The coronavirus crisis has pushed schooling on to remote platforms. It’s an opportunity to rethink how education should work.

Dr. Duc Vuong, World’s #1 Weight Loss Surgeon, Author of 13 books, explains how coronavirus kills its victims.
Talk with Dr. V Live at https://www.facebook.com/doctorvuong
Your comments are my oxygen, please take a second and say ‘Hi’ in the comments and let me and my team know what you thought of the video … p.s. It would mean the world to me if you hit the subscribe button wink
Do you struggle with Weight Regain? Get DR. V’s FREE 16 Page REPORT “15 Ways To Stop Weight Regain” now. https://www.sleeveacademy.com/regain
Dr. V helps people break through unwanted patterns and start over by teaching them simple, practical life strategies.
This is great information for gastric sleeve, gastric bypass, duodenal switch, minigastric bypass, or any weight loss surgery.
If you like this video, then come learn from Dr. V in person at his next live Weekend Workshop. Click here.
Dr. Duc Vuong is the World’s #1 Weight Loss Surgeon, author of 13 books, and the leading expert in education for the bariatric patient. His particular passion is in helping people break self-limiting cycles and start over again, regardless of the situation. He teaches transformational tools to impact mental, physical, and financial wellness. He believes that everyone can have more because they can be more.
Multiple institutions and medical societies have praised his intensive educational system. As the author of 13 books and several online courses, his aim is to fill the shortage of educational resources for patients who have had or are considering weight loss surgery.
Although trained in Western medicine, he blends traditional Eastern teachings with the latest in science and technology. Dr. Vuong was featured in TLC’s hit show, 900 Pound Man: Race Against Time, and is currently working on his own weekly television show.
Learn more about Dr. V at https://www.DucVuong.com


Many people are turning to Zoom in this time. I suggested my Dad use it for his church…but…Watch Out! After #coronavirus domains, experts find a massive surge in suspicious “Zoom” named domains in the last 7 days, potentially registered by hackers to exploit #Zoom’s overnight success in this pandemic time to spread #malware… #COVID19
Covid-19 impact: hackers begin exploiting zoom’s overnight success to spread malware during coronavirus outbreak with fake domains and websites.

Circa 2018: In January 2017, while one of us was serving as a homeland security advisor to outgoing President Barack Obama, a deadly pandemic was among the scenarios that the outgoing and incoming U.S. Cabinet officials discussed in a daylong exercise that focused on honing interagency coordination and rapid federal response to potential crises. The exercise is an important element of the preparations during transitions between administrations, and it seemed things were off to a good start with a commitment to continuity and a focus on biodefense, preparedness, and the Global Health Security Agenda—an initiative begun by the Obama administration to help build health security capacity in the most critically at-risk countries around the world and to prevent the spread of infectious disease. But that commitment was short-lived.
Deadly diseases like Ebola and the avian flu are only one flight away. The U.S. government must start taking preparedness seriously.
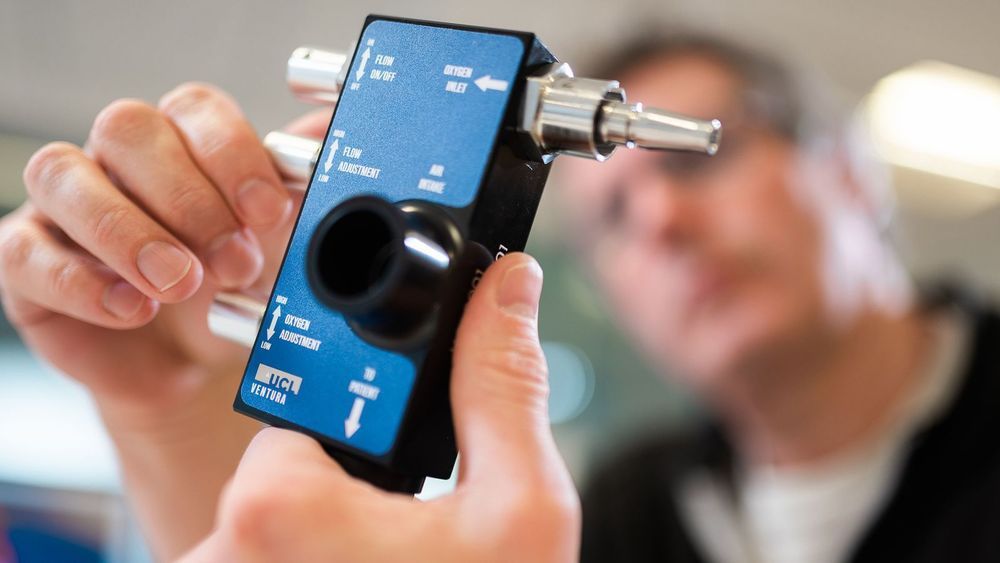


