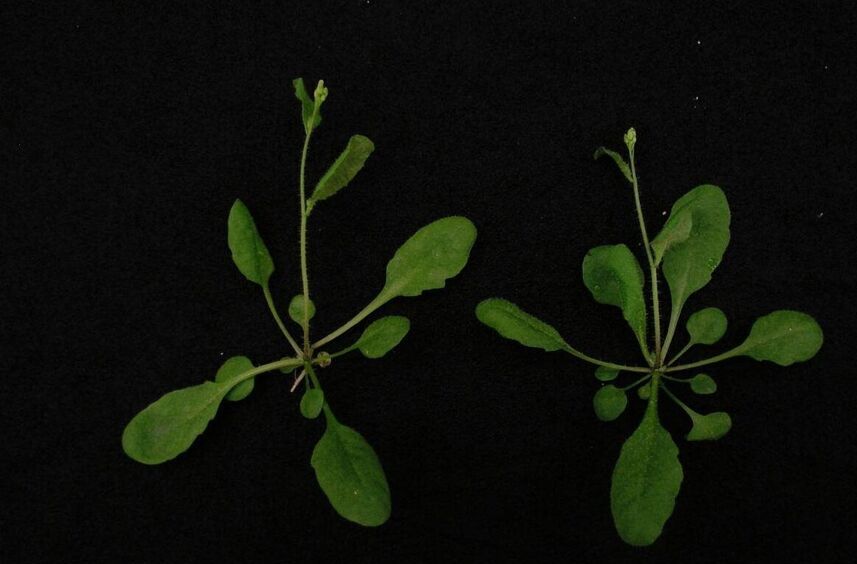
For the first time, CRISPR-Cas9-based gene drive technology has been developed in plants. Enabling the inheritance of both copies of a target gene from a single parent could greatly reduce the generations needed for plant breeding. Establishing this genome editing technology in plants may allow for breeding resilient crops that are better able to withstand drought and disease.
#GenomeEditing #AgBio #CRISPR #Cas9
Gene drives have been established in insects, including fruit flies and mosquitoes, and mammals such as mice. Now, for the first time, the CRISPR-Cas9-based technology that disrupts Mendelian inheritance and allows for selective acquisition of target genes has been developed in plants. Establishing this genome editing technology in plants may allow for breeding resilient crops that are better able to withstand drought and disease.
The research is published in Nature Communications in the paper, “Selective inheritance of target genes from only one parent of sexually reproduced F1 progeny in Arabidopsis.”
“This work defies the genetic constraints of sexual reproduction that an offspring inherits 50% of their genetic materials from each parent,” said Yunde Zhao, PhD, professor of cell and developmental biology at the University of California, San Diego (UCSD). “This work enables inheritance of both copies of the desired genes from only a single parent. The findings can greatly reduce the generations needed for plant breeding.”