SENS Research Foundation works to develop, promote, and ensure widespread access to therapies that cure and prevent the diseases and disabilities of aging by comprehensively repairing the damage that builds up in our bodies over time.
Category: biotech/medical – Page 178

Stress genes clear dead cells, offering new disease insights
A new study from The University of Texas at Arlington details a novel strategy for how the body clears out dead cells during stress, revealing unexpected roles for well-known stress-response genes—a discovery that could help scientists better understand diseases affecting the immune system, brain and metabolism.
“The body is constantly creating new cells and removing old cells once they die,” said Aladin Elkhalil, lead author of the study and a third-year doctoral student in the lab of Piya Ghose, assistant professor of biology at UT Arlington. “This removal of dead cells is just as important as creating new ones, because if the body is unable to rid itself of dead cells, it can lead to various health problems”
Published in PLOS Genetics, the study was conducted on the roundworm C. elegans by Dr. Ghose, Elkhalil and Alec Whited, another graduate student in the Ghose lab. This tiny, transparent organism is a widely used tool in genetic research because its see-through body allows scientists to observe live cell behavior, including how cells die. The research team took advantage of these unique features in several innovative ways.


HKUST Scientists Achieve Breakthrough in Light Manipulation Using Gyromagnetic Zero-Index Metamaterials
The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST)-led research team has adopted gyromagnetic double-zero-index metamaterials (GDZIMs) — a new optical extreme-parameter material – and developed a groundbreaking method to control light using GDZIMs. This discovery could revolutionize fields like optical communications, biomedical imaging, and nanotechnology, enabling advances in integrated photonic chips, high-fidelity optical communication, and quantum light sources.
Published in Nature, the study was co-led by Prof. CHAN Che-Ting, Interim Director of the HKUST Jockey Club Institute for Advanced Study and Chair Professor in the Department of Physics, and Dr. ZHANG Ruoyang, Visiting Scholar in the Department of Physics at HKUST.
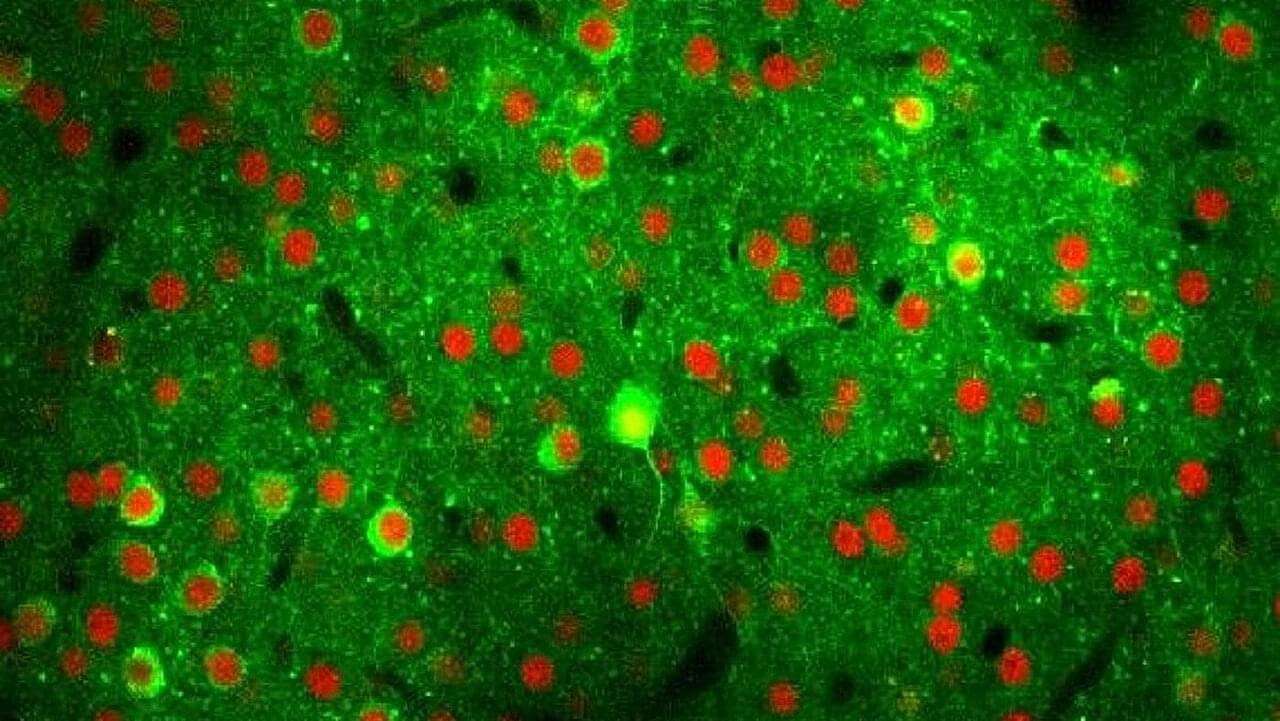
Neighborly help in the brain: Cerebral cortex networks rapidly reorganize to compensate for lost neurons
How the brain largely maintains its function when neurons are lost—this is what researchers at the University Medical Center Mainz, the Frankfurt Institute for Advanced Studies (FIAS) and Hebrew University (Jerusalem) have deciphered. They show that neuronal networks in the cerebral cortex reorganize within a short period of time, with other nerve cells taking over the tasks of the lost neurons.
