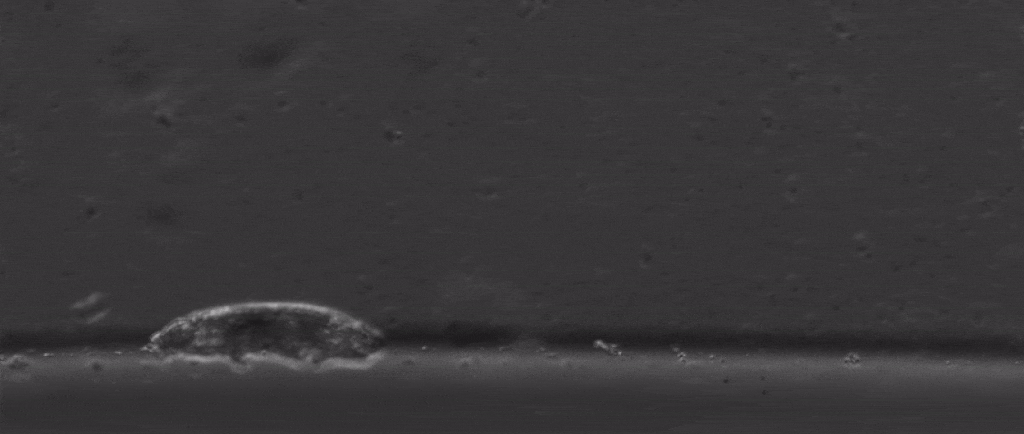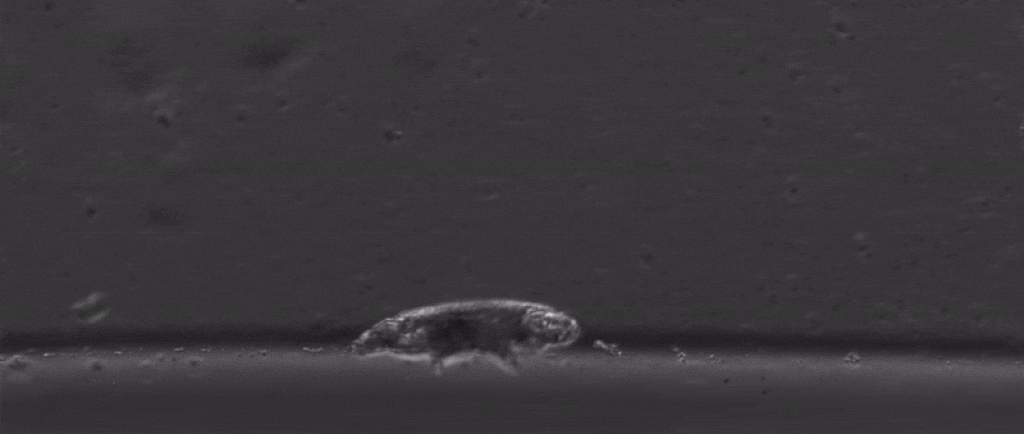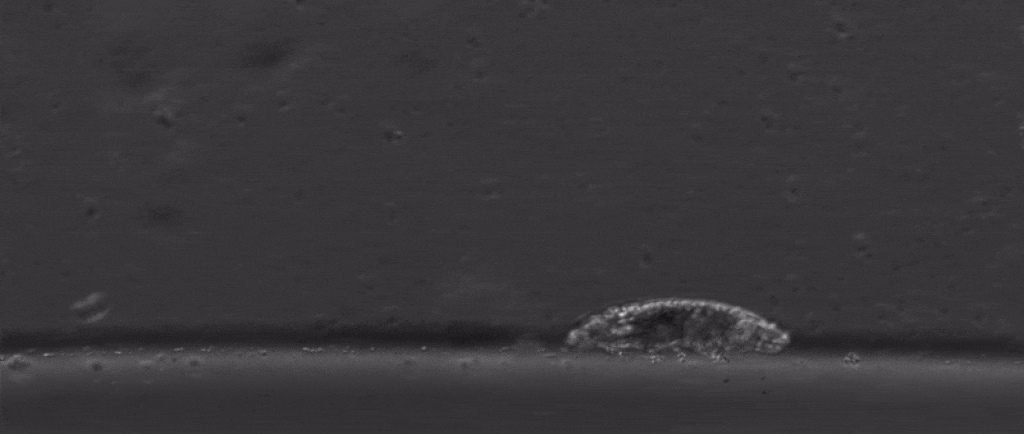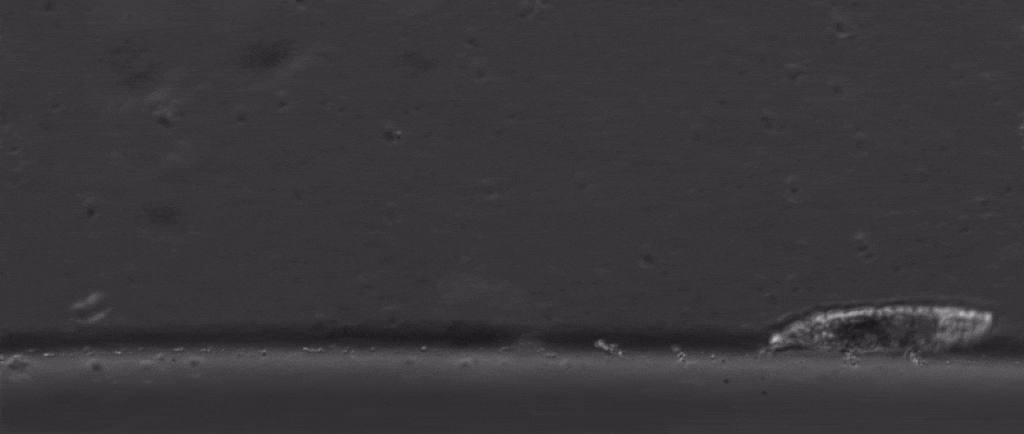
Tardigrades are undoubtedly weird. Dehydrate them into glass, then fire them out of a gun, and once you rehydrate them you can still have a living creature. Their outsides aren’t the only thing that’s tough either, with scientists finding last year that they also have special DNA armor proteins.
But if we take a step back from their immense capacity for being beaten up, there are many other mysterious things about them. For starters, how do these tiny creatures walk?
After all, they’re one of the only animals with soft little bodies like this that can walk, plus they’re one of the smallest animals with legs that we know of.