Though women live longer than men on average, “we’re suffering longer,” says Dr. Vonda Wright. Here’s what she suggests for healthy aging in women.



Discover the world’s best science and medicine | Nature.com

Batteries, like humans, require medicine to function at their best. In battery technology, this medicine comes in the form of electrolyte additives, which enhance performance by forming stable interfaces, lowering resistance and boosting energy capacity, resulting in improved efficiency and longevity.
Finding the right electrolyte additive for a battery is much like prescribing the right medicine. With hundreds of possibilities to consider, identifying the best additive for each battery is a challenge due to the vast number of possibilities and the time-consuming nature of traditional experimental methods.
Researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory are using machine learning models to analyze known electrolyte additives and predict combinations that could improve battery performance. They trained models to forecast key battery metrics, like resistance and energy capacity, and applied these models to suggest new additive combinations for testing.
World’s first pig lung transplant in brain-dead man lasts nine days in China.
In a medical first, a pig lung was transplanted into a brain-dead human, where it functioned for nine days.
Surgeons at Guangzhou Medical University, China, performed the cross-species lung transplantation.
The recipient, a 39-year-old man who had suffered a brain hemorrhage, received the left lung from a Chinese Bama Xiang pig that had undergone genetic modifications.
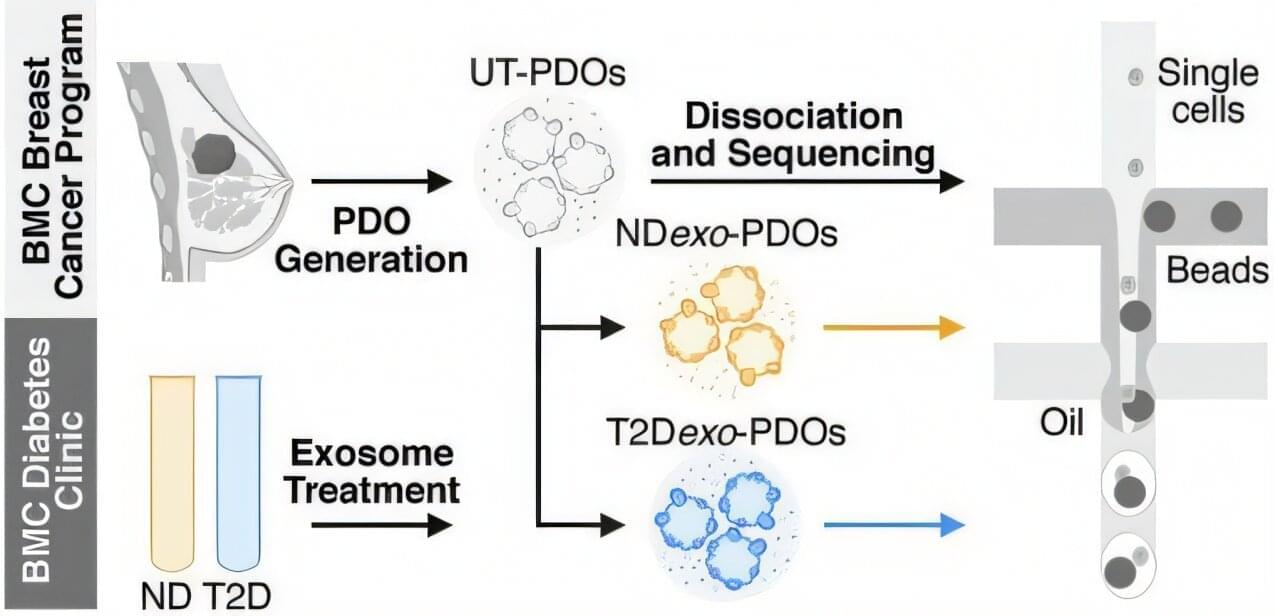
People with type 2 obesity-driven diabetes tend to have more aggressive breast cancers, but no one knows exactly why. A new study by researchers at Boston University Chobanian & Avedisian School of Medicine and published in Communications Biology found that tiny particles in the blood, known as exosomes, which are altered by diabetes, can reprogram immune cells inside tumors, making them weaker and allowing the cancer to grow and spread more easily.
“This is the first study to directly link exosomes from people with type 2 diabetes to suppressed immune activity inside human breast tumors,” said corresponding author Gerald Denis, Ph.D., the Shipley Prostate Cancer Research Professor at BU.
In the study, researchers used tumor samples from breast cancer patients to grow 3D tumor models in the lab. Known as patient-derived organoids, these models contain the immune cells originally found in the tumor. These mini-tumors were treated with blood exosomes from people with and without diabetes but also without any cancer. The researchers analyzed the organoids using single-cell RNA sequencing to see how the exosomes affected the immune cells and the tumor itself.