These findings could form the basis for future research into natural aging processes and neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s or Parkinson’s. The study is published in the journal Nature Neuroscience.
Nerve cells (neurons) are the most important building blocks of the brain. They form the basis for all mental and physical functions such as thinking, feeling, movement, and perception. In the course of life, nerve cells in the brain can be lost for various reasons: They die off due to age-related processes, are damaged by toxins such as alcohol, or neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s lead to a more rapid progressive loss of neurons.

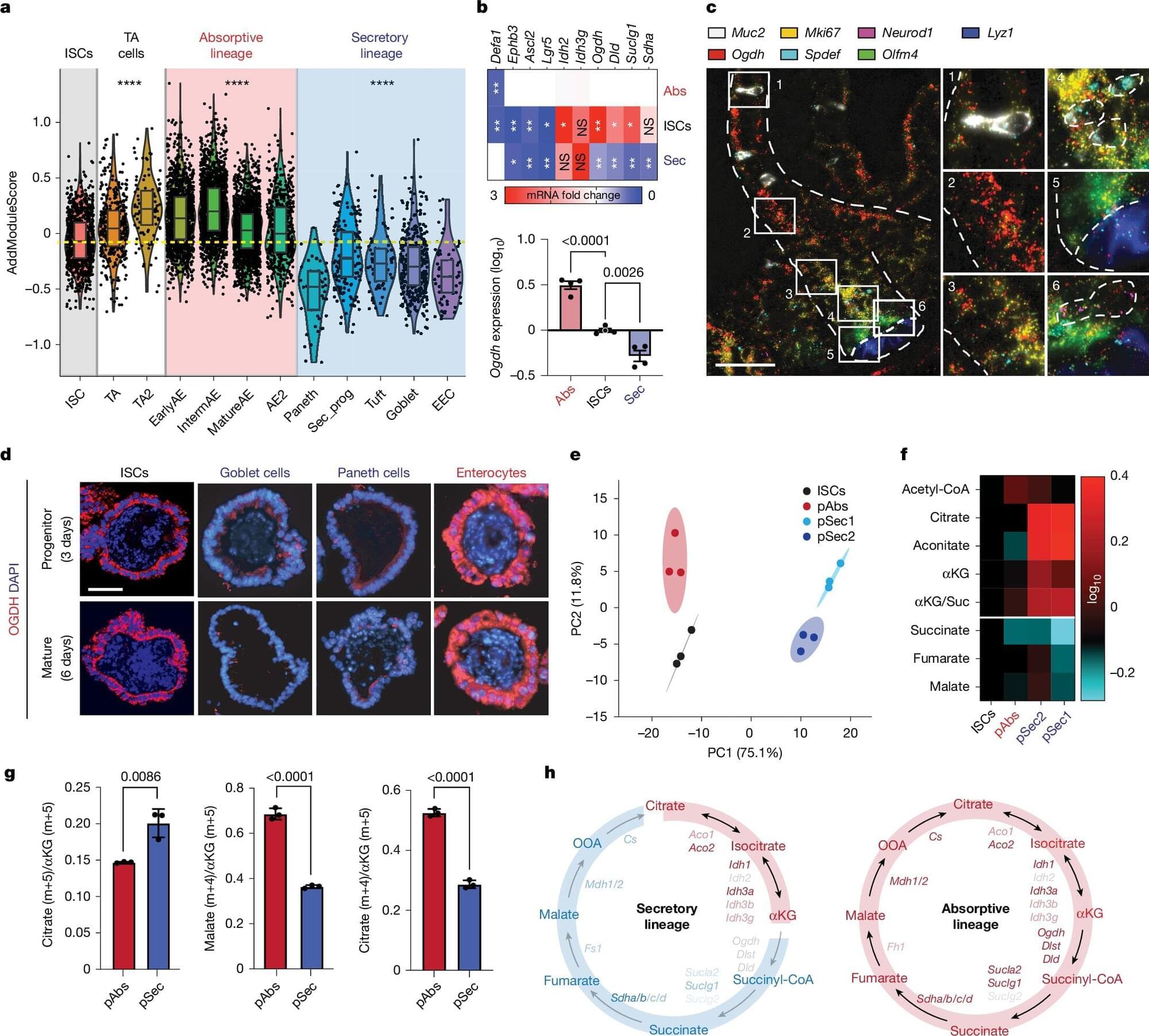
A single enzymatic switch steers cell fate in intestinal regeneration
Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center researchers have identified a metabolic switch that determines whether intestinal stem cells become absorptive or secretory cells. Manipulating the enzyme OGDH either fuels cell expansion or redirects fate, with potential consequences for colitis recovery and regenerative therapy.
