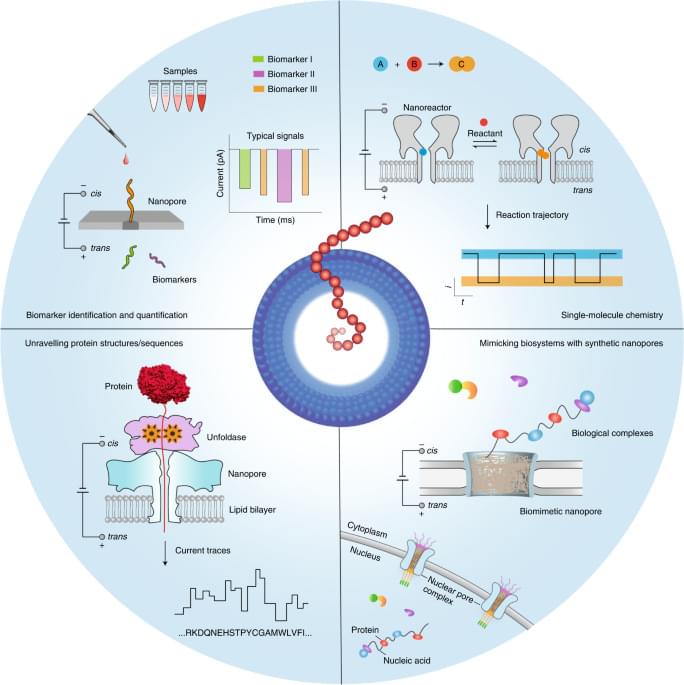
Ideally, the nanopore dimensions should be comparable to those of the analyte for the presence of the analyte to produce a measurable change in the ionic current amplitude above the noise level. Nanopores can be formed in several ways, with a wide range of pore diameters. Biological nanopores are formed by the self-assembly of either protein subunits, peptides or even DNA scaffolds in lipid bilayers or block copolymer membranes1,3,6,17,18. They possess atomically precise dimensions controlled by biopolymer sequences, providing the ability to recognize biomolecules with constriction diameters of ~1–10 nm. Solid-state nanopores are crafted in thin inorganic or plastic membranes (for example, SiNx), which allows the nanopores to have extended diameters of up to hundreds of nanometres, permitting the entry or analysis of large biomolecules and complexes. The tools for fabricating solid-state nanopores, which include electron/ion milling4,5, laser-based optical etching19,20 and the dielectric breakdown of ultrathin solid membranes21,22, can be used to manipulate nanopore size at the nanometre scale, but allow only limited control over the surface structure at the atomic level in contrast to biological nanopores. The chemical modification and genetic engineering of biological nanopores, or the introduction of biomolecules to functionalize solid-state nanopores23, can further enhance the interactions between a nanopore and analytes, improving the overall sensitivity and selectivity of the device2,17,24,25,26. This feature allows nanopores to controllably capture, identify and transport a wide variety of molecules and ions from bulk solution.
Nanopore technology was initially developed for the practicable stochastic sensing of ions and small molecules2,27,28. Subsequently, many developmental efforts were focused on DNA sequencing1,7,8,9. Now, however, nanopore applications extend well beyond sequencing, as the methodology has been adapted to analyse molecular heterogeneities and stochastic processes in many different biochemical systems (Fig. 1). First, a key advantage of nanopores lies in their ability to successively capture many single molecules one after the other at a relatively high rate, which allows nanopores to explore large populations of molecules at the single-molecule level in reasonable timeframes. Second, nanopores essentially convert the structural and chemical properties of the analytes into a measurable ionic current signal, even achieving enantiomer discrimination29. The technology can be used to report on multiple molecular features while circumventing the need for labelling chemistries, which may complicate the overall analysis process and affect the molecular structures. For example, nanopores can discriminate nearly 13 different amino acids in a label-free manner, including some with minute structural differences30. An important aspect is the ability of nanopores to identify species31 that lack suitable labels for signal amplification or whose information is hidden in the noise of analytical devices. Consequently, nanopores may serve well in molecular diagnostic applications required for precision medicine, which achieves the identification of nucleic acid, protein or metabolite analytes and other biomarkers11,32,33,34,35. Third, nanopores provide a well-defined scaffold for controllably designing and constructing biomimetic systems, which involve a complex network of biomolecular interactions. These nanopore systems track the binding dynamics of transported biomolecules as they interact with nanopore surfaces, hence serving as a platform for unravelling complex biological processes (for example, the transport properties of nuclear pore complexes)36,37,38,39. Fourth, chemical groups can be spatially aligned within a protein nanopore, providing a confined chemical environment for site-selective or regioselective covalent chemistry. This strategy has been used to engineer protein nanoreactors to monitor bond-breaking and bond-making events40,41.
Here we discuss the latest advances in nanopore technologies beyond DNA sequencing and the future trajectory of the field, as well as the opportunities and main challenges for the next decade. We specifically address the emerging nanopore methods for protein analysis and protein sequencing, single-molecule covalent chemistry, single-molecule analysis of clinical samples and insights into the use of biomimetic pores for analysing complex biological processes.