Researchers at La Jolla Institute for Immunology (LJI) have demonstrated how cancer-fighting T cells can be engineered to clear tumors without succumbing to T cell exhaustion, a phenomenon that results in T cells giving up the antitumor fight after prolonged periods of overactivity. The newly reported findings demonstrated the key role of the transcription factor BATF in the cellular pathway that triggers T cell exhaustion, and showed how increasing levels of BATF in these cells boosts their cancer-fighting ability, with the help of another transcription factor IRF4. The results suggest a potential approach to increasing the effectiveness of CAR T cell-based immunotherapy against tumors, which is important because T cell exhaustion plagues even the most cutting-edge cancer immunotherapies.
“The idea is to give the cells a little bit of armor against the exhaustion program,” said LJI professor Patrick Hogan, PhD. “The cells can go into the tumor to do their job, and then they can stick around as memory cells.” The LJI team, headed by Hogan and LJI professor Anjana Rao, PhD, report on their studies in Nature Immunology, in a paper titled, “BATF and IRF4 cooperate to counter exhaustion in tumor-infiltrating CAR T cells.”
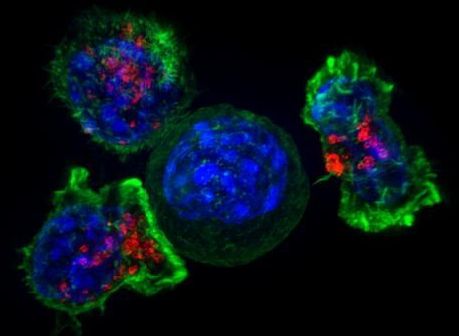
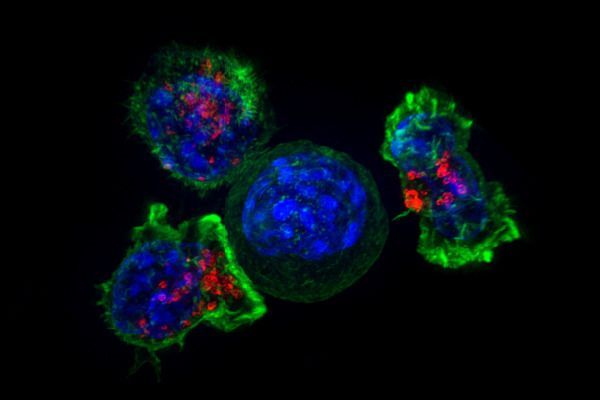
Fighting a tumor is a marathon, not a sprint. For cancer-fighting CD8+ T cells, the race is sometimes just too long, and they quite fighting. “CD8+ T cells that encounter antigen together with effective costimulatory signals mount strong effector responses that are able to clear pathogen-infected cells and tumor cells,” the team wrote. “In contrast, CD8+ T cells that infiltrate solid tumors and are exposed to prolonged antigen stimulation in the absence of adequate costimulation enter a hyporesponsive (exhausted or dysfunctional) state in which they do not effectively destroy tumor cells.”