An article about Jacob Gunn Glanville and team’s work.
As scientists race to create a vaccine, a parallel quest to engineer effective antibody treatments for the coronavirus is vital, too—and may provide relief sooner.


A new weapon in the arsenal against the coronavirus may be sitting in your home entertainment console. A team led by physicist Chris Barty of the University of California, Irvine is researching the use of diodes from Blu-ray digital video disc devices as deep-ultraviolet laser photon sources to rapidly disinfect surfaces and the indoor air that swirls around us.
Barty, UC Irvine distinguished professor of physics & astronomy, said that such UV light sterilizers would be cheap compared to current medical- and scientific-grade systems and that it’d be possible to deploy them almost anywhere.
“If these sources are successful, I think you could build them into a mask and clean the air that’s coming in and out of you,” he said. “Or you could set these things up in the air circulation ducts of major buildings, and the airflow that goes through could be sterilized.”
More than 100 teams around the world are racing to develop a coronavirus vaccine. Dr. Ofer Levy and a group of Harvard Medical School researchers are among them, but the vaccine they’re working on is a little different. It’s specifically designed for those most vulnerable to the disease: the elderly.
“Most vaccines are developed with a one-size-fits-all concept,” Levy told Business Insider. “Academic centers and companies typically develop a vaccine assuming that you will respond to the vaccine the same way, whether you’re a man or a woman, whether you’re young or elderly, whether you live in the US or Africa, whether you give the vaccine in the summer or winter, whether you give it in the morning or the evening.”
Vaccines generally aren’t as effective for the elderly. A Harvard lab is working on a COVID-19 vaccine that would be most effective for them.
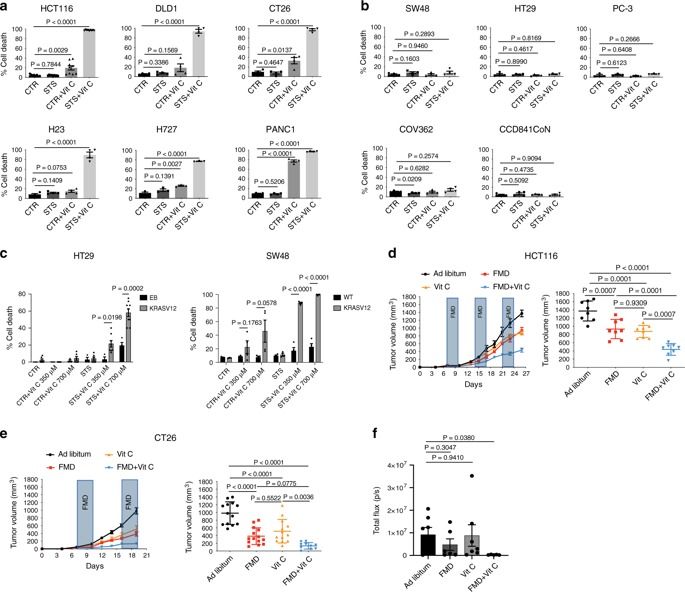
Fasting-mimicking diets delay tumor progression and sensitize a wide range of tumors to chemotherapy, but their therapeutic potential in combination with non-cytotoxic compounds is poorly understood. Here we show that vitamin C anticancer activity is limited by the up-regulation of the stress-inducible protein heme-oxygenase-1. The fasting-mimicking diet selectivity reverses vitamin C-induced up-regulation of heme-oxygenase-1 and ferritin in KRAS-mutant cancer cells, consequently increasing reactive iron, oxygen species, and cell death; an effect further potentiated by chemotherapy. In support of a potential role of ferritin in colorectal cancer progression, an analysis of The Cancer Genome Atlas Database indicates that KRAS mutated colorectal cancer patients with low intratumor ferritin mRNA levels display longer 3- and 5-year overall survival. Collectively, our data indicate that the combination of a fasting-mimicking diet and vitamin C represents a promising low toxicity intervention to be tested in randomized clinical trials against colorectal cancer and possibly other KRAS mutated tumors.

