Scientists at Wake Forest University School of Medicine, in collaboration with researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine, have made a breakthrough in understanding why many cancer patients develop nerve damage after chemotherapy. Their new study reveals that a stress response inside certain immune cells can trigger this debilitating side effect. This discovery could open the door to new ways to prevent or treat nerve damage in cancer patients.
The study appears in Science Translational Medicine.
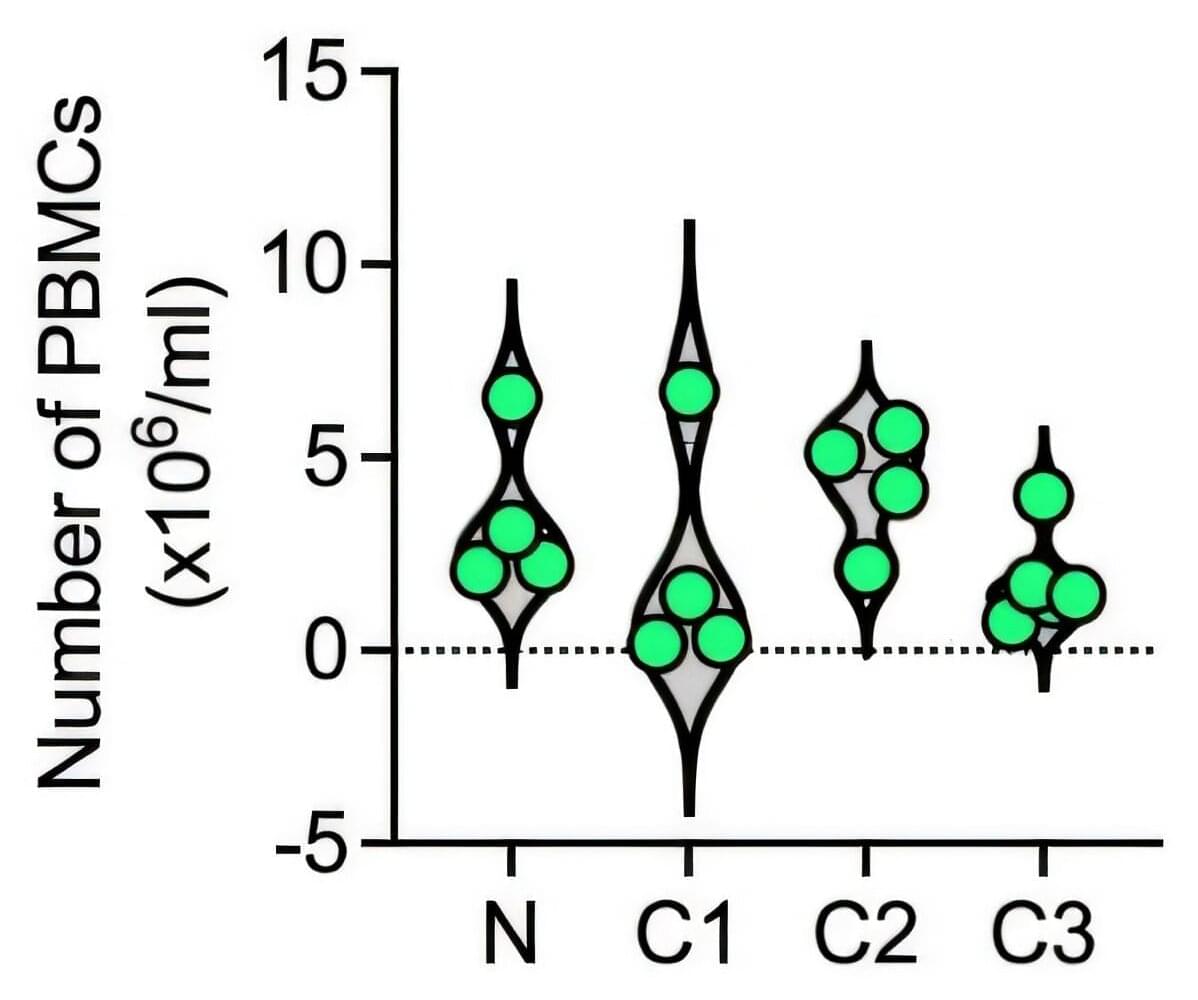
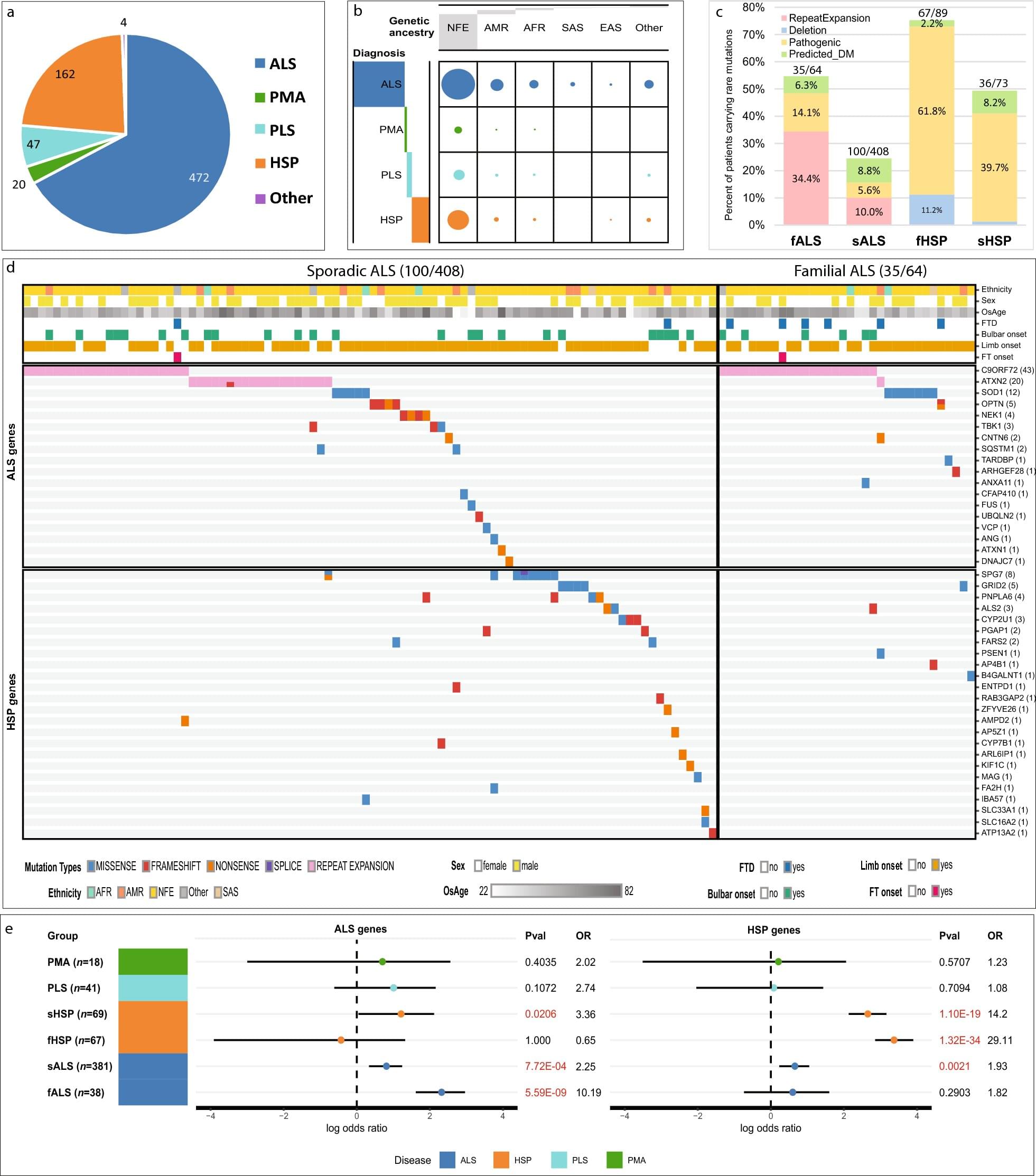
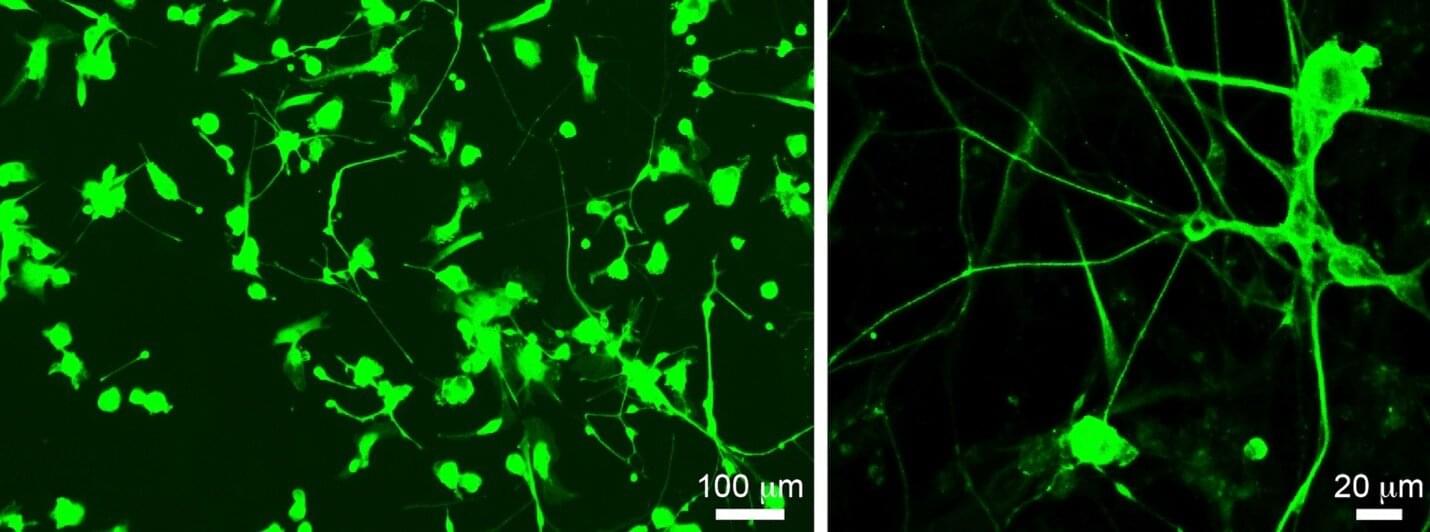
Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy is a common and often severe side effect of cancer treatment, especially with drugs like paclitaxel. It can cause tingling, numbness and pain in the hands and feet, sometimes forcing patients to stop life-saving treatment early. Up to half of all patients receiving chemotherapy may experience this condition, but until now, the exact cause has remained a mystery.