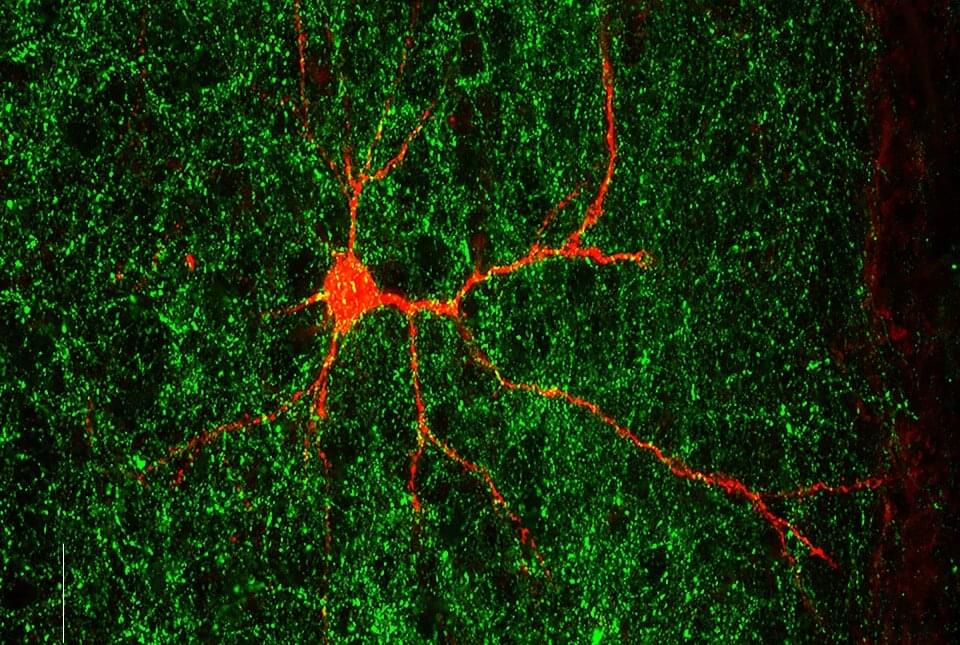
A gene linked to autism spectrum disorders plays a critical role in early brain development and may shape the formation of both normal and atypical nerve connections in the brain, according to a new study by Weill Cornell Medicine investigators.
The study, published Nov. 28 in Neuron, employed a combination of sophisticated genetic experiments in mice and analysis of human brain imaging data to better understand why mutations in a gene called Gabrb3 are linked to a high risk of developing autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and a related condition called Angelman Syndrome. Both conditions involve abnormal behaviors and unusual responses to sensory stimuli, which appear to stem, at least in part, from the formation of atypical connections between neurons in the brain.
“Neuron al connections in the brain, and developmental synchronization of neuronal networks, are perturbed in individuals with autism spectrum disorders, and there are specific genes that are implicated in the pathogenesis of ASD,” said co-first author Dr. Rachel Babij, a former student in the Weill Cornell/Rockefeller/Sloan Kettering Tri-Institutional MD-Ph. D. program in the laboratory of Natalia De Marco García, an associate professor in the Feil Family Brain and Mind Research Institute at Weill Cornell Medicine.