Stem cells in the intestine maintain a delicate balance between self-renewal and differentiation, continuously replenishing the epithelial lining of the gut.
As they divide, some daughter cells become absorptive enterocytes that expand the surface for nutrient uptake, while others branch into secretory cells that manufacture mucus, antimicrobial peptides, and hormones essential for gut immunity. Injury and inflammation can tip this balance, depleting secretory lineages and disrupting tissue integrity.
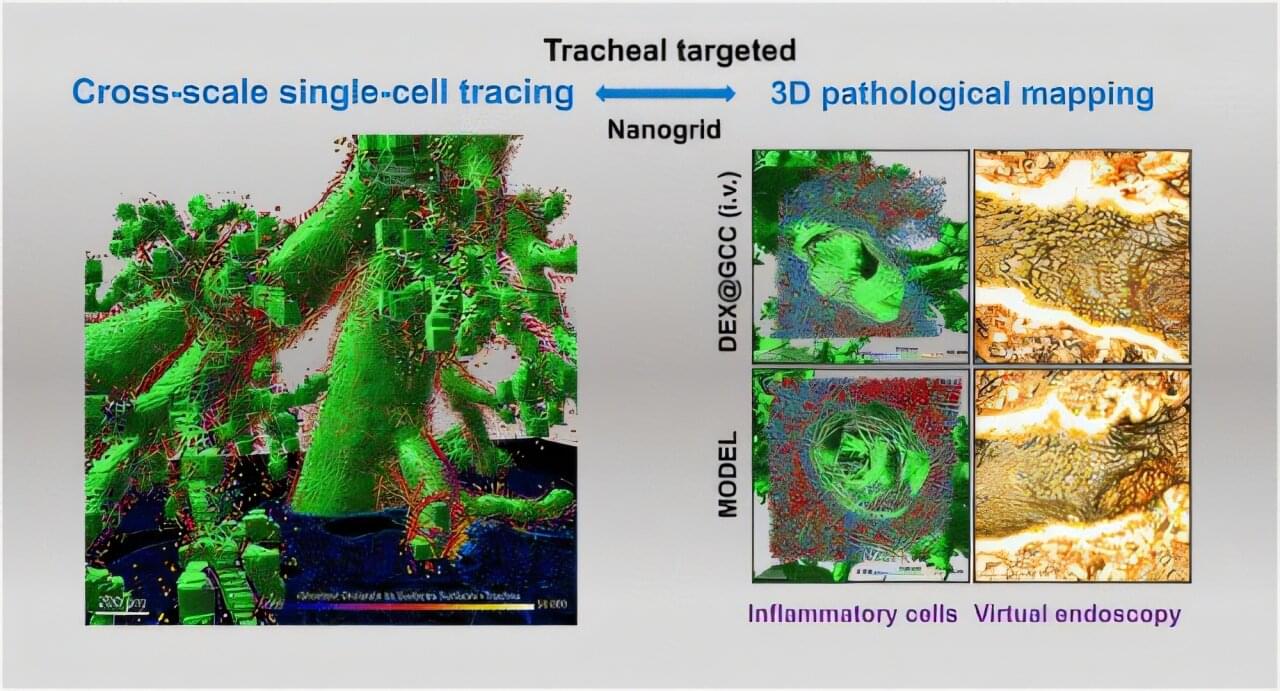
Nanogrid drug delivery systems developed for precise lung inflammation treatment
Understanding how drug delivery systems distribute in vivo remains a major challenge in developing nanomedicines. Especially in the lung, the complex and dynamic microenvironment often limits the effectiveness of existing approaches.
“Structural pharmaceutics” has been introduced as a new strategy to connect nanoparticle structures with physiological structures through advanced three-dimensional (3D) imaging and cross-scale characterizations.
In a study published in ACS Nano, a team led by Yin Xianzhen from the Lingang Laboratory and Zhang Jiwen from the Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica of the Chinese Academy of Sciences developed a precise targeting strategy for tracheal inflammation.