This process is often performed by a highly trained expert, and deep learning has shown promise in automating this labor-intensive task.
The big challenge is that deep learning-based methods are data hungry—they require a large amount of pixel-by-pixel annotated images to learn, explained Li Zhang, a Ph.D. student in the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering at the University of California San Diego. Creating such datasets demands expert labor, time and cost. And for many medical conditions and clinical settings, that level of data simply doesn’t exist.