Psychotherapy leads to measurable changes in brain structure. Researchers at Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU) and the University of Münster have demonstrated this for the first time in a study in Translational Psychiatry by using cognitive behavioral therapy.
The team analyzed the brains of 30 patients suffering from acute depression. After therapy, most of them showed changes in areas responsible for processing emotions. The observed effects are similar to those already known from studies on medication.
Around 280 million people suffer from severe depression worldwide. This depression leads to changes in the brain mass of the anterior hippocampus and amygdala. Both areas are part of the limbic system and are primarily responsible for processing and controlling emotions. In psychotherapy, cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is an established method for treating depression.
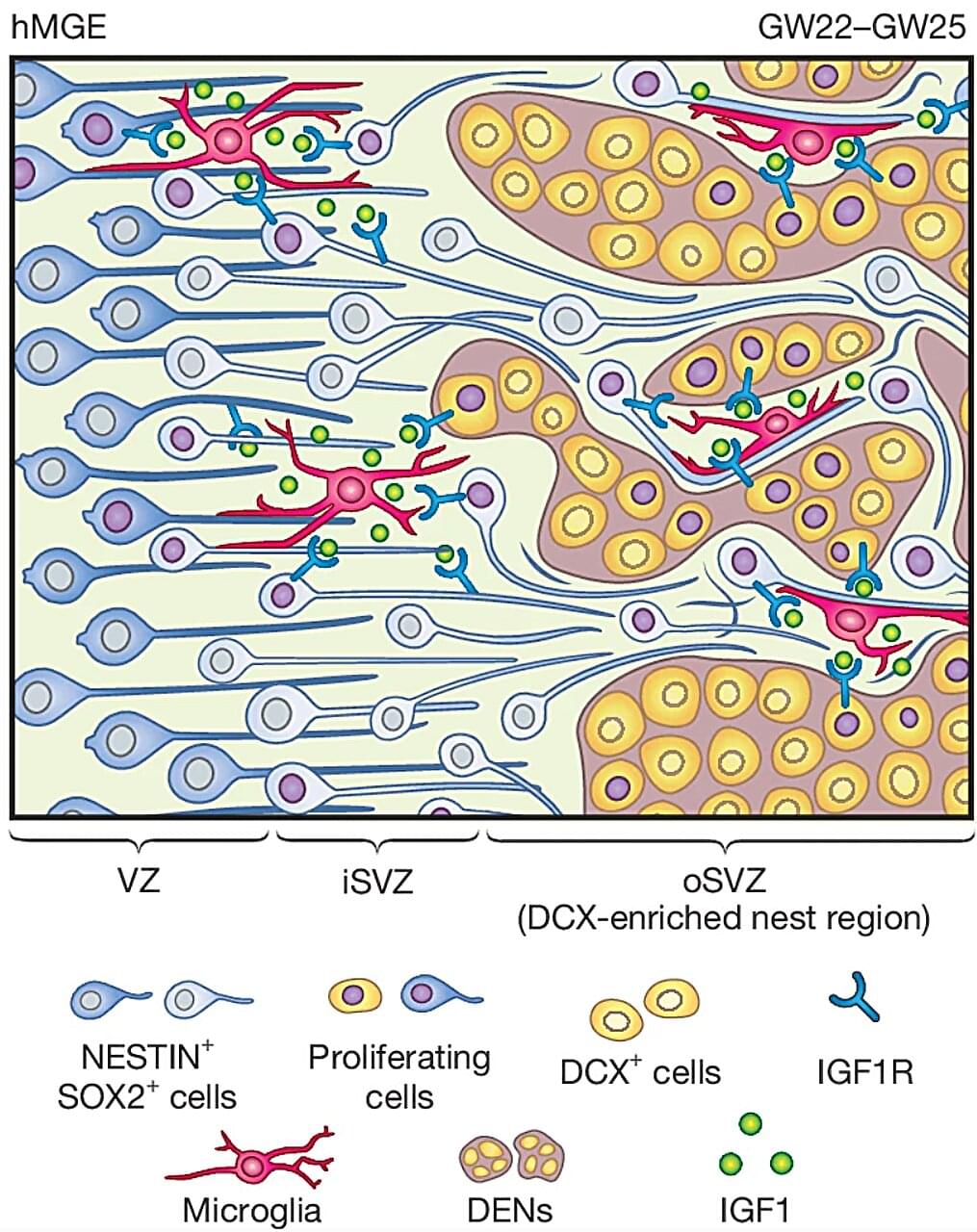
While there is a vast amount of information about the human brain and how it develops and works, much of the organ is still uncharted territory. But new research published in the journal Nature is giving us new insights into a type of brain cell called the GABAergic interneuron and its role in the developing brain. These findings could help explain how conditions like autism and brain disorders in children develop.
GABAergic interneurons are a vital part of the brain. They release the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), which regulates brain activity by switching neurons on and off. Disruptions in their functions can lead to a number of disorders, including epilepsy, schizophrenia and autism.

DNA aptamers are powerful molecular tools in biosensing, bioimaging and therapeutics. However, a limited understanding of their tertiary structures and binding mechanisms hinders their further optimizations and applications.
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP), a central metabolite in cellular energy metabolism, is a key target for aptamer development. A DNA aptamer 1301b has recently been reported to bind to one molecule of ATP with a dissociation constant (KD) of ~2.5 µM. However, the structural basis for ATP recognition by 1301b remains unclear, lacking guiding principles for rational optimization.
In a study published in PNAS, a team led by Prof. Tan Weihong, Prof. Han Da, and Prof. Guo Pei from the Hangzhou Institute of Medicine (HIM) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences determined the tertiary structure of a DNA aptamer-ATP 1:1 binding complex, revealed the recognition mechanism, and engineered an optimized DNA aptamer with a submicromolar KD for ATP binding, which exhibited the highest affinity reported for ATP-binding DNA aptamers to date.