Clinicians and mechanical engineers from University College London (UCL) worked with Mercedes to create the continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) device, which has been approved by the NHS.
The potentially life-saving technology has already been used in China, where coronavirus first emerged in December, and also in hospitals in Italy — the epicentre of the pandemic in Europe. The device helps COVID-19 patients with serious lung infections caused by the disease — such as pneumonia — to breathe more easily, when oxygen alone does not prove sufficient.
Formula One teams are among the British firms joining forces to provide UK hospitals with vital equipment for COVID-19 patients.
Just like any other virus, the coronavirus needs a host to survive. Viruses enter the cells of the human body to cause disease by attaching to a specific receptor site on the host cell membrane. To do this, they attach to proteins in the capsid through glycoproteins found in the envelope of the virus.
Now, infection biologists form the German Primate Center — Leibniz Institute for Primate Research in Göttingen, together with colleagues at Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, have found how the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 penetrates the cells.
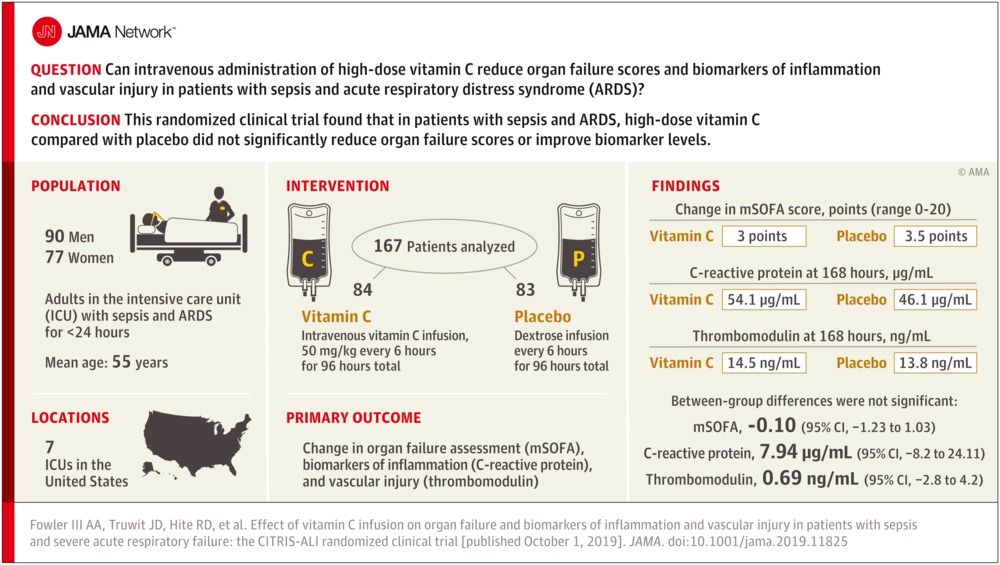
Can intravenous administration of high-dose vitamin C reduce organ failure scores and biomarkers of inflammation and vascular injury among patients with sepsis and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)?
This randomized clinical trial compares the effects of treatment with intravenous vitamin C, hydrocortisone, and thiamine compared with intravenous hydrocortisone alone on duration of time alive and free of vasopressor use over 7 days in patients with septic shock.
Tomoko Fujii, MD, PhD; Nora Luethi, MD; Paul J. Young, MBChB, PhD; Daniel R. Frei, BSc, MBChB; Glenn M. Eastwood, PhD; Craig J. French, MB, BS; Adam M. Deane, MB, BS, PhD; Yahya Shehabi, MB, BS, PhD; Ludhmila A. Hajjar, MD, PhD; Gisele Oliveira, MD; Andrew A. Udy, MBChB, PhD; Neil Orford, MB, BS, PhD; Samantha J. Edney, BSN; Anna L. Hunt, BN, PGDipHSM, PGDipClinRes; Harriet L. Judd, BSN, PGDipHC; Laurent Bitker, MD; Luca Cioccari, MD; Thummaporn Naorungroj, MD; Fumitaka Yanase, MD; Samantha Bates, BN, PGDipCritCare; Forbes McGain, MB, BS, PhD; Elizabeth P. Hudson, MD; Wisam Al-Bassam, MBChB; Dhiraj Bhatia Dwivedi, BScNsg, MBA; Chloe Peppin, BN, PGDipCritCare; Phoebe McCracken, MPH; Judit Orosz, MD; Michael Bailey, PhD; Rinaldo Bellomo, MD, PhD; for the VITAMINS Trial Investigators.
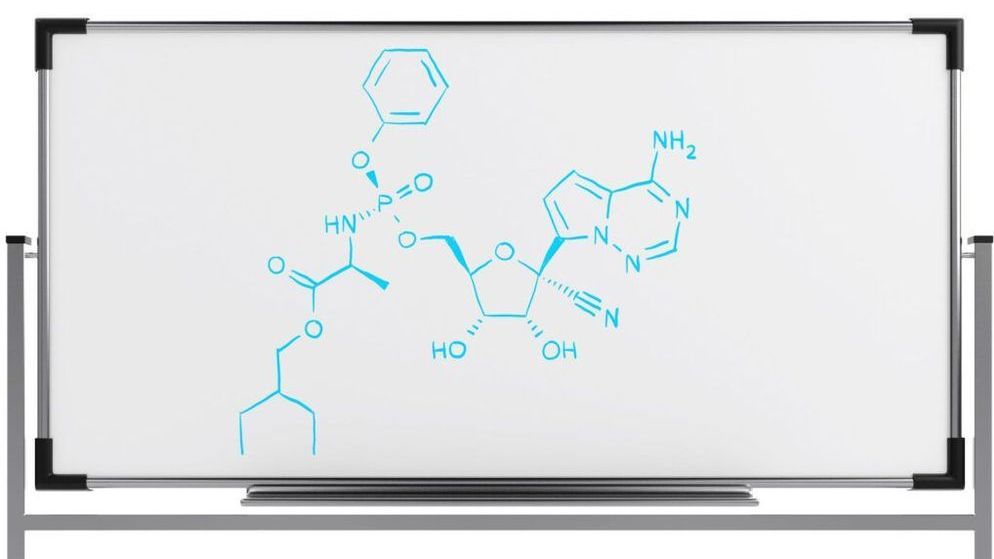
Now, the descendant of that molecule — Gilead Sciences’ remdesivir — is being rushed to patients with infections from the novel coronavirus in hopes that it can reduce the intensity and duration of Covid-19 and ease the burden of the pandemic on health systems.
Remdesivir is now in the spotlight as scientists and governments scramble to hasten patients’ recovery and ease the pandemic’s burden on health systems.