Three critically ill patients at Baptist Hospital in Miami were the first in the U.S. to be successfully treated with stem cells.
The patients were suffering from acute respiratory distress syndrome, or ARDS, and doctors infused them intravenously with cells derived from the lining of umbilical cords.
These are called mesenchymal stem cells and within days after the infusion, the patients who needed 100% oxygen on ventilator support, saw their requirement slashed in half. This significant reduction was also accompanied by a drop in inflammatory markers, meaning that the harmful inflammation crippling the lungs was not only arrested but reversed, according to Baptist Health South
DNA damage is common to our cells, but when we’re young our bodies can fix it pretty easily. Unfortunately we lose that ability over time, leading to many of the symptoms of aging that we know all too well. A new study from MIT has found that reactivating a certain enzyme improves repair of DNA damage in neurons, which helps Alzheimer’s patients and others with cognitive decline.
Previous studies by the team have shown that an enzyme called HDAC1 seems to be involved in DNA repair in neurons. For the new study, the researchers examined what happens when HDAC1 doesn’t do its job.
The team engineered mice to be deficient in HDAC1, and monitored their health compared to normal mice. Things looked good during the animals’ youth – there were no differences in DNA damage or behavior between the two groups. But as they aged, the decline became clear.
If you’re interested in superlongevity and superintelligence, then I have a book to recommend., by Sonia Contera, is a book about the intersection of biotech and nanotech. Interesting and well written for the layman, the book covers some of the latest developments in nanotechnology as it applies to biological matters. Although there are many topics, I was primarily interested in the DNA nanobots, DNA origami, and the protein nanotechnology sections. My interest is piqued in these arenas due to my expectation that DNA nanobots and protein nanobots, as well as complex self-assembled custom nanostructures, are going to be key to some of the longevity technologies and some of the possible substrates for mind uploading that are key to superlongevity and superintelligence. There are also sections in the book on 3D bioprinted organs — progress and possibilities, as well as difficulties.
There is even a section that clearly was written specifically to address a discussion that has engaged my friends, Dinorah Delfin and Dan Faggella. The title is:
FUTURE DEVICES: QUANTUM PHYSICS MEETS BIOLOGY MEETS NANOTECHNOLOGY
Now, some might be tempted to consider that particular combination to be “woo woo”, however, please keep in mind the author’s credentials. Sonia Contera is a professor of biological physics in the Department of Physics at the University of Oxford.
Increasingly, scientists are gaining control over matter at the nanometer scale. Spearheaded by physical scientists operating at the interfaces of physics and biology, advances in nanoscience and technology are transforming how people think about life and treat human health.

A United Arab Emirates research institute has developed a coronavirus treatment using stem cells “which could be a game-changer in the global fight” against the outbreak, a government official announced on Friday.
Read the latest coronavirus updates in our dedicated section.
The Abu Dhabi Stem Cell Center has developed a treatment method that regenerates lung cells and prevents the immune system from overreacting, Hend Al Otaiba, Director of Strategic Communications with the Ministry of Foreign Affairs, said in a Twitter thread.

The director of our institute, Sir Paul Nurse, borrowed another wartime analogy when he imagined academic labs as a flotilla of ‘little ships’, as at Dunkirk, that could be set up quickly to help rescue a rather desperate situation. The protocols we’ve developed have been downloaded more than 5,000 times, and we’ve helped other testing laboratories (including the big ones that are now coming online) with re-agents and scientific advice. We’ve been able to get recovering doctors and nurses back to work quicker, and crucially we’ve been able to identify healthcare workers who may have been spreading the virus unwittingly to the most vulnerable.
The team at the Crick is extremely multi-national. Wartime analogies are not helpful when they promote national exceptionalism, still less when they imply an individual battle between patient and virus. They are helpful when it comes to getting people to think clearly and act swiftly. The frustration when we’ve run up against what might be politely described as ‘NHS bureaucracy’ has been intense. When we’ve dealt with local NHS partners who are determined and dynamic, we’ve been able to save lives. In this sense there really is a war on, and for once I’m happy to see politicians treat it in this way.
We will win this war through immunity. Understanding immunity to respiratory viruses is really difficult — more like decoding Enigma than developing radar. We will need new technology as well as optimising existing tests. So far, the best tests can give a reasonable estimate of whether someone has been exposed to the virus. They cannot yet tell you if you are immune to it. The trouble with coronaviruses is that they have evolved to evade immunity. They possess all sorts of unknown weaponry that dampens down our immune responses.